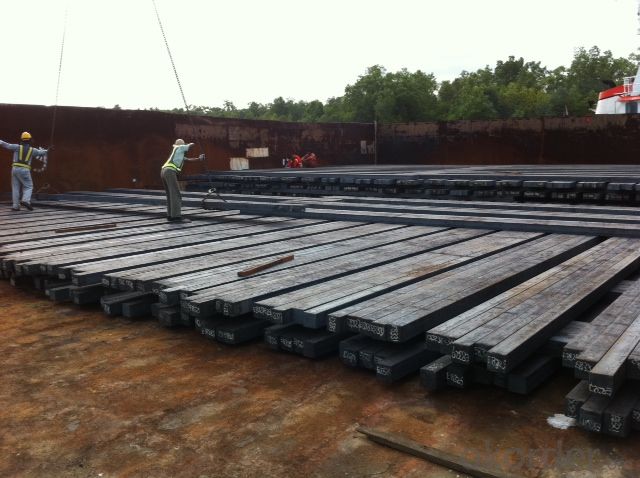
Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
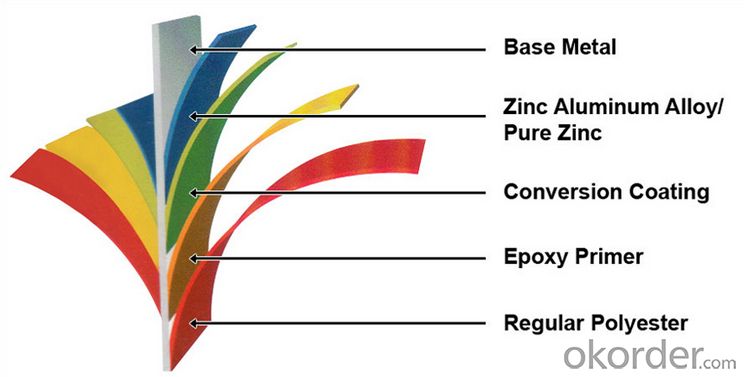
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
Uncoated CR steel sheet
With the features of in line with the international highest standards in demension and shape, excellent surface finish and properties, the products are mainly used in home appliance and automobile industries.
Galvanized steel sheet(include HDG and EG)
With the features of good corrosion resistance, the products are mainly used in automobile, home appliance, electronics, building and machinery manufacture industries, etc.
Precoated steel sheet
With the features of enviromental protection and good processablility, long lasting surface durability, rich in colors, the products are maily used in building, home appliance and furniture industries, etc.
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: How are steel billets stored to prevent rusting?
- Steel billets are typically stored in covered areas or warehouses to protect them from exposure to moisture and humidity, which can lead to rusting. They are also often coated with a rust inhibitor or protective oil prior to storage to provide an additional barrier against corrosion.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of agricultural vehicles?
- Steel billets are used in the production of agricultural vehicles as they serve as the raw material for various components and parts. These billets are heated and then formed into desired shapes using processes like forging or casting. They are used to manufacture key structural components such as chassis, axles, and frames, providing the necessary strength and durability for heavy-duty applications in agricultural vehicles.
- Q: What are the challenges faced in the production of steel billets?
- There are several challenges faced in the production of steel billets. One of the main challenges is the sourcing of raw materials. Steel billets are typically produced from iron ore, which needs to be mined and processed before it can be used. The availability and quality of iron ore can vary, making it challenging to secure a consistent supply. Another challenge is the energy-intensive nature of steel production. The process of converting iron ore into steel billets requires significant amounts of energy, mainly in the form of electricity and fossil fuels. This can lead to high production costs and contribute to environmental concerns, such as greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the production of steel billets involves complex metallurgical processes. The steel needs to be heated to high temperatures and undergo various treatments to achieve the desired properties. Ensuring consistent quality and meeting specific customer requirements can be challenging, as any deviations in the production process can affect the final product's performance. Maintaining a safe working environment is also a significant challenge in steel billet production. The production process involves handling heavy machinery, molten metal, and potentially hazardous chemicals. Effective safety measures and protocols need to be implemented to protect workers and prevent accidents. Lastly, the market dynamics and competition in the steel industry pose challenges in the production of steel billets. Fluctuating demand, changes in customer preferences, and price volatility can impact production planning and profitability. Steel producers need to stay competitive by continuously improving efficiency, reducing costs, and adapting to market trends. Overall, the production of steel billets faces challenges related to raw material sourcing, energy consumption, metallurgical processes, safety, and market dynamics. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technological advancements, efficient operations, and strategic decision-making to ensure a sustainable and successful production process.
- Q: How are steel billets distributed in the market?
- Steel billets are distributed in the market through various channels such as steel mills, steel service centers, and steel distributors. These entities source the billets from steel producers and then supply them to various industries and customers, including construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure. The distribution process involves logistics, warehousing, and transportation to ensure timely delivery to the end-users.
- Q: What is the typical tensile strength of a steel billet?
- The tensile strength of a steel billet can vary depending on its specific grade and composition. Typically, steel billets have a tensile strength ranging from 370 to 550 megapascals (MPa). This range is commonly observed in low to medium carbon steels, which are utilized in various industries like construction, automotive, and manufacturing. It should be noted that higher-grade steels, including alloy steels, can exhibit considerably higher tensile strengths, surpassing 1000 MPa. Ultimately, the intended application and project requirements dictate the tensile strength of a steel billet.
- Q: What are the common sizes of steel billets used in construction?
- The common sizes of steel billets used in construction vary depending on the specific project and requirements. However, some commonly used sizes range from 100mm x 100mm to 200mm x 200mm, with lengths typically ranging from 6 meters to 12 meters.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of construction materials?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of construction materials through a process called hot rolling. These billets are heated and then passed through a series of rollers to shape them into various forms such as bars, rods, or beams. These shaped steel products are then used in the construction industry to create structural frameworks, support systems, and other components required for buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet surface defects?
- There are several types of steel billet surface defects, including cracks, scale, surface laps, scratches, and pitting.
- Q: What does the billet of the steel plant refer to?And steel what is the difference?
- Many species, usually by chemical composition, production process, rolling shape, supply form, diameter, and use in the structure the classification of steel bars for concrete reinforcement refers to straight or strip steel plate reinforced concrete reinforcement steel, its shape is divided into round steel bar and deformed steel two. Steel bars in concrete under tensile stress.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall safety of a product?
- Steel billets contribute to the overall safety of a product in several ways. Firstly, steel billets are manufactured using a controlled process that ensures a high level of quality and consistency in the material. This means that the steel produced from these billets will have consistent mechanical properties, such as strength and toughness, which are crucial for ensuring the safety of the final product. Additionally, steel billets undergo various testing and inspections during the manufacturing process to ensure that they meet the required specifications and standards. This includes checks for surface defects, internal soundness, and proper chemical composition. By ensuring that the steel billets are defect-free and meet the necessary quality standards, the risk of failure or malfunction in the final product is significantly reduced. Furthermore, steel billets are known for their exceptional strength and durability. Steel is a highly robust material that can withstand high temperatures, pressure, and impacts without deforming or breaking. This inherent strength makes steel billets particularly suitable for applications where safety is a priority, such as in the construction of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure. Moreover, steel billets can be easily shaped and formed into various components and structures, allowing for precise manufacturing and design. This versatility enables engineers and designers to create products with optimal safety features, such as reinforced beams or structures that can withstand extreme loads or impacts. The ability to customize steel billets to meet specific safety requirements ensures that the final product is tailored to address potential safety risks and hazards. Lastly, steel billets are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments or exposure to corrosive substances. The resistance to corrosion ensures that the structural integrity of the product is maintained over time, reducing the likelihood of failures due to material degradation. In conclusion, steel billets contribute to the overall safety of a product by providing a high-quality, defect-free, strong, and durable material that can be customized to meet specific safety requirements. The controlled manufacturing process, rigorous testing, and inherent properties of steel make it an ideal choice for ensuring the safety and reliability of various products.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 160mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























