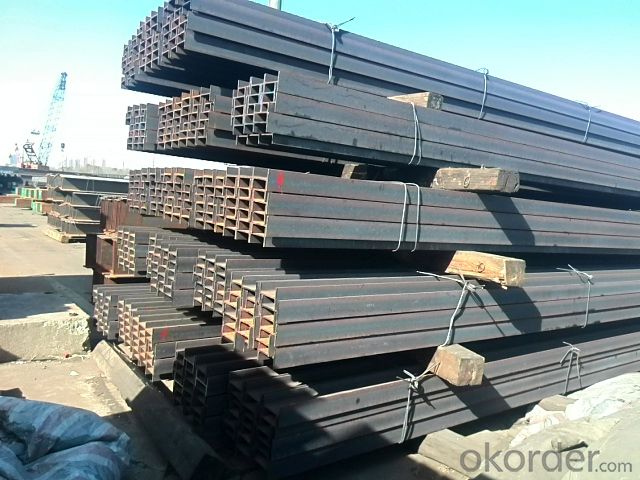
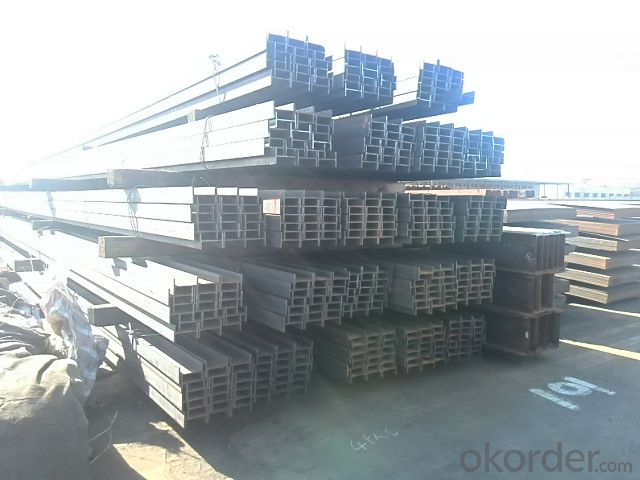
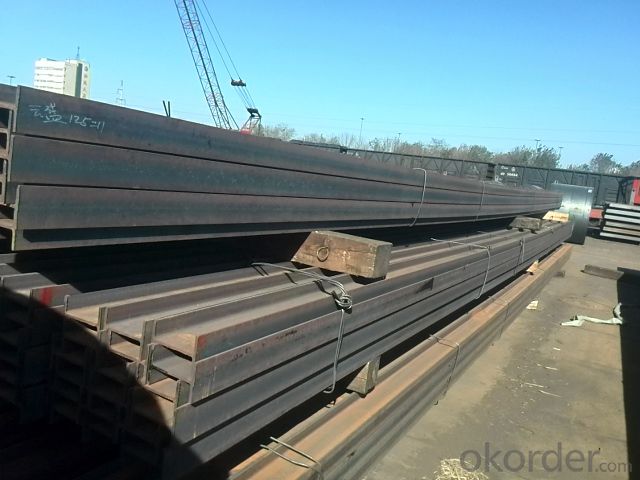
Hot Rolled Steel H Beam Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel H-beam Q345
1. Standard: JIS 3192
2. Grade: Q345,SS400 or Equivalent
3. Length: 10m, 12m as following table
4. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
5.Payment: TT or L/C
6. Sizes:
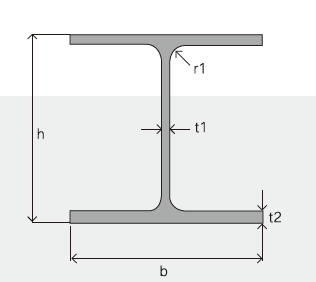
H x B (mm) | T1 | T2 | JIS Weight (kg/m) | GB Weight (kg/m) |
100*100 | 6 | 8 | 16.9 | 17.2 |
125*125 | 6.5 | 9 | 23.6 | 23.8 |
150*75 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 14.3 |
148*100 | 6 | 9 | 20.7 | 21.4 |
150*150 | 7 | 10 | 31.1 | 31.9 |
175*90 | 5 | 8 | 18 | 18.2 |
175*175 | 7.5 | 11 | 40.4 | 40.4 |
198*99 | 4.5 | 7 | 17.8 | 18.5 |
200*100 | 5.5 | 8 | 20.9 | 21.7 |
194*150 | 6 | 9 | 29.9 | 31.2 |
200*200 | 8 | 12 | 49.9 | 50.5 |
248*124 | 5 | 8 | 25.1 | 25.8 |
250*125 | 6 | 9 | 29 | 29.7 |
244*175 | 7 | 11 | 43.6 | 44.1 |
250*250 | 9 | 14 | 71.8 | 72.4 |
298*149 | 5.5 | 8 | 32 | 32.6 |
298*201 | 9 | 14 | 65.4 |
|
300*150 | 6.5 | 9 | 36.7 | 37.3 |
294*200 | 8 | 12 | 55.8 | 57.3 |
300*300 | 10 | 15 | 93 | 94.5 |
346*174 | 6 | 9 | 41.2 | 41.8 |
350*175 | 7 | 11 | 49.4 | 50 |
340*250 | 9 | 14 | 78.1 | 79.7 |
350*350 | 12 | 19 | 135 | 137 |
400*200 | 8 | 13 | 65.4 | 66 |
390*300 | 10 | 16 | 105 | 107 |
400*400 | 13 | 21 | 172 | 172 |
446*199 | 8 | 12 | 65.1 | 66.7 |
450*200 | 9 | 14 | 77.9 | 79.5 |
440*300 | 11 | 18 | 121 | 124 |
496*199 | 9 | 14 | 77.9 | 79.5 |
500*200 | 10 | 16 | 88.2 | 89.6 |
488*300 | 11 | 18 | 125 | 129 |
596*199 | 10 | 15 | 92.5 | 95.1 |
600*200 | 11 | 17 | 103.4 | 106 |
588*300 | 12 | 20 | 147 | 151 |
700*300 | 13 | 24 | 182 | 185 |
800*300 | 14 | 26 | 207 | 210 |
900*300 | 16 | 28 | 240.1 | 243 |
Usage & Applications of Hot Rolled Steel H-beam
Commercial building structure ;Pre-engineered buildings; Machinery support structure; Prefabricated structure; Medium scale bridges; Ship-building structure.etc.


Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Steel H-beam Q345
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
Production flow of Hot Rolled Steel H-beam Q345
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
- Q: Can steel angles be used for manufacturing support brackets?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for manufacturing support brackets. Steel angles are commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries due to their strength and durability. They provide excellent support and structural integrity, making them ideal for creating support brackets. Steel angles are available in various sizes and thicknesses, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the bracket. Additionally, steel angles can be easily welded, drilled, and machined to fit the desired specifications, making them a versatile choice for manufacturing support brackets.
- Q: What is the typical shear strength of steel angles?
- The shear strength of steel angles can vary depending on several factors such as the grade of steel, the size and shape of the angle, and adherence to industry standards or specific applications. However, steel angles generally possess high shear strength. For standard structural steel angles, the shear strength typically ranges from around 50,000 to 75,000 pounds per square inch (psi). This range is applicable to common steel grades including A36, A572, and A588. These angles find frequent use in construction, infrastructure, and engineering projects where shear forces are of concern. It is important to acknowledge that the shear strength of steel angles can be influenced by additional factors such as the presence of holes or notches, welding or fabrication processes, and the overall design and load distribution. Hence, it is crucial to consult relevant design codes or engineering specifications to ascertain the specific shear strength requirements for a given application. To ensure the accurate determination of shear strength for steel angles in a particular project, it is recommended to consult with a structural engineer or an experienced professional.
- Q: How do steel angles perform under seismic loads?
- Steel angles are widely used in construction to provide support and reinforcement for structures. Their inherent properties and design flexibility make them highly effective in seismic conditions. A major advantage of steel angles is their impressive strength-to-weight ratio. This enables them to withstand the intense forces and movements caused by earthquakes without significant deformation or failure. The angle's compact shape also helps distribute the load efficiently, reducing stress concentrations and potential weak points. Furthermore, steel angles can be easily connected to other structural elements, creating a robust and reliable connection system. This is crucial in seismic design, where the ability to transfer forces and accommodate movements is vital. To further enhance their performance under seismic loads, steel angles can be designed with specific features. For example, the addition of stiffeners or bracing elements can increase their resistance to lateral forces, minimizing the risk of buckling or collapse. Using thicker and stronger steel grades can also improve their capacity to absorb and dissipate seismic energy. Various seismic design codes and standards provide guidelines and requirements for the use of steel angles in earthquake-resistant structures. These codes consider factors such as maximum stress levels, connection details, and overall structural behavior during seismic events. In conclusion, steel angles excel in seismic conditions due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, efficient load distribution, and design flexibility. When properly designed and implemented, they effectively withstand the forces and movements generated during earthquakes, ensuring the structural integrity and safety of buildings.
- Q: How do steel angles compare to wooden beams?
- Steel angles and wooden beams possess distinct characteristics and abilities that render them suitable for diverse applications. Steel angles, being comprised of steel, demonstrate exceptional strength and longevity. They exhibit remarkable tensile strength and resist bending and warping even when subjected to substantial loads. This renders them an excellent choice for providing structural support in constructions such as buildings, bridges, and other similar projects. Moreover, steel angles possess the advantage of being non-combustible, thereby enhancing fire safety. Conversely, wooden beams offer their own set of advantages. As a natural material, wood is readily accessible and renewable, making it a more environmentally conscious option when compared to steel. Additionally, wooden beams possess an inherent aesthetic appeal, particularly in traditional or rustic designs. They can be effortlessly customized and shaped, enabling the creation of intricate and imaginative designs. Nevertheless, wooden beams do have certain limitations with regards to strength and durability. They do not exhibit the same level of robustness as steel angles and are susceptible to bending, warping, and rotting over time. Additionally, wood is combustible, which can pose safety concerns. In conclusion, both steel angles and wooden beams possess their own unique strengths and weaknesses. Steel angles excel in projects necessitating high strength and durability, while wooden beams offer a more natural and visually appealing option. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on specific project requirements, budgetary considerations, and personal preferences.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface finishing for steel angles?
- There are several different methods of surface finishing for steel angles, each with its own advantages and considerations. The most common methods include painting, galvanizing, powder coating, and shot blasting. Painting is a popular method for surface finishing steel angles as it provides a protective barrier against corrosion and adds an aesthetic appeal. The angle is typically cleaned and primed before applying multiple coats of paint. This method allows for a wide range of color options and can be easily touched up if damaged. Galvanizing involves coating the steel angle with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. This method is particularly effective in harsh environments where the angle may be exposed to moisture or chemicals. Hot-dip galvanizing is the most common method, where the angle is immersed in a bath of molten zinc. This creates a durable and long-lasting finish that requires minimal maintenance. Powder coating is another popular surface finishing method that involves applying a dry powder to the angle and then curing it with heat to form a protective layer. This method offers excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and UV rays. It also provides a smooth and consistent finish, with a wide range of colors available. Shot blasting is a mechanical method of surface finishing that involves blasting the steel angle with high-speed abrasive particles. This removes any rust, mill scale, or other contaminants from the surface, resulting in a clean and smooth finish. Shot blasting also creates a rough texture that improves paint adhesion, making it an ideal pre-treatment before painting or powder coating. It is important to consider the specific requirements of the steel angle's application when choosing a surface finishing method. Factors such as the environment, expected lifespan, aesthetic preferences, and budget should all be taken into account. Consulting with a professional or the steel manufacturer can help determine the most suitable method of surface finishing for steel angles in a particular situation.
- Q: How do you clean steel angles?
- Cleaning steel angles can be done using a few simple steps. First, gather the necessary supplies, including a mild detergent or soap, warm water, a soft cloth or sponge, and a non-abrasive brush or scrub pad. Start by filling a bucket or sink with warm water and adding a small amount of mild detergent or soap. Mix the solution gently until it foams slightly. Wet the cloth or sponge with the soapy water and gently scrub the steel angles, ensuring to cover all areas and remove any dirt or grime. For tougher stains or stubborn debris, use the non-abrasive brush or scrub pad to gently scrub the surface. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or steel wool as these can scratch or damage the steel surface. Additionally, acidic or corrosive cleaners should be avoided as they can cause discoloration or rusting of the steel. Once you have thoroughly cleaned the steel angles, rinse them with clean water to remove any remaining soap residue. Dry the angles with a clean, soft cloth to prevent water spots or streaks from forming. Regular cleaning and maintenance of steel angles is important to keep them looking their best and to prevent any corrosive damage. By following these steps, you can effectively clean steel angles and maintain their appearance for years to come.
- Q: Are steel angles resistant to UV radiation or fading?
- No, steel angles are not resistant to UV radiation or fading.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in sports or recreational facilities?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in sports or recreational facilities. Steel angles are commonly used in the construction industry due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They are often used in the construction of sports and recreational facilities such as stadiums, arenas, gymnasiums, and indoor/outdoor courts. Steel angles are typically used to provide structural support and stability to the building. They can be used in the framing of walls, roofs, and floors, as well as in the construction of bleachers, seating areas, and staircases. Steel angles can also be used to create barriers, fences, and safety rails, ensuring the safety of athletes and spectators. In addition to their structural applications, steel angles can also be used for aesthetic purposes. They can be used as decorative elements, such as in the design of entrance gates, signage, and lighting fixtures. Steel angles can be painted or coated in various colors or finishes to match the overall design theme of the sports or recreational facility. Overall, steel angles are a versatile and practical choice for use in sports and recreational facilities. Their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal make them suitable for a wide range of applications within these facilities.
- Q: What is the typical lead time for steel angle orders?
- The typical lead time for steel angle orders can vary depending on the supplier and the specific order requirements. However, it is common for lead times to range from a few days to a couple of weeks.
- Q: What is the difference between galvanized steel angle and ordinary angle iron?
- Ordinary steel angle and cold galvanized steel angle per ton difference of about 500 yuan;
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel H Beam Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























