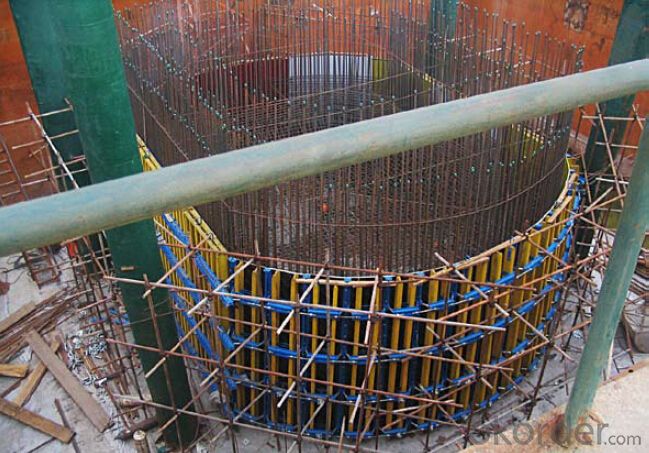
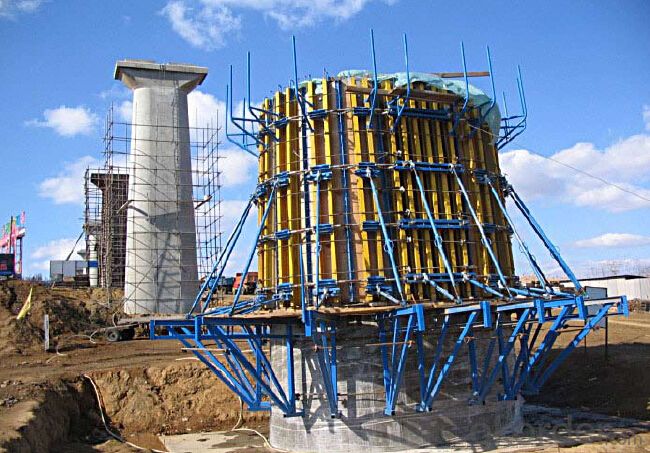
Adjustable arced steel formwork
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
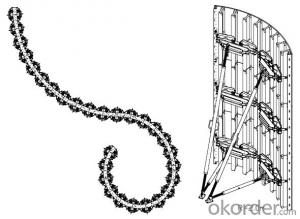
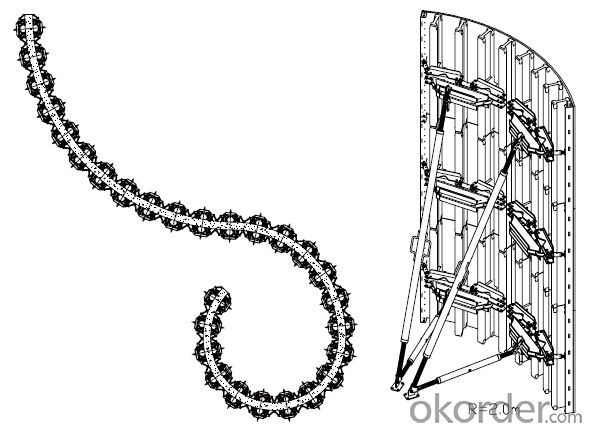
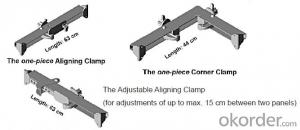
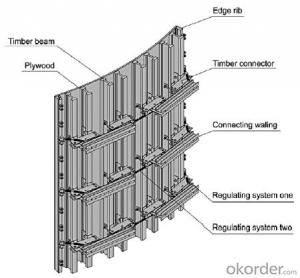
Adjustable Arced Formwork
For pouring arced wall or column with radius more than 1m.
Characteristics:
◆ Adjustable radius, flexible application.
◆ Easy operating, economical efficiency.


- Q: How does steel formwork accommodate for different concrete curing methods?
- Due to its durability, flexibility, and ease of use, steel formwork is a versatile construction material that can accommodate various concrete curing methods. To begin with, different curing methods can be employed with steel formwork, including wet curing, dry curing, and accelerated curing. Wet curing involves maintaining the concrete's moisture and hydration for a specific period, while dry curing involves controlling the concrete's environment with low humidity. On the other hand, accelerated curing utilizes external heat sources to expedite the curing process. Steel formwork is particularly suitable for wet curing as it effectively retains moisture and prevents water loss from the concrete. The tightly fitted steel panels create a watertight enclosure that minimizes evaporation. This ensures that the concrete remains adequately hydrated during curing, promoting proper strength development and minimizing the risk of cracking or shrinkage. Likewise, steel formwork easily accommodates dry curing methods. The steel panels act as a barrier between the concrete and the surrounding environment, allowing precise control of humidity levels. This is especially beneficial in hot or dry climates, where maintaining a low humidity environment is critical for preventing premature moisture loss and ensuring proper curing. Furthermore, steel formwork is compatible with accelerated curing techniques. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it suitable for applications where external heat sources are used to expedite the curing process. The steel panels can withstand elevated temperatures without warping or compromising their structural integrity. Additionally, steel formwork can be easily adjusted or modified to meet specific curing requirements. The modular nature of steel formwork allows for flexibility in design and construction. By rearranging or adding steel panels, the formwork can be customized to create different shapes, sizes, or configurations. This flexibility is particularly advantageous when dealing with complex or unique concrete structures. In summary, steel formwork is a reliable choice for accommodating various concrete curing methods. Its durability, flexibility, and adaptability make it the preferred option in construction projects that require precise control over the curing process to achieve optimal concrete strength and quality.
- Q: What are the common safety guidelines when working with steel formwork in hazardous areas?
- When working with steel formwork in hazardous areas, it is important to adhere to certain safety guidelines to ensure the protection of workers and prevent accidents. Here are some common safety guidelines to follow: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): All workers should wear appropriate PPE such as safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and hard hats to protect themselves from potential hazards. 2. Training and Education: Workers should receive proper training on how to work with steel formwork and be educated about the potential hazards associated with the specific hazardous areas they will be working in. This includes knowing how to handle steel formwork safely and understanding emergency procedures. 3. Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Before starting any work, a thorough assessment of the hazardous area should be conducted to identify potential risks and hazards. This will help in implementing appropriate safety measures and controls. 4. Fall Protection: If working at heights, proper fall protection measures should be in place, such as guardrails, safety harnesses, and safety nets. Workers should be trained on the correct use of fall protection equipment and systems. 5. Fire Safety: In hazardous areas, there may be an increased risk of fire. Ensure that fire extinguishers are readily available, workers are trained in their use, and emergency evacuation plans are in place. 6. Electrical Safety: Any electrical equipment or tools used in the vicinity of the steel formwork should be properly grounded and regularly inspected for safety. Workers should be cautious and avoid contact with live wires. 7. Proper Handling and Storage: When working with steel formwork, it is crucial to handle and store the materials properly to prevent injuries. This includes using appropriate lifting equipment, securing the formwork properly, and storing it in designated areas to avoid tripping hazards. 8. Adequate Ventilation: If working in confined spaces, ensure proper ventilation is in place to prevent the buildup of toxic gases or fumes. Workers should be trained on the signs and symptoms of exposure to hazardous substances. 9. Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Regular inspections of the steel formwork and surrounding areas should be conducted to identify any potential safety hazards. Any necessary repairs or maintenance should be carried out promptly. 10. Communication and Emergency Procedures: Clear communication should be established between workers, supervisors, and other stakeholders to ensure everyone is aware of the potential hazards and emergency procedures. Regular safety meetings and drills can help reinforce this communication. By following these common safety guidelines, workers can minimize the risks associated with working with steel formwork in hazardous areas and create a safer working environment.
- Q: How does steel formwork handle different concrete air content requirements?
- Steel formwork is a construction material that is both durable and versatile. It effectively manages various concrete air content needs. Concrete air content refers to the amount of trapped air in the concrete mixture. This is crucial for enhancing workability, durability, and resistance to freezing and thawing cycles. The purpose of steel formwork is to provide a sturdy and rigid structure that shapes and contains the poured concrete during the curing process. Since the formwork is made of steel, it is impermeable, meaning it does not allow air to pass through. This ensures that no air escapes the concrete mixture, thus maintaining the desired air content. To accommodate different concrete air content requirements, steel formwork can be customized or adjusted accordingly. For instance, if a higher air content is needed, the formwork can be designed with additional space or voids to accommodate the desired amount of air in the concrete. Conversely, if a lower air content is required, the formwork can be designed to minimize air entrapment by ensuring tight connections and smooth surfaces. Furthermore, steel formwork can be used in conjunction with other techniques to control the air content in concrete. For example, it can be combined with air-entraining admixtures, which are additives mixed with the concrete to purposely introduce air bubbles. These admixtures ensure a more uniform distribution of air throughout the concrete, and the steel formwork aids in retaining this air during the pouring and curing process. In conclusion, steel formwork is an ideal choice for managing different concrete air content requirements due to its impermeability and customizable nature. It provides a dependable and strong structure to contain the concrete while maintaining the desired air content. It can also be combined with other techniques such as air-entraining admixtures to further control the air content in concrete.
- Q: What are the different types of finishes available for steel formwork?
- Steel formwork offers a variety of finishes, each with its own advantages and characteristics. Here are some commonly used finishes: 1. Smooth finish: This is the most basic option, leaving the steel formwork untreated. It creates a clean and smooth surface, perfect for achieving a polished concrete finish. 2. Galvanized finish: To protect against corrosion, the steel formwork is coated with a layer of zinc. This durable finish can withstand harsh weather conditions, so it is ideal for outdoor applications. 3. Powder-coated finish: A dry powder is applied to the steel formwork and then baked on, resulting in a decorative and long-lasting coating. It is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading, and offers a wide range of colors for customization. 4. Painted finish: Another common choice is to paint the steel formwork. This not only enhances its aesthetics but also provides protection against corrosion. The type of paint used can vary based on project requirements, such as epoxy or acrylic paints. 5. Shot-blasted finish: By projecting small steel shots at high velocity onto the formwork surface, shot blasting removes impurities, rust, or old coatings, creating a clean and textured finish. This type of finish is often desired for better concrete adhesion. 6. Treated finish: Some steel formwork can be treated with special coatings or chemicals to enhance its properties. For instance, anti-stick coatings prevent concrete from sticking to the formwork, making it easier to remove after curing. Other treatments may include rust inhibitors or fire-resistant coatings. When choosing a finish for steel formwork, factors such as intended use, environmental conditions, desired aesthetics, and budget should be considered. Consulting a professional or manufacturer can help determine the most suitable finish for a specific project.
- Q: What are the different types of form ties used in steel formwork systems?
- In steel formwork systems, there exist various form ties that serve to establish a secure bond between the formwork panels and supporting structures. 1. Conventional Form Ties: The most commonly employed form ties are those comprised of a steel rod with cones or washers on both ends. These rods are inserted through the formwork panels and secured using nuts or wedges, resulting in a robust connection. 2. Coil Ties: These ties are constructed from a continuous loop of wire, often galvanized to resist corrosion. They are simple to install and remove, and can accommodate different concrete wall thicknesses by adjusting the loop length. 3. She-Bolts: Alternatively referred to as she-bolts or coil bolts, these form ties consist of a threaded rod embedded in the concrete wall, along with a plate and nut on the external side. They establish a sturdy connection and find common usage in scenarios where frequent formwork removal and repositioning is necessary. 4. Snap Ties: Equipped with a flat plate on one end and a snap-tie wedge on the other, these ties are easily and swiftly installed without any special tools. They offer a dependable connection and are suitable for light to medium-duty applications. 5. Plastic Cone Ties: Designed for use with reusable plastic formwork systems, these ties are made from plastic material. They possess a lightweight nature, are easy to handle, and exhibit excellent resistance to chemical corrosion. 6. Flat Ties: Strip or bar-shaped, flat ties are utilized to connect formwork panels. Typically crafted from steel, they can be readily bent or cut to the desired length. These ties are frequently employed in scenarios where the wall thickness is minimal. 7. Wedge Bolts: Comprising a threaded rod, a wedge-shaped plate, and a nut, these form ties are inserted into a hole in the formwork panel. Tightening the nut secures the connection. Wedge bolts are commonly employed in situations requiring high strength and rapid installation. These aforementioned examples merely represent a selection of the various form ties adopted within steel formwork systems. The choice of form tie is contingent upon factors such as the application, concrete wall thickness, desired strength, and ease of installation and removal.
- Q: What are the considerations when designing steel formwork for retaining structures?
- When designing steel formwork for retaining structures, there are several important considerations that need to be taken into account. Firstly, the structural stability of the formwork needs to be ensured, as it will be subjected to significant loads and pressures from the weight of the concrete and the earth it is retaining. The formwork needs to be designed to withstand these loads without deformation or failure. Additionally, the formwork should be easy to assemble, disassemble, and adjust. This is important for efficiency during construction and for future maintenance or repairs if needed. The design should allow for quick and easy installation of the formwork system. Another consideration is the durability of the formwork. Steel formwork should be resistant to corrosion, as it will be exposed to moisture from the concrete. Proper surface treatment and protective coatings should be applied to ensure its longevity. Furthermore, the formwork should be designed to provide a smooth and consistent finish to the concrete. This is important for the aesthetic appearance of the retaining structure and for ensuring the desired structural integrity. Lastly, cost-effectiveness is an important consideration. The design of the steel formwork should aim to minimize material usage and labor costs, while still meeting the required performance and safety standards. Overall, when designing steel formwork for retaining structures, the considerations include structural stability, ease of assembly and adjustment, durability, concrete finish quality, and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for high-rise construction projects?
- Yes, steel formwork can be used for high-rise construction projects. Steel formwork provides durability, strength, and stability required for the construction of tall structures. Its ability to withstand high pressures and repeated use makes it suitable for the demanding conditions of high-rise construction. Additionally, steel formwork allows for efficient and precise construction, resulting in quality finishes and faster project completion.
- Q: What are the limitations of using steel formwork?
- There are several limitations of using steel formwork in construction projects. Firstly, steel formwork is relatively expensive compared to other types of formwork materials such as wood or aluminum. This can significantly increase construction costs, especially for large-scale projects. Secondly, steel formwork is heavy and requires heavy machinery and equipment for transportation and installation. This can be challenging in areas with limited access or on sites with uneven terrain. Additionally, steel formwork requires skilled labor for proper installation and dismantling. This can create delays and increase labor costs if the workforce is not experienced in working with steel formwork. Moreover, steel formwork is not as flexible as other types of formwork materials. It may not be suitable for complex or irregular shapes, which can limit design possibilities. Another limitation is the potential for corrosion. Steel formwork is vulnerable to rust and corrosion, especially in environments with high moisture or chemical exposure. Regular maintenance and corrosion protection measures are essential to ensure the longevity of steel formwork. Lastly, steel formwork is not as environmentally friendly as other alternatives. Steel production involves significant energy consumption and carbon emissions, which can contribute to environmental degradation. Overall, while steel formwork offers strength and durability, its limitations in terms of cost, weight, flexibility, corrosion susceptibility, and environmental impact should be carefully considered before choosing it for construction projects.
- Q: What are the different types of steel formwork?
- There are several different types of steel formwork used in construction projects. These include: 1. Traditional steel formwork: This type of formwork is made from steel plates and angles, and it is commonly used for simple structures or where the formwork needs to be reused multiple times. Traditional steel formwork is durable and can withstand heavy loads, but it can be time-consuming to set up and dismantle. 2. Modular steel formwork: This formwork system consists of prefabricated modules that can be easily assembled and disassembled on-site. It is highly versatile and can be used for a wide range of structures, including walls, columns, and slabs. Modular steel formwork is lightweight and easy to handle, reducing labor costs and construction time. 3. Tunnel formwork: This type of formwork is specifically designed for constructing tunnel structures. It consists of steel panels that are bolted together to create a continuous formwork system. Tunnel formwork is efficient and allows for rapid construction, making it suitable for large-scale projects such as subway tunnels or underground structures. 4. Slip formwork: Slip formwork is a method where a continuous concrete pour is used to create a vertical structure, such as a tower or chimney. Steel formwork is used to create the initial mold, which is continuously moved upward as the concrete is poured. Slip formwork allows for fast construction and is commonly used for high-rise buildings or structures with a consistent cross-section. 5. Climbing formwork: This formwork system is used for constructing tall vertical structures, such as skyscrapers or bridge piers. Steel formwork is attached to the structure and then hydraulically lifted or climbed as the construction progresses. Climbing formwork allows for continuous construction and eliminates the need for external scaffolding. Each type of steel formwork has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the project, including budget, construction time, and complexity.
- Q: Is steel formwork suitable for projects with high concrete temperature requirements?
- Steel formwork is generally not considered suitable for projects with high concrete temperature requirements. This is because steel has a high thermal conductivity, meaning it can rapidly transfer and dissipate heat. When exposed to high concrete temperatures, steel formwork can become extremely hot, potentially leading to deformation, warping, or even failure. In contrast, materials with lower thermal conductivity, such as timber or plastic formwork, are better suited for projects with high concrete temperature requirements. These materials provide better insulation and can handle the increased heat without compromising their structural integrity. However, it's important to note that there are certain types of steel formwork that are specifically designed to withstand higher concrete temperatures. These specialized formwork systems are typically made from heat-resistant alloys or have additional insulation layers to minimize the impact of temperature on the steel. Ultimately, the suitability of steel formwork for projects with high concrete temperature requirements depends on the specific type of steel formwork being used and its ability to withstand and dissipate heat effectively. It is recommended to consult with structural engineers and formwork suppliers to determine the most appropriate formwork material for such projects.
Send your message to us
Adjustable arced steel formwork
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords