Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Mould Powders / Continuous Casting Powders and Granules
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
The Mould Powders are composed essentially of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 with addition of fluxing agents and carbon.
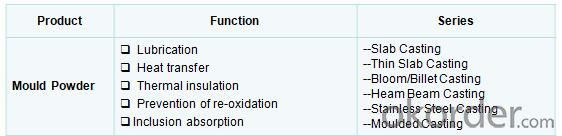
Mold Powders have different functions:
Lubrication between the solidifying strand and mould wall
Control of heat transfer between the strand and mould
Thermal insulation of the liquid steel surface
Prevention of re-oxidation
Inclusion absorption
The above functions are controlled by the following properties:
Basicity
Viscosity
Melting speed
Melting behaviour
Crystallization
The choice of a mould powder depends on:
Mould size
Oscillation conditions
Casting speed
Steel grade
Technical Data:
FAQ
Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:CNBM is a large-scale central governmental industrial group with its own manufacturing sector, research and development sector, trading sector and logistics sector.
Q:I have some special requirement about specifications.
A:We have a well-rounded product range, which endows us with the capability of applying many special specifications. Please feel free to contact us with yours.
Q:Do you accept OEM service?
A:Yes, we do.
Q:What is your delivery time?
A:It depends on the size/complexity of your order and our own production schedule. Usually we provide a faster delivery than the industry's average.
Q:What is the payment term?
A:Our payment terms are negotiable.
Q:Can I have my own logo on the product?
A:Sure, we can apply your own logo on the products according to your drawings.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance and longevity of furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the performance and longevity of furnaces by providing superior thermal insulation properties, excellent resistance to thermal shocks, and high mechanical strength. They create a seamless lining, eliminating joints and weak points, which reduces heat loss and prevents the penetration of molten metals or aggressive chemicals. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in design and installation, allowing for customized shapes and sizes to maximize the efficiency of the furnace. Overall, their use enhances the overall heat transfer, reduces energy consumption, and extends the lifespan of the furnace.
- Q: What are the common manufacturing processes used for monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are commonly manufactured using the following processes: 1. Mixing: The initial step involves accurately measuring and combining the raw materials to create a uniform mixture. 2. Wetting: The mixture is then moistened with water or a liquid binder to enhance its workability and plasticity, facilitating shaping and molding. 3. Forming: Various techniques such as casting, gunning, ramming, or extrusion are employed to shape the wet mixture. Casting entails pouring it into a mold, gunning involves spraying it onto a surface, ramming compacts it using a tool, and extrusion forces it through a die to create specific shapes. 4. Drying: The formed monolithic refractory is dried in a controlled environment with specific temperature and humidity conditions to eliminate excess moisture, preventing cracks or warping. 5. Firing: The dried monolithic refractory is then subjected to high temperatures to achieve the desired properties. This process, known as sintering, promotes particle bonding, increasing the material's strength and stability. 6. Finishing: Following the firing process, additional finishing processes like grinding, polishing, or coating may be employed to enhance the surface quality and overall performance of the monolithic refractory. By employing these standard manufacturing procedures, high-quality monolithic refractories with consistent properties and performance characteristics are produced.
- Q: What are the main causes of monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry can be attributed to various causes. Thermal cycling stands out as one of the primary factors. The extreme temperatures encountered during iron and steel manufacturing, including melting, casting, and heat treating, expose the refractory lining to significant thermal stress. This repetitive expansion and contraction of the material can lead to cracking, spalling, or even complete disintegration of the refractory. Chemical attack is another common cause of failure. The iron and steel industry utilizes different chemicals, such as molten metal, slag, and gases, which can react with the refractory lining. This chemical interaction can result in erosion, corrosion, or chemical decomposition of the refractory material, ultimately causing failure over time. Mechanical stress also plays a significant role in monolithic refractory failure. The heavy machinery and equipment employed in iron and steel production produce vibrations, shocks, and impacts that can weaken or damage the refractory lining. Additionally, improper installation or design can create stress concentration points, making the refractory more susceptible to failure. Furthermore, refractory failure can be attributed to improper maintenance and operational practices. Inadequate cooling or heating procedures, improper drying and curing of the refractory, and insufficient cleaning and inspection can all affect the longevity and performance of the material. Neglecting regular maintenance and timely repairs can exacerbate minor issues, eventually leading to more significant failures. Lastly, the choice and quality of refractory material are crucial factors in failure. Opting for an unsuitable refractory for a specific application or using low-quality materials can result in premature failure. Considering factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress is essential when selecting the refractory lining to ensure its suitability and durability in the iron and steel industry. To summarize, the main causes of monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry include thermal cycling, chemical attack, mechanical stress, improper maintenance and operational practices, and the choice and quality of refractory material. Addressing these factors through proper installation, regular maintenance, and careful material selection can help mitigate refractory failures and enhance the overall efficiency and productivity of iron and steel production processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes by forming a strong and durable barrier against high temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses. These refractories are designed to be resistant to thermal shock and erosion, ensuring that the lining remains intact and unaffected by the molten metal or slag. They also provide insulation, minimizing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. Overall, monolithic refractories act as a reliable shield, extending the lifespan of the ladles and tundishes and preventing any detrimental effects on the lining.
- Q: What are the different types of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry?
- In the iron and steel industry, several types of monolithic refractories are used due to their excellent thermal resistance, high strength, and durability. These refractories are essential in various applications to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions. The different types of monolithic refractories commonly used in the iron and steel industry include: 1. Castables: These are precast refractory materials that are mixed with water to form a slurry, which is then poured or cast into molds. Castables are widely used in iron and steel industries for lining ladles, tundishes, and other furnaces due to their high strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock. 2. Ramming Mass: Ramming mass is a refractory material that is used for lining induction furnaces and other melting units. It is made up of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. Ramming mass is applied by ramming or tamping it into place, forming a dense lining that can withstand high temperatures and chemical attacks. 3. Gunning Mix: Gunning mix is a refractory material that is applied using a pneumatic gunning machine. It is used for repairing or lining various areas of furnaces and is particularly useful for hot repairs. Gunning mix consists of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives, which are sprayed onto the lining surface and then compacted. 4. Plastic Refractories: Plastic refractories are mixtures of refractory aggregates and binders that have a high plasticity and can be easily molded or shaped. They are used for repairing or patching refractory linings in iron and steel industries. Plastic refractories are typically applied by hand or using a trowel and are suitable for both hot and cold applications. 5. Mortars: Refractory mortars are used for jointing or repairing refractory bricks or other monolithic refractories. They are made up of refractory powders, binders, and water. Mortars provide excellent adhesion between bricks or monolithic materials, ensuring a strong and durable lining in furnaces, ladles, and other high-temperature equipment. These different types of monolithic refractories play a vital role in the iron and steel industry by providing reliable and long-lasting linings, ensuring efficient operations and minimizing downtime.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. Monolithic refractories are versatile and can be shaped to fit the specific requirements of these furnaces. They offer excellent thermal insulation, high temperature resistance, and durability, making them suitable for withstanding the extreme conditions within these furnaces. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be easily installed, repaired, and replaced, making them a practical choice for lining these types of furnaces.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be customized for specific iron and steel processing requirements?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be customized for specific iron and steel processing requirements. Monolithic refractories are known for their versatility and ability to be tailored to various applications. The composition, physical properties, and installation techniques of monolithic refractories can be adjusted to meet the specific needs of iron and steel processing. For example, the choice of raw materials used in the manufacturing of monolithic refractories can be customized to withstand the high temperatures and harsh chemical environments encountered in iron and steel processing. Different types of aggregates, binders, and additives can be selected to enhance the refractory's resistance to thermal shock, erosion, and corrosion. Furthermore, the installation method of monolithic refractories can be adapted to suit the specific requirements of iron and steel processing. Whether it is gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying, the installation technique can be customized to ensure optimal performance and longevity in the given application. Additionally, monolithic refractories can also be tailored to specific shapes and sizes to fit the various equipment and structures used in iron and steel processing. This allows for a more precise and efficient lining of furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and other vessels, thereby improving the overall productivity and performance of the process. In summary, monolithic refractories can be customized to meet the specific iron and steel processing requirements by adjusting their composition, physical properties, installation techniques, and shape. This customization ensures that the refractories can withstand the extreme conditions encountered in these industries, leading to improved performance, longer service life, and enhanced productivity.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry?
- To combat corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories are designed with a combination of composition and application techniques. Firstly, the composition includes high-quality raw materials like alumina, magnesia, and silica, which possess exceptional resistance to corrosion and erosion. For example, alumina can withstand high temperatures and chemical attacks, making it an ideal choice for protecting against the corrosive nature of the industry. Additionally, the application techniques used in installing monolithic refractories are crucial for their resistance. These techniques, such as gunning, ramming, or casting, ensure a tight and seamless bond between the refractory and the steel structure, reducing the chances of corrosion and erosion. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different parts of the iron and steel industry. For areas exposed to molten metal, refractories with high thermal conductivity and resistance to chemical attack are utilized. This customization enhances the refractory's effectiveness in resisting corrosion and erosion. Moreover, monolithic refractories often incorporate additives or binders to further enhance their resistance. These additives provide extra protection against chemical attacks from molten metal or corrosive gases, making the refractory even more durable in harsh conditions. In summary, monolithic refractories effectively resist corrosion and erosion in the iron and steel industry due to their composition, application techniques, customization, and the inclusion of additives. By combining these factors, these refractories ensure the longevity and efficiency of steel structures in the challenging environments of the industry.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the lifespan of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that can affect the lifespan of monolithic refractories. These include the type of material used in the refractory, the operating conditions such as temperature and pressure, the presence of corrosive or abrasive substances, the frequency and intensity of thermal cycling, and the quality of installation and maintenance. Additionally, factors like mechanical stresses, chemical reactions, and thermal shock can also contribute to the degradation and reduced lifespan of monolithic refractories.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing downtime in iron and steel plants by offering several key advantages over traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are highly versatile and can be easily molded and installed, allowing for quicker repairs and replacements. Unlike brick refractories that require time-consuming and labor-intensive processes, such as bricklaying and mortar application, monolithic materials can be directly applied in a castable or gunning form, significantly reducing the downtime required for repairs. Additionally, monolithic refractories provide better thermal insulation and improved resistance to thermal shocks, which are common occurrences in iron and steel plants. This enhanced thermal performance helps to maintain stable operating temperatures and prevents sudden temperature fluctuations that can lead to refractory failure and subsequent downtime. By minimizing these thermal shocks, monolithic refractories increase the overall lifespan of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer superior chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. Iron and steel plants often encounter aggressive chemical environments due to the presence of molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions, preventing chemical attacks and erosion of the refractory lining. As a result, the need for unscheduled shutdowns due to refractory degradation is significantly reduced. Lastly, monolithic refractories provide better dimensional stability, minimizing the risk of cracks and spalling that can occur due to thermal cycling and mechanical stress. This increased resistance to wear and tear ensures that the refractory lining remains intact for a longer period, reducing the frequency of maintenance and enhancing the overall operational efficiency of the iron and steel plant. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants by offering faster installation, improved thermal insulation, superior chemical resistance, and enhanced dimensional stability. Their versatility and performance advantages make them a reliable choice for maintaining a reliable and efficient refractory lining, ultimately reducing the frequency and duration of plant shutdowns.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Mould Powders / Continuous Casting Powders and Granules
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























