Raw Material For Steel
Raw Material For Steel Related Searches
Iron Raw Material Purchasing Raw Materials Raw Construction Materials Types Of Raw Materials Used In Industries Stainless Steel Material Stainless Steel Materials Grinding Wheels For Steel Indigenous Raw Materials Material Stainless Steel Glue For Stainless Steel Solder For Stainless Steel Forging Stainless Steel High Speed Steel Raw Materials Los Angeles Steel Cleaning Chemicals Cheap Stainless Steel Pre Engineering Steel Structure Grinding Tools For Metal Rimming Steel Welder For Stainless Steel Cold Rolled Steel Stone Steel Stainless Steel For Sale Stainless Steel For Piercings Coatings For Stainless Steel Caulking For Stainless Steel Steel Screws Stainless Steel Metals Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Steel Frames For FurnitureRaw Material For Steel Supplier & Manufacturer from China
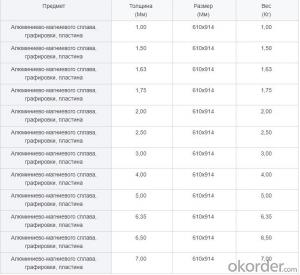
Raw Material For Steel encompasses a variety of essential materials that are crucial for the production of steel. These materials include iron ore, coke, limestone, and other key components that contribute to the creation of high-quality steel products. The application of Raw Material For Steel is vast, as it is used in numerous industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and many others. The usage scenarios for this product range from the production of structural steel for buildings to the creation of specialized alloys for advanced engineering applications.Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Raw Material For Steel, boasting a large inventory that caters to the diverse needs of various industries. By offering a comprehensive range of raw materials, Okorder.com ensures that customers have access to the necessary components for steel production at competitive prices. This extensive inventory allows for efficient sourcing and streamlined supply chain management, making Okorder.com a reliable partner for businesses in the steel manufacturing sector.
Hot Products