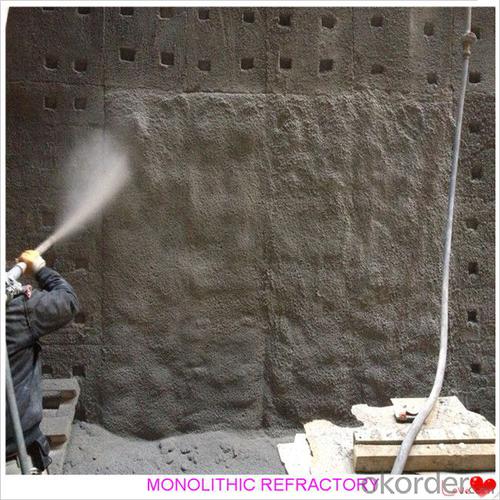
Monolithic High Duty Castable Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
High Duty Castable For Fireplace and Industrial Furnace Cement Industry
Product Description:
High duty castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by the clients. The High duty castables are used high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and made of under superfine powder adding technology.
Product Advantages:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, also has a fine working ability.They should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
For feature of High duty castable, they have excellent abrasion resistance, thermal shock resistance, high-temperature resistance, anti-corrode and have high intensity.
Designed for refractory lining of blast furnace iron and slag runners, skimmers and soon
They can be used in troughs of small and mid size BFs and in all positions of the troughs where fast tapping is required.
Product Specifications:

FAQ:
1. How you can control your quality?
For each production processing, we have complete QC system for the chemical composition
and Physical properties. After production, all the goods will be tested, and the quality certificate
will be shipped along with goods.
2. What's your delivery time?
It usually needs about 20days- 45 days after receiving the deposit.
3. Do you provide free samples?
Yes, we can provide a free sample for testing, If we have sample in stock,
The quantity based on the material type, The buyer should bear all the shipping costs.
4. What's your payment terms?
We can accept 30% deposit, 70% balance before shipment for ordrs over $ 2000.
5. Can we visit your Company?
Yes, certainly. You are very welcome to China and we will be honored to have a customer and friend.
Product Picture:




- Q: How does the composition of monolithic refractories impact their performance?
- The composition of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in determining their performance. Monolithic refractories are essentially unshaped refractory materials that are used to line furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. They are preferred over traditional brick and mortar refractories due to their ease of installation and ability to conform to complex shapes. The composition of monolithic refractories includes various components such as aggregates, binders, and additives. The type and proportion of these constituents significantly influence the physical, mechanical, and thermal properties of the refractory material. Aggregates are the major component of monolithic refractories and provide the structural integrity. They can be made of various materials like alumina, silica, magnesia, and carbon. Each aggregate has its own unique properties that determine the refractory's resistance to heat, chemical attack, and mechanical stress. For example, alumina aggregates offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, while carbon-based aggregates are preferred for their high thermal conductivity. Binders are added to the mix to provide cohesion and improve the refractory's strength. Common binders include clay, calcium aluminate cement, and colloidal silica. The selection of binders depends on the desired strength, workability, and setting time of the refractory material. Additives are incorporated in the composition to enhance specific properties. They can improve the refractory's resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, or chemical attack. Additives like zirconium oxide, silicon carbide, and graphite are often used to enhance the performance of monolithic refractories in specific applications. The proper combination and proportion of these constituents are crucial for achieving the desired performance of monolithic refractories. The composition affects the refractory's thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, density, porosity, and chemical resistance. For instance, a higher alumina content would improve the refractory's resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, while a higher silica content would enhance its insulating properties. In conclusion, the composition of monolithic refractories has a significant impact on their performance. The selection of aggregates, binders, and additives must be carefully considered to achieve the desired properties and ensure optimal performance in specific high-temperature applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants?
- The efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants is greatly improved by the use of monolithic refractories. Specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions, these refractories are an ideal choice for steel plants. One important way in which monolithic refractories enhance furnace efficiency is by decreasing heat loss. With their excellent insulation properties, these refractories minimize the transfer of heat from the furnace to its surroundings. As a result, less energy is wasted and the furnace can maintain its desired temperature more effectively. Furthermore, monolithic refractories contribute to a more uniform and controlled distribution of heat within the furnace. They can be easily shaped and installed to create a seamless lining, ensuring that heat is evenly spread throughout the furnace chamber. This even distribution of heat eliminates any hotspots or cold spots, resulting in a more efficient heating process. Another crucial role of monolithic refractories is reducing downtime and maintenance requirements. Unlike traditional brick linings, which are prone to cracking and erosion, monolithic refractories offer superior resistance to wear and tear. This increased durability reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, allowing for uninterrupted furnace operation and increased overall efficiency. Moreover, monolithic refractories help improve energy efficiency by decreasing fuel consumption. The superior insulation properties of these refractories help retain heat within the furnace, reducing the amount of energy needed to maintain the desired temperature. This leads to significant energy savings for steel plants, as less fuel is required to achieve the same heating results. In conclusion, the efficiency of reheating furnaces in steel plants is significantly enhanced by the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories reduce heat loss, ensure uniform heat distribution, minimize downtime and maintenance, and decrease fuel consumption. By incorporating these refractories into their furnace linings, steel plants can increase productivity, reduce energy costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a vital role in the reduction of energy consumption in iron and steel production. These refractories are heat-resistant materials utilized to line the walls and floors of furnaces and other high-temperature equipment. One of the main ways monolithic refractories aid in energy reduction is through their exceptional thermal insulation properties. These materials possess low thermal conductivity, which effectively minimizes heat loss from the furnace or equipment. By keeping heat loss to a minimum, monolithic refractories help maintain a consistent and high temperature inside the furnace, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency. This allows for better utilization of generated heat, reducing the need for additional energy input and ultimately leading to energy savings. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. This enables them to withstand the extreme temperatures and rapid temperature changes frequently encountered in iron and steel production processes. By having a robust and dependable lining, these refractories prevent heat leakage and ensure efficient heat transfer to desired areas, reducing energy wastage. Furthermore, monolithic refractories contribute to energy reduction by resisting chemical attack and erosion. In iron and steel production, furnaces and equipment linings are exposed to aggressive substances like molten metal, slag, and gases. Monolithic refractories exhibit excellent resistance to these corrosive elements, prolonging their lifespan and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This not only saves energy required for maintenance but also avoids production interruptions and associated energy losses. In conclusion, monolithic refractories aid in the reduction of energy consumption in iron and steel production by providing effective thermal insulation, withstanding extreme temperatures, and resisting chemical attack. By optimizing heat management and extending equipment durability, these refractories significantly contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings in the industry.
- Q: What are the advancements in monolithic refractory technology for the iron and steel industry?
- In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of monolithic refractory technology for the iron and steel industry. Monolithic refractories, which are heat-resistant materials used to line the walls and floors of high-temperature industrial processes, have seen notable advancements. One of the key breakthroughs in monolithic refractory technology is the development of new and improved materials. Traditional refractory materials like firebricks have been replaced by more advanced options such as castables and gunning mixes. These upgraded materials offer superior performance in terms of thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistance, and erosion resistance. They can endure higher temperatures and can be applied more efficiently, resulting in enhanced process efficiency and reduced maintenance downtime. Another significant advancement is the utilization of advanced additives in monolithic refractories. These additives have the ability to enhance the properties of the refractory material, such as increasing its resistance to corrosion and erosion. They also improve the bond between the refractory and the substrate, ensuring a longer lifespan for the lining. Furthermore, the progress in monolithic refractory technology has led to the development of innovative installation techniques. Shotcreting, for example, has gained popularity due to its efficiency and ability to provide a uniform lining by spraying the refractory material onto the surface. Similarly, the use of gunning machines, which pump the refractory material at high velocity, has improved the speed and accuracy of installation. Moreover, there have been advancements in the design of monolithic refractories tailored specifically for various applications in the iron and steel industry. Refractories for blast furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and other critical equipment have been optimized to withstand the unique challenges and harsh conditions of these processes. The development of specialized monolithic refractories has resulted in increased productivity, reduced energy consumption, and improved product quality in the iron and steel industry. In conclusion, advancements in monolithic refractory technology for the iron and steel industry have brought about improved materials, advanced additives, innovative installation techniques, and specialized designs. These advancements have significantly enhanced the performance, durability, and efficiency of refractory linings in high-temperature industrial processes. Consequently, the iron and steel industry can benefit from increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved product quality.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the repair and maintenance of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories are extensively used in the repair and maintenance of ladles and tundishes in the steel industry. These refractories are specially designed to withstand the extreme conditions of high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical erosion that occur during the steelmaking process. When it comes to the repair of ladles, monolithic refractories are used to line the inner walls of the ladle. Ladles are subjected to intense heat and corrosive molten metal, and the refractory lining provides insulation and protection against these harsh conditions. The lining also helps to maintain the desired temperature of the molten metal, ensuring that it remains in a suitable state for processing. In the case of tundishes, monolithic refractories are used to line the bottom and sides of the tundish, as well as the nozzle and impact pad. Tundishes are responsible for distributing molten metal to multiple casting molds and are exposed to high temperatures and thermal shocks. The refractory lining helps to maintain the necessary temperature and prevent any leakage of molten metal. During the repair and maintenance process, monolithic refractories are applied as a dense, high-strength material that is easy to shape and install. They can be shaped into various forms such as bricks, castables, and gunning mixes, depending on the specific requirements of the ladle or tundish. These refractories are often applied using specialized techniques, such as gunning or casting, to ensure proper adhesion and longevity. In addition to their thermal and chemical resistance properties, monolithic refractories also offer excellent mechanical strength and resistance to abrasion. This is crucial in ladles and tundishes, as they are subjected to constant wear and tear from the movement of molten metal and the handling of refractory materials during repair and maintenance. Overall, monolithic refractories play a critical role in the repair and maintenance of ladles and tundishes in the steel industry. They provide the necessary insulation, protection, and durability required to withstand the demanding conditions of steelmaking.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration?
- Monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through several mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made up of high-quality materials that have excellent resistance to slag attack. These materials, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, have a high melting point and can withstand the corrosive nature of the slag. Secondly, monolithic refractories are designed with a dense and compact structure that minimizes the porosity. Slag penetration occurs when the molten slag infiltrates the pores and cracks of the refractory material. By reducing the porosity, monolithic refractories create a barrier that restricts the entry of slag into the refractory lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be chemically bonded to the substrate, forming a strong and impermeable bond. This bond further enhances the resistance to slag penetration by preventing any gaps or weak points where the slag can penetrate. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be designed with a high thermal shock resistance. Slag penetration is often intensified by thermal cycling, where the refractory material undergoes rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories with high thermal shock resistance can withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling, thus reducing the risk of slag penetration. Furthermore, the proper installation and maintenance of monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring their effectiveness against slag penetration. The refractory lining needs to be properly designed, using appropriate thickness and geometry, to provide maximum protection against slag attack. Regular inspection and repair of any damaged or worn-out areas can also prevent slag penetration. In conclusion, monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through their excellent resistance to slag attack, dense structure, chemical bonding, high thermal shock resistance, and proper installation and maintenance. These factors work together to create a strong and impermeable barrier that protects the underlying substrate from the corrosive effects of slag.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories?
- Considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories include assessing the extent of the damage, identifying the cause of the damage, selecting the appropriate repair material, ensuring proper bonding and curing, and following manufacturer's instructions and recommended procedures. Additionally, factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress should be taken into account to ensure the repaired refractory maintains its performance and longevity.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories and how are they used in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that is composed of a single, homogeneous structure. They are used in the iron and steel industry for various applications such as lining furnaces, ladles, and other high-temperature equipment. These refractories are typically made from a combination of aggregates, binders, and additives, which are mixed with water to form a plastic consistency. Once applied, they are dried and fired to create a strong and durable lining that can withstand extreme temperatures and chemical reactions. Monolithic refractories offer advantages like easy installation, excellent thermal shock resistance, and superior performance, making them crucial components in the iron and steel manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories?
- The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories is affected by various factors. These include the composition of the refractory material, the density of the material, the porosity of the material, and the presence of any additives or impurities. The composition of the refractory material plays a significant role in determining its thermal conductivity. Different types of refractory materials, such as alumina-based, silica-based, or magnesia-based, exhibit different thermal conductivities due to their distinct chemical compositions. Materials with higher alumina content generally display higher thermal conductivities compared to those with higher silica content. The density of the refractory material also impacts its thermal conductivity. Materials with higher densities generally exhibit higher thermal conductivities because the closely packed particles enable more efficient heat transfer. Conversely, materials with lower densities tend to have lower thermal conductivities as the presence of air pockets or voids hinders heat transfer. Another crucial factor is the porosity of the refractory material. Porosity refers to the presence of small pores or spaces within the material. Higher porosity leads to lower thermal conductivity as the air or gas trapped within the pores acts as an insulator, reducing the material's ability to conduct heat. Therefore, materials with lower porosity tend to have higher thermal conductivities. The presence of additives or impurities in the refractory material also affects its thermal conductivity. Certain additives or impurities, such as carbon or metallic oxides, can either enhance or inhibit heat transfer in the material. For example, the addition of carbon can increase thermal conductivity due to its high thermal conductivity, while the presence of metallic oxides may decrease thermal conductivity due to their lower thermal conductivities. In conclusion, the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories is influenced by factors such as composition, density, porosity, and the presence of additives or impurities. Understanding and controlling these factors are crucial in designing and selecting refractory materials with optimal thermal conductivity for specific applications.
- Q: What are the key properties of pumpable refractories used for monolithic refractory applications?
- The key properties of pumpable refractories used for monolithic refractory applications include high flowability, good workability, excellent bonding strength, and high resistance to thermal shock. These pumpable refractories should also possess good pumpability and be able to withstand the intense heat and mechanical stress in the application environment. Additionally, they should have low water demand, high chemical resistance, and the ability to maintain their properties even after exposure to high temperatures.
Send your message to us
Monolithic High Duty Castable Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords