Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE mullite based mortar for hot blast stove made as per international standards, is known for its low thermal conductivity, high refractoriness, and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Technical data of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Item | High Alumina Mortar | |
Al2O3(%)≥ | 70 | |
M.O.R. (MPa) ≥ | 110℃×24h | 4 |
1200℃×3h | — | |
1300℃×2h | 6 | |
1400℃×2h | — | |
1500℃×2h | — | |
Grain size(%) | 110℃×24h (≤) | 1 |
1200℃×3h (≥) | 50 | |
Refractoriness (℃) ≥ | 1790 | |
Refractoriness Under Load(℃) ≥ | 1550 | |
Adhesive Time(min) | 1-2 | |
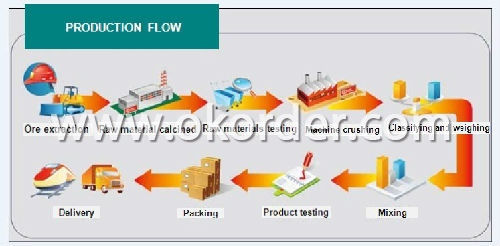
Production line and Packing of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove


Feature of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Excellent mechanical strength
Low thermal conductivity
High refractoriness
Application of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE tmullite based mortar for hot blast stove can be used widely for same material masonry.
Production Flow of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Q: What are the key trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- It is worth noting that there are several notable trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry. First and foremost, there is an increasing demand for monolithic refractories due to their superior performance characteristics in comparison to traditional brick refractories. Monolithic refractories provide higher thermal shock resistance, superior insulation properties, and improved resistance to chemical attacks. As a result, they are being used more extensively in various applications within the iron and steel industry. Secondly, there is a shift towards the utilization of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables in monolithic refractories. These materials contain a reduced amount of cement, leading to enhanced refractory properties such as increased strength, better corrosion resistance, and improved resistance to thermal spalling. This trend is driven by the need to enhance the overall efficiency and longevity of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Another significant trend is the development of advanced monolithic refractories that prioritize sustainability and environmental performance. The iron and steel industry is facing mounting pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and minimize its impact on the environment. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on the use of environmentally friendly binders and additives in monolithic refractories. These novel materials not only offer excellent refractory properties but also contribute to the industry's sustainability objectives. Moreover, there is an increasing focus on the development of monolithic refractories capable of withstanding extreme operating conditions. Iron and steel manufacturing processes involve high temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and severe mechanical stresses. Consequently, there is a need for monolithic refractories that can withstand these harsh conditions without compromising their performance. The industry is investing in research and development to create refractories that exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and erosion. Lastly, there is a growing adoption of digital and smart technologies for the monitoring and maintenance of monolithic refractories. Advances in sensor technology and data analytics have made it possible to collect real-time data on the condition and performance of refractory linings. This enables proactive maintenance, early detection of potential issues, and optimization of refractory usage, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings. In conclusion, the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry is witnessing key trends such as the demand for superior performance, the shift towards low-cement and ultra-low cement castables, the development of sustainable materials, the focus on extreme operating conditions, and the adoption of digital and smart technologies for monitoring and maintenance. These trends reflect the industry's continuous efforts to enhance the efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: What are the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry?
- Over the past few years, significant progress has been made in the field of monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry. These refractories are vital in the production of iron and steel, as they provide insulation and withstand high temperatures in furnaces and other equipment. One major advancement is the development of advanced alumina-based castables. These castables offer exceptional thermal shock resistance, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them perfect for the iron and steel industry. They can endure extreme temperatures and mechanical stress, resulting in longer service life and less maintenance downtime. Another noteworthy development is the introduction of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables. Compared to traditional castables, these have reduced cement content, leading to improved refractory properties. They have higher hot strength, lower porosity, and increased resistance to slag and metal corrosion. This enhances productivity and efficiency in the iron and steel manufacturing processes. Moreover, insulating refractories have seen advancements in their usage. Insulating castables and bricks are now used to line ladles, tundishes, and other equipment, providing better insulation and energy efficiency. These materials help reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, there have been significant improvements in the installation techniques of monolithic refractories. Traditional brick lining methods require skilled labor and a longer installation time. However, the introduction of gunning and shotcreting techniques has made the process faster and more efficient. These techniques involve spraying refractory materials onto the lining surface, ensuring better adherence and reducing the risk of lining failure. Overall, recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry have focused on enhancing thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, insulation properties, and installation techniques. These advancements have led to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved productivity in the iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in rotary kiln applications?
- Due to their unique properties and characteristics, monolithic refractories prove highly effective in rotary kiln applications. Unlike traditional brick and mortar refractories, these refractories are designed to be installed as a single, solid unit. One of the primary advantages of monolithic refractories in rotary kilns is their incredible ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal stresses. Operating at temperatures as high as 3000 degrees Fahrenheit, rotary kilns subject refractories to extreme conditions. However, monolithic refractories excel in handling such temperatures without cracking or failing, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the kiln. Another crucial performance aspect of monolithic refractories in rotary kilns is their resistance to chemical attack. Industries like cement production often employ rotary kilns, where the materials being processed can be highly corrosive. Monolithic refractories offer excellent protection against chemical attack, safeguarding the kiln from deterioration and extending its service life. Moreover, monolithic refractories are renowned for their exceptional thermal conductivity and insulation properties. This aids in maintaining consistent and efficient heat transfer within the kiln, thereby enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the process. Furthermore, the installation of monolithic refractories in rotary kilns is relatively quick and straightforward compared to traditional brick and mortar refractories. The monolithic materials can be cast or gunned into place, creating a seamless lining that eliminates the need for individual bricks and mortar joints. This not only saves time during installation but also minimizes the potential for weak points or gaps in the lining, guaranteeing a more durable and effective refractory system. In conclusion, monolithic refractories offer outstanding performance in rotary kiln applications. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, resist chemical attack, provide efficient heat transfer, and offer easy installation make them the preferred choice for industries relying on rotary kilns in their production processes.
- Q: How long is the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications?
- The lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications can vary depending on several factors. These factors include the type of refractory material used, the specific application, the operational conditions, and the maintenance practices implemented. In general, monolithic refractories used in iron and steel applications are designed to withstand high temperatures, thermal shock, chemical attack, and mechanical stress. They are expected to have a relatively long lifespan compared to other refractory materials. Under normal operating conditions and proper maintenance, monolithic refractories can typically last anywhere from several months to several years in iron and steel applications. However, it is important to note that certain areas of the application may experience more severe conditions and may require more frequent repairs or replacements. Regular inspections and monitoring of the refractories' condition are crucial to identify any signs of deterioration or damage. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be carried out promptly to prevent further damage and minimize downtime. It is also worth mentioning that advancements in refractory technology and materials have led to the development of more durable and long-lasting monolithic refractories. These advancements have increased the lifespan of refractories in iron and steel applications, ultimately improving the overall efficiency and productivity of the operations.
- Q: What are the advantages of using plastic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Plastic refractories provide numerous benefits in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, their thermal insulation properties are exceptional. They possess a low thermal conductivity, enabling them to effectively retain heat and prevent excessive heat loss during manufacturing. This is critical for the proper functioning of furnaces and equipment, as maintaining high temperatures is essential. Secondly, plastic refractories exhibit superior resistance to chemical attack and corrosion. They can endure exposure to various chemicals, including molten metals and slag, without deteriorating or losing their structure. This is particularly important in an industry where materials frequently encounter highly corrosive substances. Moreover, plastic refractories offer the advantage of easy installation and repair. Unlike other refractory materials, they can be easily shaped and molded into the desired form. This allows for precise fitting and swift installation. Additionally, if damaged or worn, they can be easily repaired or patched, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, plastic refractories possess excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. This enables them to endure the physical stresses and mechanical forces present in the iron and steel industry, such as vibrations, impacts, and mechanical loading. Their high resistance to wear and tear ensures longevity and reduces the need for frequent replacements. Lastly, plastic refractories have a high resistance to thermal shock. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is advantageous in an industry where materials are subjected to extreme temperature differentials, such as during the heating and cooling cycles of furnaces. In conclusion, the utilization of plastic refractories in the iron and steel industry provides numerous advantages including excellent thermal insulation, resistance to chemical attack, ease of installation and repair, good mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and high thermal shock resistance. These properties make plastic refractories an ideal choice for various applications, ensuring efficient and reliable operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand mechanical stress in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry withstand mechanical stress primarily due to their composition and installation techniques. These refractories are made from a single, solid material, which provides them with excellent strength and resistance to mechanical pressure. Additionally, they are typically installed using specialized techniques, such as gunning or ramming, which ensure proper bonding and densification. These factors collectively enable monolithic refractories to effectively withstand the intense mechanical stress encountered in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace roof applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace roof applications. These refractories are known for their excellent thermal shock resistance, which is crucial in the extreme temperature conditions inside a reheating furnace. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, ensuring the longevity and durability of the furnace roof. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer superior insulation properties, which help in maintaining the desired temperature inside the furnace. These refractories have low thermal conductivity, preventing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. This not only improves the energy efficiency of the furnace but also contributes to cost savings for the operators. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent resistance to chemical attacks from gases and molten metals present in the furnace environment. They are designed to withstand corrosive atmospheres and prevent the penetration of harmful substances, thus prolonging the life of the roof refractory. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair options. Their ability to be cast or gunned in place allows for a seamless and precise application to the roof structure. This feature also enables quick and efficient repairs or maintenance, minimizing downtime and production losses. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a reliable and efficient choice for reheating furnace roof applications. Their exceptional thermal shock resistance, insulation properties, chemical resistance, and ease of installation make them an ideal solution for maintaining the structural integrity and performance of the furnace roof.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall reliability of iron and steel processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall reliability of iron and steel processes in several ways. Firstly, they provide excellent thermal insulation, which helps in maintaining consistent and controlled temperatures within the furnaces and other equipment involved in the production process. This ensures the stability of the process and avoids any sudden temperature fluctuations that could lead to equipment failure or product quality issues. Secondly, monolithic refractories offer high resistance to thermal shocks and mechanical stresses, which are common in iron and steelmaking operations. These refractories can withstand extreme temperatures, rapid heating and cooling cycles, and the corrosive nature of molten metals, thereby prolonging the lifespan of the equipment and reducing the frequency of repairs or replacements. Moreover, monolithic refractories have a superior ability to resist chemical attacks from molten metals, slag, and other harsh substances encountered in iron and steel processes. This resistance prevents the refractories from deteriorating or corroding over time, ensuring their integrity and preventing any contamination of the metal being produced. Lastly, the use of monolithic refractories allows for greater design flexibility and ease of installation compared to traditional brick refractories. This flexibility enables the construction of complex shapes and structures, optimizing the efficiency and productivity of iron and steelmaking processes. Overall, monolithic refractories contribute significantly to the reliability of iron and steel processes by providing excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shocks and chemical attacks, and facilitating flexible design and installation options.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractory bricks?
- Monolithic refractories refer to a type of refractory material that is composed of a single, homogeneous structure, as opposed to traditional refractory bricks which are made by binding individual bricks together. This fundamental difference in structure leads to several distinctions between monolithic refractories and traditional refractory bricks. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer greater flexibility and versatility in terms of shape and installation. Since they are not bound by individual bricks, monolithic refractories can be easily molded and shaped to fit specific applications and complex geometries. This makes them ideal for lining various types of furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Secondly, monolithic refractories typically have superior thermal shock resistance compared to traditional refractory bricks. Their uniform structure allows for better distribution of heat, minimizing the risk of thermal stress and cracking. This characteristic makes monolithic refractories particularly suitable for applications with rapid temperature fluctuations or severe thermal cycling. Additionally, monolithic refractories often exhibit better overall performance in terms of strength, mechanical properties, and resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams in monolithic refractories eliminates potential weak points, resulting in a more durable and reliable lining. Moreover, the homogeneous structure of monolithic refractories provides better resistance to corrosive agents, ensuring prolonged service life in harsh environments. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer advantages in terms of installation and maintenance. Their monolithic nature simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and time requirements. Additionally, repairs and maintenance of monolithic refractories can be carried out more easily and cost-effectively compared to traditional refractory bricks, which may require the replacement of entire sections or bricks. In summary, monolithic refractories differ from traditional refractory bricks in their structure, flexibility, thermal shock resistance, performance, and installation characteristics. These differences make monolithic refractories a preferred choice in many high-temperature applications, offering improved efficiency, durability, and ease of use.
- Q: What are the benefits of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry has several advantages. Firstly, they have excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning they can withstand extreme temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is crucial in an industry where materials are exposed to high temperatures during processes such as melting, casting, and heat treatment. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior corrosion resistance, making them highly durable against the corrosive effects of molten metals and slag. This is particularly important in the iron and steel industry, where materials come into contact with aggressive molten iron, steel, and various chemical compounds. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. They can withstand mechanical stress, vibrations, and impacts commonly encountered in the iron and steel industry. This ensures a longer lifespan for the refractories, reduces downtime for repairs or replacements, and improves overall operational efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer ease of installation and repair. Unlike traditional refractory bricks that require complex and time-consuming masonry work, monolithic refractories can be quickly and easily installed using simple methods such as casting, gunning, or spraying. This saves time and labor costs during initial installation and subsequent maintenance or repairs. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide flexibility in design and application. They can be customized to specific shapes and sizes, allowing for tailored linings in different parts of the iron and steel manufacturing process. This versatility enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of refractory linings, optimizing production output and ensuring consistent quality of the finished iron and steel products. In conclusion, there are numerous benefits to using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry. They offer exceptional thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and abrasion resistance. They are also easy to install and repair, and their flexibility allows for customized designs. Overall, monolithic refractories contribute to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced product quality in the iron and steel industry.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 200 Million |
| Main Markets | North America;Asia;Western Europe;Africa;Russia;Middle East |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 20% - 30% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 10-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 150,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | Installation guide, OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | High; Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords