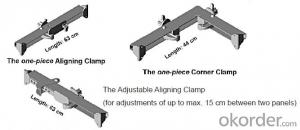
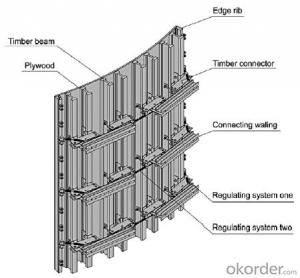
Single-side climbing bracket SCB180 for formwork and scaffolding system
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Single-side Climbing Bracket SCB180:
With CNBM SCB 180 climbing systems, the loads from the fresh concrete pressure are transferred through the brackets by means of V-strongbacks and compression braces into the scaffold anchors.
Typical applications for the SCB 180 are dams, locks, cooling towers, pier heads, tunnels, and bank vaults.
The formwork is simply tilted backwards when striking takes place. The 1.80 m wide bracket requires only a minimum of space.
Characteristics:
◆ Economical and safe anchoring
The M30/D20 climbing cones have been designed especially for single-sided concreting using
SCB180 in dam construction, and to allow the transfer of high tensile and shear forces into the still
fresh, unreinforced concrete. Without wall-through tie-rods, finished concrete is perfect.
◆ Stable and cost-effective for high loads
generous bracket spacings allow large-area formwork units with optimal utilization of the bearing
capacity. This leads to extremely economical solutions.
◆ Simple and flexible planning
With SCB180 single-sided climbing formwork, circular structures can also be concreted without
undergoing any large planning process. Even use on inclined walls is feasible without any special
measures because additional concrete loads or lifting forces can be safely transferred into the
structure.


- Q: Can steel formwork be used for hotel construction projects?
- Yes, steel formwork can be used for hotel construction projects. Steel formwork is a versatile and durable solution for constructing concrete structures, including hotels. It offers several advantages such as high strength, durability, and reusability. Steel formwork is capable of withstanding the pressure exerted by wet concrete and can be easily assembled and dismantled, making it suitable for use in various construction projects, including hotels. Additionally, steel formwork provides a smooth and accurate finish to concrete structures, ensuring high-quality construction.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for both vertical and horizontal applications?
- Indeed, both vertical and horizontal applications can make use of steel formwork. Renowned for its versatility and strength, steel formwork proves itself suitable for a multitude of construction projects. It serves as an ideal tool for crafting formwork not only for vertical elements such as walls, columns, and beams, but also for horizontal elements like slabs and foundations. Thanks to its inflexible nature, steel formwork guarantees meticulous shaping and ensures the concrete remains securely in place during pouring and curing. Moreover, the reusability of steel formwork renders it an economical option for construction projects necessitating frequent formwork alterations or repetitive utilization.
- Q: How does steel formwork handle concrete bleeding?
- Steel formwork handles concrete bleeding by providing a strong and rigid structure that prevents excessive flow of water and cement particles from the concrete mixture. The smooth surface of steel formwork also helps in reducing the bleeding by allowing the trapped air and excess water to escape easily. Overall, steel formwork ensures better control over concrete bleeding and helps in achieving a more uniform and compacted concrete structure.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for structures with high chemical resistance requirements?
- No, steel formwork is not suitable for structures with high chemical resistance requirements as steel is prone to corrosion and may react with chemicals, compromising the integrity of the structure. Alternative materials, such as chemically resistant plastics or specialized coatings, would be more appropriate in such cases.
- Q: How does steel formwork contribute to the overall stability of a structure?
- Steel formwork is a crucial component in the construction industry that greatly contributes to the overall stability of a structure. It is widely used in the casting of concrete elements such as walls, slabs, columns, and beams. One of the primary ways that steel formwork enhances stability is by providing a rigid and robust framework for the pouring and setting of concrete. The steel panels and frames are designed to withstand the pressure exerted by the wet concrete, ensuring that it retains its shape and does not deform during the curing process. This helps to prevent any potential structural deficiencies or unevenness that may compromise the stability of the final structure. Furthermore, steel formwork offers exceptional strength and durability, making it suitable for various construction projects. The high tensile strength of steel allows it to withstand heavy loads, which is particularly important in the construction of large-scale structures with significant weight-bearing requirements. This strength also ensures that the formwork can be reused multiple times, reducing the overall construction costs and environmental impact. Additionally, steel formwork provides excellent dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and dimensions throughout the construction process. This characteristic is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the structure, as any deviations or variations in shape may result in structural instability. Moreover, steel formwork is highly resistant to moisture and other environmental factors, which can be detrimental to the stability of a structure. Its corrosion-resistant properties make it suitable for use in outdoor construction sites, where exposure to rain, humidity, and other elements may occur. This resistance to corrosion ensures that the formwork remains intact and does not weaken over time, thereby contributing to the long-term stability of the structure. In conclusion, steel formwork plays a vital role in enhancing the overall stability of a structure. Its rigid and robust framework, combined with its strength, durability, dimensional stability, and resistance to environmental factors, ensures that the concrete is properly formed and retains its structural integrity. By providing a stable and secure foundation for the construction process, steel formwork significantly contributes to the stability and safety of the final structure.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for staircases and ramps?
- Yes, steel formwork can be used for staircases and ramps. Steel formwork is a versatile and durable option for creating complex shapes and structures. It provides the necessary strength and stability required to support the weight and loadings associated with staircases and ramps. Additionally, steel formwork can be easily assembled and disassembled, allowing for efficient construction and customization of staircases and ramps. Its flexibility also enables the creation of various designs and sizes to meet specific project requirements. Overall, steel formwork is a suitable choice for constructing staircases and ramps due to its strength, durability, versatility, and ease of use.
- Q: What are the common design considerations for steel formwork in high-rise buildings?
- When designing steel formwork for high-rise buildings, there are several important factors to consider. These considerations are crucial for ensuring that the formwork system is structurally sound, safe, and efficient. 1. Load capacity is a key consideration. The formwork must be able to withstand the weight of the concrete, workers, equipment, and other loads without deforming or failing. 2. Stability is also important. High-rise buildings are exposed to external forces like wind and seismic loads, so the formwork system must be stable and resistant to these forces. Proper bracing, tie-downs, and anchorage systems should be included in the design. 3. Durability is essential due to the harsh conditions of construction sites. The steel formwork must be able to withstand moisture, chemicals, and physical impact. Material selection and protective coatings should be carefully chosen to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term durability. 4. Flexibility is necessary because high-rise buildings often have complex geometries. The formwork system should be able to accommodate different floor layouts, wall configurations, and column sizes. Modular formwork systems are commonly used for their flexibility and ease of adjustment. 5. Safety is of utmost importance in high-rise construction. The formwork system should include safety features like non-slip surfaces, guardrails, access platforms, and fall protection systems. Sufficient space for workers to move around and perform their tasks safely should also be considered. 6. Construction timeline is a critical factor. The formwork system should be designed for fast and efficient construction, minimizing downtime and delays. This could involve using pre-fabricated components, easy assembly and disassembly methods, and efficient material handling systems. 7. Cost-effectiveness is another consideration. The design should optimize cost-effectiveness without compromising quality and safety. This includes factors like material selection, formwork reuse, efficient labor usage, and waste reduction. In summary, the design considerations for steel formwork in high-rise buildings revolve around load capacity, stability, durability, flexibility, safety, construction timeline, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully addressing these considerations, designers can ensure a successful and efficient construction process for high-rise buildings.
- Q: Production of steel plate for bridge steel plate SPHC and Q235 which material is good? What is the difference?
- SPHC this brand is actually the first brand in Germany, Japan also used,
- Q: What are the different types of release agents used with steel formwork?
- There are several types of release agents used with steel formwork, including petroleum-based agents, water-based agents, silicone-based agents, and wax-based agents. These release agents are applied to the surface of the formwork to prevent the concrete from sticking to it during the pouring and curing process. Each type of release agent has its own advantages and suitability for different applications, depending on factors such as the desired finish, ease of application, and environmental considerations.
- Q: How does steel formwork handle different concrete pouring temperatures?
- Steel formwork is highly versatile and can handle different concrete pouring temperatures effectively. Due to the inherent strength and durability of steel, it can withstand high temperatures without warping or deforming. This allows it to safely accommodate the heat generated during the curing process of concrete, ensuring that the formwork remains intact and maintains its shape. Additionally, steel formwork has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in dissipating excess heat and maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the structure. Overall, steel formwork is well-suited to handle various concrete pouring temperatures, making it a reliable choice for construction projects.
Send your message to us
Single-side climbing bracket SCB180 for formwork and scaffolding system
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches