GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
Standard: ASTM A36, EN10025, JIS, GB, etc.
Grade:S275, S355, SS400, Q235B, A36, Q345, etc
Sizes: 80MM-270MM
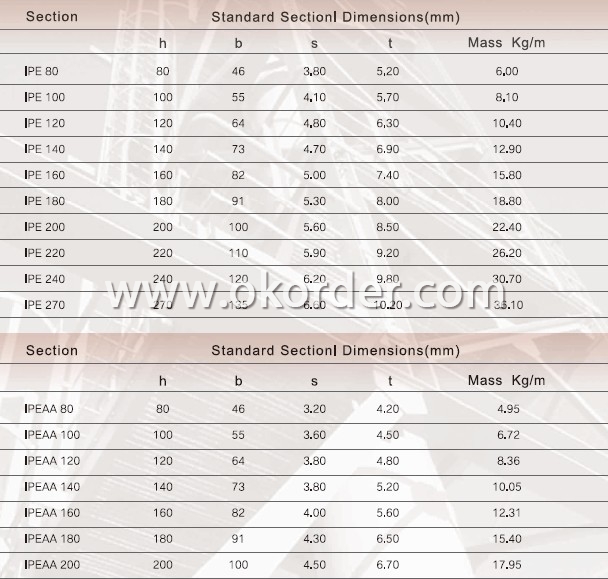
Applications of GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
Hot Rolled Steel I Beam is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.
Package & Delivery Terms of GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
1. Package: All the hot rolled steel I beam will be tired by wire rod in bundles
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Shipment: In containers or in bulk cargo

6. Delivery time: All the hot rolled steel I Beam will be at the port of the shipment within 45 days after receiving the L/C at sight ot the advance pyment by T/T
7. Payment: L/C at sight; 30% advance payment before production, 70% before shipment by T/T, etc.
Production flow of GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in educational or school buildings?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in educational or school buildings. Steel I-beams are commonly used in construction due to their strength and load-bearing capabilities. They provide structural support for the building, ensuring its stability and safety. In educational or school buildings, where large open spaces are often desired, steel I-beams are often used to create large, open classrooms or auditoriums without the need for excessive columns or supports. Additionally, steel I-beams can be used to create multi-story buildings, allowing for efficient use of limited space in crowded school campuses. Overall, steel I-beams are a reliable and versatile option for constructing educational or school buildings.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in schools or educational buildings?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in schools or educational buildings. Steel I-beams are commonly used in construction due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They provide structural support and can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for large educational buildings such as schools. Additionally, steel I-beams allow for open floor plans, facilitating flexible classroom layouts and integration of technology.
- Q: What are the common types of connections for steel I-beams in composite structures?
- The common types of connections for steel I-beams in composite structures include welded connections, bolted connections, and shear stud connections.
- Q: What are the potential hazards associated with steel I-beam installation?
- There are several potential hazards associated with steel I-beam installation that need to be taken into consideration. Firstly, the sheer weight of steel I-beams can pose a significant risk if not handled properly. These beams can weigh several hundred pounds or more, and if they are not properly secured during installation, they can fall and cause serious injuries or even fatalities to workers or bystanders. It is important to use appropriate lifting equipment and follow proper safety protocols to ensure the safe handling and installation of steel I-beams. Secondly, the installation process itself can be hazardous. Steel I-beams are often installed at elevated heights, which can increase the risk of falls. Workers must be equipped with fall protection gear, such as harnesses and safety nets, and proper scaffolding or platforms should be used to provide a stable work surface. Additionally, workers should be trained on proper lifting techniques and be aware of potential pinch points or crush hazards during installation. Another hazard associated with steel I-beam installation is the risk of structural collapse. If the beams are not properly aligned, secured, or supported, it can lead to structural failure, which can be catastrophic. It is crucial to have a qualified engineer or structural specialist oversee the installation process to ensure that all load-bearing requirements are met and that the beams are installed correctly. Lastly, there may be additional hazards related to the specific environment in which the steel I-beams are being installed. For example, if the installation is taking place in a confined space or in an area with limited ventilation, there may be risks associated with poor air quality or exposure to hazardous substances. It is important to assess and mitigate these potential hazards before beginning the installation process. Overall, the potential hazards associated with steel I-beam installation highlight the need for proper planning, training, and adherence to safety protocols. By following best practices and ensuring that all necessary safety measures are in place, the risks can be minimized, and the installation process can be completed safely and efficiently.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in bridge or overpass construction?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in bridge or overpass construction. Steel I-beams are commonly used in the construction of bridges and overpasses due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They are ideal for supporting heavy loads and providing structural stability, making them a popular choice for many civil engineering projects. Steel I-beams can be designed and fabricated to meet specific project requirements, allowing for customization and optimization of the bridge or overpass design. Additionally, steel I-beams are resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh weather conditions, making them suitable for long-term use in outdoor structures. Overall, steel I-beams are a reliable and effective choice for bridge and overpass construction.
- Q: What are the environmental impacts of steel I-beam production?
- The environmental impacts of steel I-beam production include carbon dioxide emissions from the energy-intensive manufacturing process, deforestation and habitat destruction due to iron ore extraction, water pollution from mining activities, and the generation of waste materials such as slag and scale. Additionally, the transportation of raw materials and finished products contributes to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, advancements in technology and sustainable practices are being implemented to reduce these impacts.
- Q: What are the different load capacities of steel I-beams?
- The load capacities of steel I-beams may differ based on various factors, including the beam's size, shape, and material grade. Typically, steel I-beams are designed to withstand heavy loads and are commonly used in construction projects. The load capacity of a steel I-beam is usually determined by its cross-sectional dimensions, which consist of the depth (or height), flange width, and web thickness. A higher load capacity is achieved with larger dimensions. Regarding standardized sizes, steel I-beams are often categorized by their nominal depth and weight per foot. Depths can range from 3 inches to over 24 inches, and the load capacity of each size depends on the specific design and specifications. Engineers and architects rely on structural analysis and calculations to determine the load capacity of a particular steel I-beam. This involves considering factors such as the steel's material properties, load distribution, and overall structural design. It's important to note that additional factors, such as the type of steel used (e.g., mild steel, high-strength steel), presence of reinforcement (e.g., flange plates, stiffeners), and intended application, can also affect load capacities. In conclusion, the load capacities of steel I-beams can vary significantly based on factors such as size, shape, material grade, and other design considerations. To determine the specific load capacity for a given application, it is crucial to consult a structural engineer or refer to relevant design codes and standards.
- Q: How do steel I-beams contribute to the overall architectural design of a structure?
- Due to their exceptional strength, versatility, and load-bearing capabilities, steel I-beams play a crucial role in the overall architectural design of structures. The beams form the framework of the building and distribute weight and forces, ensuring stability and integrity. An important contribution of steel I-beams to architectural design is their ability to span long distances without excessive support columns or walls. This allows for open and flexible floor plans, creating vast and unobstructed spaces. By reducing the need for interior load-bearing walls, architects have more freedom to design layouts that meet specific needs. Steel I-beams also provide structural support for multi-story buildings, enabling architects to design taller structures with greater height and verticality. This is especially beneficial in urban environments with limited space, as it allows for efficient land usage by building upward. The strength and rigidity of steel I-beams make it possible to construct skyscrapers and high-rise buildings that can withstand various forces. In addition to their structural functionality, steel I-beams contribute to the aesthetic appeal of structures. Their sleek and minimalistic design adds a modern and industrial touch to architectural styles, which is highly desired in contemporary design. The clean lines and open spaces created by I-beams can be used to emphasize architectural features, showcase views, or create visual effects. Furthermore, steel I-beams are versatile in their application, allowing architects to incorporate them into various design elements. They can be exposed and visible, becoming an integral part of the building's aesthetic. Alternatively, they can be concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings, providing a hidden structural support system that maintains design integrity and maximizes usable space. Overall, steel I-beams are essential for architectural design, contributing to the overall strength, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal of structures. Their ability to bear heavy loads, span long distances, and create open spaces make them a preferred choice for architects aiming for both structural and design excellence.
- Q: How do Steel I-Beams perform in terms of fire resistance?
- Steel I-beams have excellent fire resistance properties. Due to the high melting point of steel, typically around 2,500°F (1,370°C), they can withstand high temperatures for an extended period without compromising their structural integrity. When exposed to fire, steel I-beams do not combust, melt, or warp easily, making them highly reliable in resisting the spread of fire within a building. Moreover, steel I-beams have low thermal conductivity, meaning they are not easily affected by heat transfer. This property allows the steel to maintain its strength and rigidity, even when exposed to intense heat. Additionally, steel I-beams are often protected with fire-resistant coatings or insulation materials to further enhance their fire resistance. It is important to note that although steel I-beams are highly fire-resistant, they can still be susceptible to thermal expansion. When exposed to extreme heat, steel expands, which may lead to structural distortions or failures if not properly accounted for in the building design. Therefore, it is crucial to incorporate appropriate fire protection measures and consider the potential effects of thermal expansion in the construction of steel I-beam structures. Overall, steel I-beams are considered a reliable and durable choice for fire resistance in construction. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain their structural integrity makes them a preferred choice in buildings where fire safety is a priority.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used for both residential and commercial construction?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used for both residential and commercial construction. They are commonly used in both types of construction due to their strength, durability, and ability to support heavy loads.
Send your message to us
GB Standard Hot Rolled Steel I Beams Q235, Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























