Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:AL2O3-SIO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
FIREF Al2O3- SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel is known for its excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel which is made strictly as per international standards. Beside, FIREF Al2O3- SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel has gained a good fame for its long operating life and easy execution and mending.
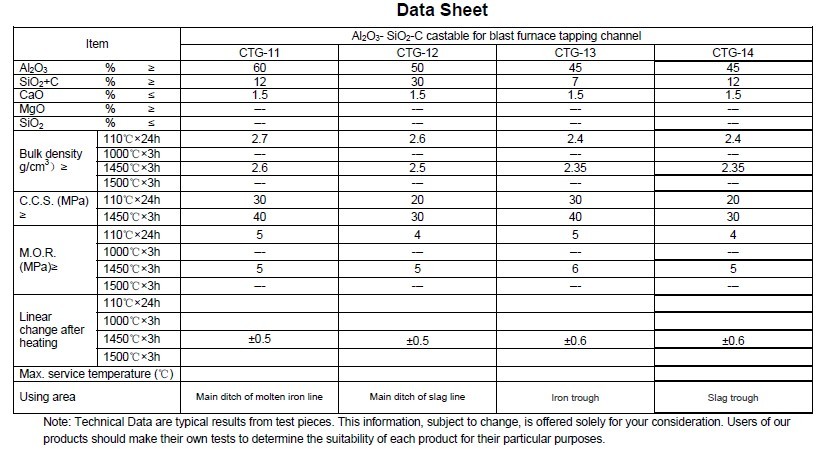
Technical data of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
Production line and packing of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel


Feature of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
Long operating life
Excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel
Easy execution and mending
Application of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
FIREF Al2O3-SiO2-C castable for blast furnace tapping channel can be used widely for in situ casting or pre-casting for tri-angle area of UHP EAF roof.
Production Flow of Al2O3-SiO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
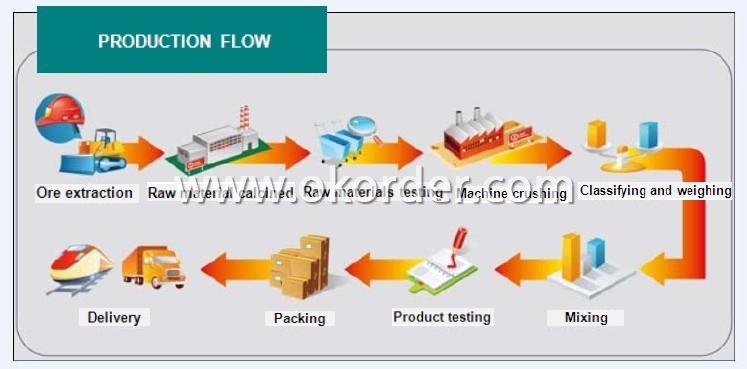
- Q: What are the common manufacturing processes used for monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are commonly manufactured using the following processes: 1. Mixing: The initial step involves accurately measuring and combining the raw materials to create a uniform mixture. 2. Wetting: The mixture is then moistened with water or a liquid binder to enhance its workability and plasticity, facilitating shaping and molding. 3. Forming: Various techniques such as casting, gunning, ramming, or extrusion are employed to shape the wet mixture. Casting entails pouring it into a mold, gunning involves spraying it onto a surface, ramming compacts it using a tool, and extrusion forces it through a die to create specific shapes. 4. Drying: The formed monolithic refractory is dried in a controlled environment with specific temperature and humidity conditions to eliminate excess moisture, preventing cracks or warping. 5. Firing: The dried monolithic refractory is then subjected to high temperatures to achieve the desired properties. This process, known as sintering, promotes particle bonding, increasing the material's strength and stability. 6. Finishing: Following the firing process, additional finishing processes like grinding, polishing, or coating may be employed to enhance the surface quality and overall performance of the monolithic refractory. By employing these standard manufacturing procedures, high-quality monolithic refractories with consistent properties and performance characteristics are produced.
- Q: What is the role of monolithic refractories in blast furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in blast furnaces as they provide high-temperature resistance and excellent durability in the harsh operating conditions of the furnace. Blast furnaces are used in the ironmaking process to convert iron ore into molten iron, and monolithic refractories are essential for lining the interior of the furnace. One of the main functions of monolithic refractories in blast furnaces is to withstand extreme temperatures. The interior of a blast furnace can reach temperatures of up to 2,500 degrees Celsius, and monolithic refractories are designed to maintain their structural integrity and protect the furnace lining from thermal shock and erosion caused by the high temperatures. Monolithic refractories also provide insulation, preventing heat loss from the furnace. This is important as it helps to maintain the desired temperature for efficient iron production. By reducing heat loss, monolithic refractories contribute to energy savings and improved overall furnace performance. Another crucial role of monolithic refractories is to resist chemical attack from the molten iron and slag. The materials used in blast furnaces, such as iron ore, coke, and limestone, undergo various chemical reactions during the ironmaking process. Monolithic refractories are engineered to resist the corrosive effects of these reactions, ensuring a longer service life for the furnace lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent mechanical strength and resistance to abrasion. The materials being processed in a blast furnace, including iron ore and coke, can be abrasive. Monolithic refractories provide a protective barrier against the abrasive action, preventing damage to the furnace lining and extending its lifespan. In summary, the role of monolithic refractories in blast furnaces is to withstand extreme temperatures, provide insulation, resist chemical attack, and offer mechanical strength against abrasion. These properties contribute to the efficient operation and longevity of blast furnaces, enabling the production of molten iron for various industrial applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production?
- The overall productivity of iron and steel production is greatly enhanced by the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories are crucial components utilized in the lining of high-temperature furnaces and other equipment employed in these industries. One of the ways in which monolithic refractories boost productivity is through their exceptional thermal insulation capabilities. By possessing high thermal conductivity, they effectively minimize heat loss from the furnaces, thereby reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency. This insulation property permits higher operating temperatures, resulting in faster and more efficient production processes. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Given the harsh conditions experienced during the iron and steel production process, such as rapid temperature fluctuations and exposure to molten metal and slag, these refractories are designed to withstand such extreme environments. This ensures prolonged service life and decreased downtime for maintenance and repairs, directly leading to increased productivity and reduced production costs. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer improved dimensional stability in comparison to traditional brick refractories. Their ability to conform to intricate shapes and structures allows for enhanced lining design, facilitating superior heat transfer and distribution. This uniformity in heat distribution contributes to improved process control and greater consistency in product quality. Moreover, the installation and repair of monolithic refractories are relatively simpler and quicker when compared to traditional brick refractories. This ease of installation and repair reduces downtime during maintenance, enabling more continuous production. The decreased downtime ultimately leads to increased productivity and higher output. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall productivity of iron and steel production through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, improved dimensional stability, and ease of installation and repair. These properties result in enhanced energy efficiency, reduced downtime, improved process control, and higher product quality, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability for the industry.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and relining monolithic refractories?
- When it comes to repairing and relining monolithic refractories, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account. Firstly, it is important to assess the extent of the damage or wear to the refractory lining. This can be done through visual inspection, as well as non-destructive testing techniques such as ultrasonic or thermal imaging. Understanding the severity and location of the damage will help in determining the appropriate repair or relining method. Another consideration is the type of monolithic refractory material being used. Different materials have different properties and performance characteristics, and this needs to be considered when selecting the repair method. For example, some materials may require high-temperature curing or specialized equipment for installation. The operating conditions of the refractory lining also need to be taken into account. Factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress can affect the performance and longevity of the lining. The repair or relining method should be selected to ensure that it can withstand these conditions and provide long-lasting protection. Additionally, the downtime and cost implications of the repair or relining process need to be considered. Some methods may require longer curing or drying times, which can result in extended shutdown periods. It is important to weigh the benefits of the repair or relining against the potential production losses and expenses associated with the downtime. Lastly, it is crucial to follow industry standards and guidelines when repairing or relining monolithic refractories. This ensures that the repairs are done correctly and in a safe manner, minimizing the risk of future damage or failure. Consulting with refractory experts or manufacturers can provide valuable insights and guidance in this regard. In conclusion, the considerations for repairing and relining monolithic refractories include assessing the extent of damage, understanding the properties of the refractory material, considering the operating conditions, evaluating downtime and cost implications, and following industry standards and guidelines.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the quality and consistency of iron and steel products?
- The use of monolithic refractories is essential for enhancing the quality and consistency of iron and steel products. These refractories, which are not shaped and can be easily molded and installed, offer several advantages over traditional brick refractories. To begin with, monolithic refractories provide superior thermal insulation properties, which effectively manage heat during the production process. By maintaining consistent and controlled temperatures, these refractories prevent thermal shocks and minimize thermal gradients, resulting in reduced cracking and distortion in the final products. As a result, the dimensional stability and overall quality of the products are improved. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent resistance to thermal spalling and erosion. They can withstand high temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stress, protecting the lining of furnaces and vessels used in iron and steel production. This resistance enhances the durability and reliability of refractory linings, preventing premature failure and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to create a seamless lining. Unlike brick refractories, which have joints and gaps that can cause heat loss and uneven distribution, monolithic refractories form a continuous lining with no weak points. This ensures uniform heat distribution and minimizes the risk of hotspots or cold spots, resulting in consistent and reliable iron and steel products. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in design and installation. They can be customized to fit various shapes and sizes, allowing for better furnace design optimization. This flexibility enables efficient use of space, improved heat transfer, and reduced energy consumption, all of which contribute to the overall quality and consistency of the final iron and steel products. In conclusion, monolithic refractories enhance the quality and consistency of iron and steel products by providing superior thermal insulation, resistance to thermal spalling and erosion, seamless linings, and flexibility in design and installation. These refractories improve the efficiency and reliability of the production process, resulting in higher-quality final products that meet the industry's stringent standards.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractory bricks?
- Monolithic refractories, unlike traditional refractory bricks, are composed of a single, homogeneous structure. This structural distinction leads to several differences between the two. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide greater flexibility and versatility in terms of shape and installation. They can be easily molded and shaped to fit specific applications and complex geometries, making them ideal for lining furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior thermal shock resistance compared to traditional refractory bricks. Their uniform structure allows for better heat distribution, minimizing the risk of thermal stress and cracking. This makes them suitable for applications with rapid temperature fluctuations or severe thermal cycling. Additionally, monolithic refractories often exhibit better overall performance in terms of strength, mechanical properties, and resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams eliminates potential weak points, resulting in a more durable and reliable lining. Moreover, the homogeneous structure provides better resistance to corrosive agents, ensuring prolonged service life in harsh environments. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer advantages in terms of installation and maintenance. Their monolithic nature simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and time requirements. Additionally, repairs and maintenance can be carried out more easily and cost-effectively compared to traditional refractory bricks, which may require the replacement of entire sections or bricks. In summary, monolithic refractories differ from traditional refractory bricks in structure, flexibility, thermal shock resistance, performance, and installation characteristics. These differences make monolithic refractories a preferred choice in many high-temperature applications, offering improved efficiency, durability, and ease of use.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent thermal shock in the iron and steel industry?
- The iron and steel industry heavily relies on monolithic refractories to prevent thermal shock. These refractories offer exceptional thermal insulation and resistance to extreme temperatures, playing a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining. Thermal shock occurs when there is a sudden and significant change in temperature, leading to stress and cracks in the refractory lining. Given the extremely high temperatures that can be reached in the iron and steel industry, the risk of thermal shock is particularly pronounced. To combat this, monolithic refractories possess a low thermal conductivity, enabling them to effectively insulate against rapid temperature fluctuations. This insulation property allows them to endure the extreme temperatures involved in the iron and steel production process without compromising their structural integrity. Moreover, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to exhibit high thermal shock resistance. This means they can effectively absorb and distribute the thermal stresses caused by temperature variations, thereby minimizing the likelihood of cracking or spalling. Aside from their exceptional thermal insulation and shock resistance, monolithic refractories also demonstrate outstanding corrosion and erosion resistance. This is especially important in the corrosive environment of the iron and steel industry, where molten metals, slag, and gases are present. By providing a dependable and long-lasting lining in furnaces, ladles, and other equipment utilized in the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories ensure that thermal shock is mitigated. Consequently, this helps to maintain the efficiency and productivity of the production process while extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- Q: What are the advantages of using monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces?
- There are several advantages of using monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer superior thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing. This is crucial in electric arc furnaces where the temperature can fluctuate significantly during the melting process. Additionally, monolithic refractories have excellent corrosion resistance, which is essential in electric arc furnaces that often come into contact with corrosive molten metals and slag. They can withstand the corrosive effects, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide ease of installation and repair. Unlike traditional bricks, they can be easily shaped and applied in various furnace designs, minimizing installation time and labor costs. In case of any damage, they can also be easily patched or replaced, allowing for quicker repairs and reduced downtime. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer improved energy efficiency due to their lower thermal conductivity. This means that less heat is lost to the surroundings, resulting in higher operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption. Overall, the advantages of using monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces include superior thermal shock and corrosion resistance, ease of installation and repair, and improved energy efficiency, making them a preferred choice for these high-temperature industrial applications.
- Q: What are the common applications of monolithic refractories in blast furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories, also referred to as unshaped refractories, find extensive use in blast furnaces due to their advantageous properties and versatile applications. Blast furnaces benefit from the following common applications of monolithic refractories: 1. Furnace lining: The walls, hearth, and roof of blast furnaces are lined with monolithic refractories. These refractories possess high thermal resistance and excellent insulating properties, safeguarding the furnace structure against extreme temperatures and thermal shocks. 2. Repair of tuyeres and tapholes: Tuyeres are nozzles that introduce air or fuel into the furnace, while tapholes are openings used for tapping molten iron or slag. Monolithic refractories are employed to repair and maintain these crucial components, as they can endure the high temperatures and chemical reactions taking place in these regions. 3. Hot repair and maintenance: The demanding operating conditions of blast furnaces necessitate frequent repairs and maintenance. Monolithic refractories are utilized for hot repair and maintenance purposes, as they can be easily applied in a plastic or semi-plastic state to fill cracks, mend damaged areas, or replace worn-out linings. 4. Resistance to erosion and corrosion: Blast furnace environments are highly corrosive due to the presence of molten iron, slag, and other molten materials. Monolithic refractories with exceptional erosion and corrosion resistance protect the furnace lining against chemical attacks, extending its lifespan. 5. Gunning mixes: Gunning mixes are extensively employed in blast furnaces for their ability to be sprayed or gunned onto the refractory lining. These mixes comprise fine refractory aggregates, bonding agents, and additives. They are applied to repair worn-out areas, seal cracks, and provide a protective layer against erosion and slag penetration. 6. Repair of slag line and iron runners: The slag line and iron runners in blast furnaces are prone to erosion and wear due to the corrosive nature of molten slag and iron. Monolithic refractories are utilized to repair and reconstruct these areas, ensuring smooth and efficient furnace operation. To summarize, monolithic refractories play a vital role in blast furnaces, fulfilling numerous functions such as furnace lining, tuyere and taphole repair, hot repair and maintenance, erosion and corrosion resistance, gunning mixes, and repair of slag line and iron runners. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stresses renders them indispensable in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of blast furnace operations.
- Q: What are the benefits of using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- Using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry has several advantages. Firstly, they have excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning they can withstand extreme temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is crucial in an industry where materials are exposed to high temperatures during processes such as melting, casting, and heat treatment. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior corrosion resistance, making them highly durable against the corrosive effects of molten metals and slag. This is particularly important in the iron and steel industry, where materials come into contact with aggressive molten iron, steel, and various chemical compounds. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. They can withstand mechanical stress, vibrations, and impacts commonly encountered in the iron and steel industry. This ensures a longer lifespan for the refractories, reduces downtime for repairs or replacements, and improves overall operational efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer ease of installation and repair. Unlike traditional refractory bricks that require complex and time-consuming masonry work, monolithic refractories can be quickly and easily installed using simple methods such as casting, gunning, or spraying. This saves time and labor costs during initial installation and subsequent maintenance or repairs. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide flexibility in design and application. They can be customized to specific shapes and sizes, allowing for tailored linings in different parts of the iron and steel manufacturing process. This versatility enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of refractory linings, optimizing production output and ensuring consistent quality of the finished iron and steel products. In conclusion, there are numerous benefits to using monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry. They offer exceptional thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and abrasion resistance. They are also easy to install and repair, and their flexibility allows for customized designs. Overall, monolithic refractories contribute to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced product quality in the iron and steel industry.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:AL2O3-SIO2-C Castable for Blast Furnace Tapping Channel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords