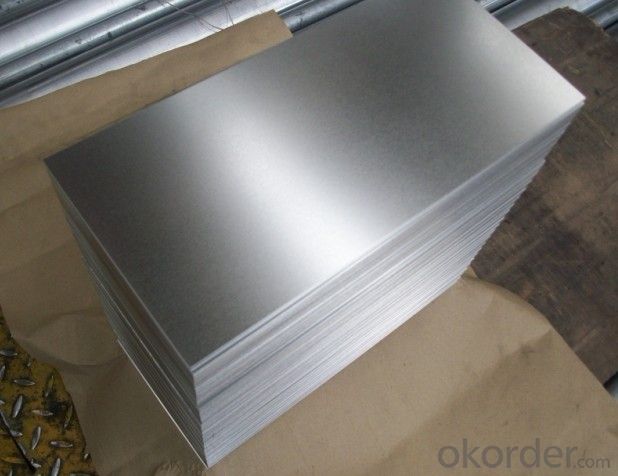
Galvanized/Aluzinc Steel Sheet with Best Quality in China
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Images
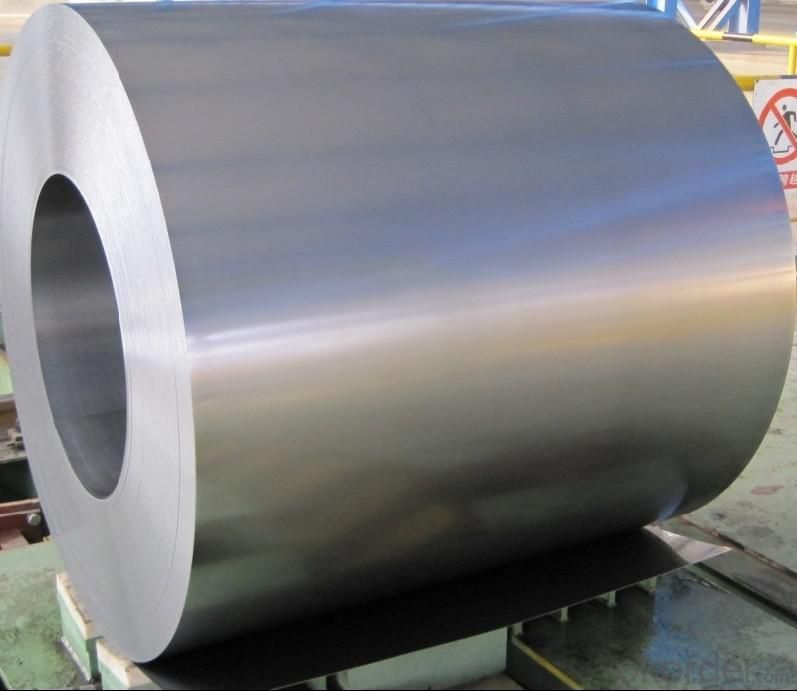


4.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Specification
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
| Processability | Yield strength | Elongation % | Elongation % | 180°cold-bending |
| Common PV | - | 270-500 | - | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
| Mechanical interlocking JY | - | 270-500 | - | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
| Structure JG | >=240 | >=370 | >=18 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
| Deep drawn SC | - | 270-380 | >=30 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
| EDDQ SC | - | 270-380 | >=30 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
2. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during storage in outdoor environments?
- Steel sheets are protected during storage in outdoor environments through the application of various protective measures. These measures may include the use of weather-resistant coatings, such as galvanization or paint, to prevent corrosion and rusting. Additionally, steel sheets can be stored on pallets or racks to minimize contact with the ground and reduce the risk of moisture accumulation. Covering the sheets with tarpaulins or using weatherproof storage containers further shields them from direct exposure to rain, snow, and sunlight. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of these protective measures and to address any potential issues promptly.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for HVAC systems?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for HVAC systems. Steel sheets are commonly used in HVAC systems due to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They provide structural integrity to the system and can withstand high temperatures and pressure. Additionally, steel sheets are easy to fabricate and can be customized to fit specific HVAC system requirements. They are also cost-effective and have a long lifespan, making them a preferred choice for HVAC system components such as ductwork, ventilation systems, and air handling units.
- Q: Can steel sheets be galvanized or coated with protective layers?
- Yes, it is possible to galvanize or coat steel sheets with protective layers. Galvanization is the process of applying a zinc coating to steel to prevent rusting. This can be done through hot-dip galvanization, where the steel is immersed in molten zinc, or through electroplating, which uses an electrolytic process to apply the zinc coating. Aside from galvanization, steel sheets can also be coated with various protective layers. These coatings may include paint, epoxy, powder coatings, or specialized coatings designed to enhance resistance to corrosion, chemicals, or abrasion. These protective coatings not only enhance the appearance of the steel but also act as a barrier against environmental factors that could potentially damage it. The choice between galvanization and coating depends on the specific application and desired level of protection. Galvanization is commonly used in outdoor applications where steel is exposed to moisture, such as in construction, automotive, and infrastructure industries, due to its excellent corrosion resistance. Coatings, on the other hand, offer a wide range of protective properties and can be suitable for various applications, including indoor environments or where specific chemical resistance is necessary. Ultimately, both galvanization and coating with protective layers are effective methods to increase the durability and lifespan of steel sheets. The selection of the appropriate method depends on factors such as the intended use, environmental conditions, and budget.
- Q: What are the different methods of joining steel sheets together?
- There exists a variety of techniques for connecting steel sheets, each possessing unique benefits and applications. Some commonly employed techniques include: 1. Welding: Utilized extensively, welding effectively joins steel sheets by melting their edges and fusing them together through the application of heat. Different welding processes, including arc welding, gas welding, and spot welding, are available, each tailored to specific applications. 2. Riveting: Riveting, a mechanical method, utilizes metal fasteners called rivets to connect steel sheets. Rivets are inserted into pre-drilled holes in the sheets and secured in place by hammering or pressing. Riveting is renowned for producing robust and long-lasting joints. 3. Bolting: Bolting employs bolts and nuts to hold steel sheets together. Holes are drilled through the sheets, and bolts are inserted from one side, with nuts tightened on the other side to secure the joint. Bolting offers the advantages of being quick, easy to assemble, and allows for disassembly if necessary. 4. Adhesive bonding: Adhesive bonding employs specialized adhesives to join steel sheets. The adhesive is applied between the surfaces to be joined and forms a strong bond as it cures. This method is commonly employed in industries where welding may distort the materials or is not feasible due to the specific materials involved. 5. Mechanical fastening: Mechanical fasteners such as screws, self-tapping screws, or nails may be used to join steel sheets. These fasteners create a sturdy connection by penetrating the sheets and holding them in place. Mechanical fastening is relatively swift and does not necessitate any specialized equipment. 6. Clinching: Clinching is a cold forming process that connects steel sheets by deforming the material without the use of external heat. It involves pressing the sheets together and forming a mechanical interlock. Clinching is frequently employed in the automotive industry due to its high-speed production capabilities and joint strength. Each technique possesses its own advantages based on factors such as joint strength, ease of assembly, cost, and specific application requirements. The selection of a joining technique depends on the intended purpose of the joint, material properties, and the environmental conditions to which the joint will be exposed.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for food-grade applications?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for food-grade applications. Stainless steel sheets, in particular, are commonly used in the food industry due to their excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning. They meet the necessary hygiene standards and are non-reactive with food, making them a suitable choice for food processing, storage, and transportation.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in cryogenic environments?
- Steel sheets perform well in cryogenic environments due to their low thermal expansion coefficient, high strength, and good ductility. At extremely low temperatures, steel retains its structural integrity, resists cracking or brittleness, and maintains its mechanical properties. This makes steel sheets suitable for various applications in cryogenic industries, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage tanks, aerospace components, and scientific research facilities.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for flooring?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for flooring, especially in industrial or commercial settings. Steel flooring offers durability, strength, and resistance to wear and tear. It is commonly used in warehouses, factories, and other high-traffic areas where heavy loads and frequent foot traffic are expected.
- Q: What is the typical impact resistance of a steel sheet?
- The typical impact resistance of a steel sheet can vary depending on factors such as the grade of steel, thickness, and any additional treatments or coatings applied. However, steel sheets generally have good impact resistance due to the inherent strength and toughness of the material.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for safety barriers or guardrails?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for safety barriers or guardrails. Steel sheets are commonly used in construction and infrastructure projects due to their strength and durability. They are often used to create robust safety barriers and guardrails that provide protection and prevent accidents in various settings such as highways, bridges, and industrial facilities.
- Q: What is the typical composition of stainless steel sheets?
- The primary constituents of stainless steel sheets are iron, chromium, and nickel, which are responsible for its distinct properties. The proportions of these three elements can vary depending on the specific grade of stainless steel being utilized. On average, stainless steel sheets typically contain approximately 10-30% chromium and 8-20% nickel. Moreover, small quantities of other elements like carbon, manganese, and molybdenum may be present to further augment the strength, corrosion resistance, and other desired characteristics of the stainless steel. The composition of stainless steel sheets is meticulously balanced to attain the desired amalgamation of durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion, which makes it a highly favored choice across industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Send your message to us
Galvanized/Aluzinc Steel Sheet with Best Quality in China
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords