Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
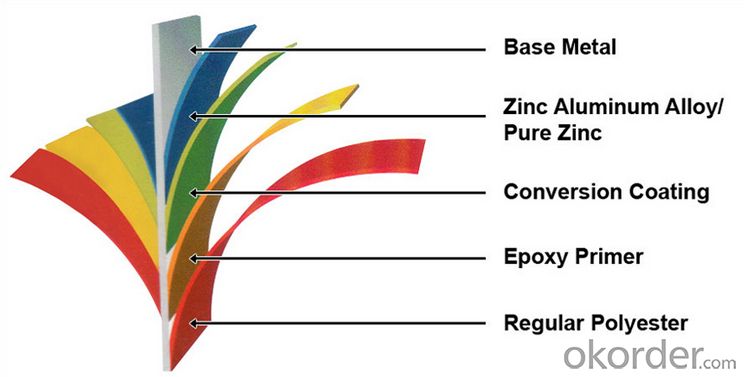
Description of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc.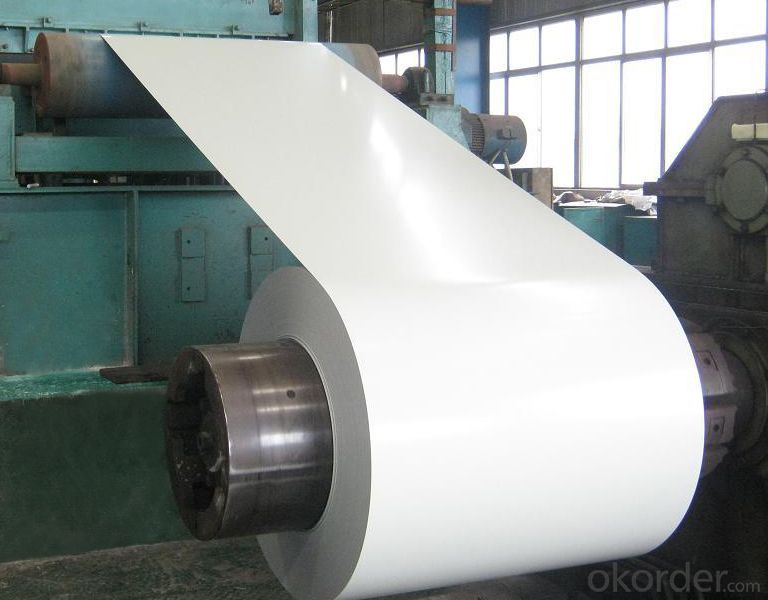 
Specifications of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of heavy machinery?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of heavy machinery as they serve as the raw material for forging, casting, and machining processes. These billets are heated, shaped, and transformed into various components such as gears, shafts, frames, and structural parts, which are essential building blocks for constructing heavy machinery. The high strength and durability of steel billets make them ideal for withstanding the heavy loads and harsh conditions that heavy machinery often operates in.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of industrial pumps?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of industrial pumps as a starting material for the production of various pump components. These billets are typically made of high-quality steel and serve as the raw material for forging or casting processes. Firstly, steel billets are used in the production of pump casings. The billets are shaped into the desired form, either by forging or casting, to create the outer shell of the pump. This casing provides structural integrity and contains the fluid being pumped. Additionally, steel billets are utilized in the manufacturing of impellers, which are vital components of industrial pumps. Impellers are responsible for generating the necessary force to move the fluid through the pump. The billets are machined, shaped, and polished to form the intricate design of the impeller, ensuring optimal fluid flow and efficiency. Furthermore, steel billets are used for manufacturing shafts and other critical components of the pump. These components require high strength and durability to withstand the demanding conditions of industrial applications. By using steel billets, manufacturers can ensure the necessary mechanical properties are met, such as resistance to corrosion, wear, and high temperatures. In summary, steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of industrial pumps. They serve as the starting material for various pump components, including casings, impellers, shafts, and more. By using high-quality steel billets, manufacturers can produce durable and efficient pumps that meet the demanding requirements of industrial applications.
- Q: What types of steel are commonly used for billets?
- Billets, commonly used in various industries, require different types of steel depending on specific needs and desired properties. For instance, carbon steel is a popular choice due to its affordability, durability, and high strength. It is an alloy of iron and carbon, suitable for applications in construction, automotive, and machinery industries. Alloy steel, on the other hand, involves the addition of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to carbon steel. This enhances the steel's strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications such as aerospace, oil and gas, and power generation. Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, finds extensive use in billets for applications where protection against corrosion is critical, like marine environments and food processing industries. It is created by adding chromium and other elements like nickel or molybdenum to carbon steel, resulting in excellent resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and chemicals. Lastly, tool steel is specifically designed for the manufacturing of tools and dies. It contains alloying elements like tungsten, vanadium, or cobalt, providing exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance properties. These billets are crucial for producing precision tools and components used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. In conclusion, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and tool steel are commonly utilized for billets. The selection of steel depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as strength, corrosion resistance, or hardness.
- Q: What are the different types of cleaning equipment used for steel billets?
- Steel billets commonly undergo cleaning using various types of equipment. These include: 1. Shot blasting machines: These machines propel small metal or mineral particles at high speed onto the surface of the billets, effectively eliminating rust, scale, and other contaminants, resulting in a clean and smooth surface. 2. Ultrasonic cleaners: Through the use of high-frequency sound waves, ultrasonic cleaning agitates a cleaning solution, effectively removing dirt, oil, and other contaminants from the billets' surface. This method is particularly useful for stubborn or hard-to-reach contaminants. 3. Acid pickling tanks: By immersing the billets in an acidic solution, acid pickling dissolves rust, scale, and other contaminants. After pickling, rinsing and drying are usually carried out. 4. Power washers: Power washers, also known as pressure washers, employ a high-pressure water spray to eliminate dirt, oil, and other contaminants from the billets' surface. This method is particularly effective for larger or heavier billets. 5. Mechanical cleaning brushes: Mechanical cleaning brushes, including wire brushes or abrasive pads, are commonly employed to manually scrub the billets' surface, removing loose dirt, rust, or scale. Typically used in conjunction with other cleaning methods. In determining the appropriate cleaning equipment for steel billets, factors such as the extent and type of contaminants, desired level of cleanliness, and the size and shape of the billets need to be considered. Different combinations of these cleaning methods may be utilized to achieve the desired outcome.
- Q: How are steel billets cut into desired lengths?
- Various cutting techniques are commonly used to cut steel billets into desired lengths. One of the most frequently employed methods is saw cutting, where a high-speed circular saw with a carbide or diamond-tipped blade is utilized. By securing the billet in place, the saw blade is brought down to create the required length. Another method is torch cutting, which involves the use of an oxy-fuel torch. This torch produces a high-temperature flame directed onto the billet, causing it to melt and be cut through. Torch cutting is preferred for larger and thicker steel billets, as it allows for greater flexibility in cutting irregular shapes or angles. Moreover, plasma cutting is another technique utilized for cutting steel billets. It employs a plasma torch that generates an electrically conductive plasma arc. This arc melts the steel and blows away the molten metal, resulting in a precise and clean cut. Plasma cutting is particularly beneficial for thicker steel billets or intricate shapes and designs. In summary, the choice of cutting technique for steel billets depends on factors such as size, thickness, precision, accuracy, and specific requirements of the end product.
- Q: What is the difference between steel and billet in the process?
- Square is a square steel hollow, with iron produced; but it is a square steel billet is generally solid, forging or casting molding.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of medical equipment?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of medical equipment as a raw material that can be shaped and machined into various components such as surgical instruments, implants, and medical device casings. The high strength and durability of steel make it suitable for producing equipment that requires precision, reliability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of aerospace components?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the production of aerospace components. Steel billets are often used as raw material for forging processes, which can be used to manufacture various aerospace components such as landing gears, engine parts, and structural components.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of wire products?
- Steel billets are an essential component in the manufacturing of wire products. They serve as the starting material for the wire production process. Steel billets are semi-finished products that are typically cast in a rectangular or square shape. These billets are made from molten steel that is solidified and then subjected to various shaping processes to form the desired dimensions. The first step in using steel billets for wire production involves heating them in a furnace to a specific temperature. This heating process, known as annealing, helps soften the steel and make it more malleable. By doing so, it becomes easier to shape the billets into wire forms. Once the billets have been heated and softened, they are then passed through a series of rollers and drawing dies. These machines gradually reduce the cross-sectional area of the billets, elongating them into the desired wire diameter. The process of reducing the diameter of the billets is called wire drawing. During the wire drawing process, the steel billets undergo multiple passes through the rollers and drawing dies. Each pass reduces the diameter of the billets further until they reach the desired wire size. This continuous reduction in diameter also improves the mechanical properties of the wire, such as its tensile strength and ductility. After the wire drawing process, the steel wire is typically coiled onto spools or reels for further processing or distribution. Depending on the intended application, the wire may undergo additional treatments, such as heat treatment or surface coating, to enhance its properties or protect it from corrosion. In summary, steel billets are used in the manufacturing of wire products by being heated, shaped, and drawn through rollers and dies to reduce their diameter and transform them into wire forms. This process allows for the production of wires with various dimensions and properties, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as construction, automotive, electrical, and manufacturing.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the oil and gas aftermarket?
- Steel billets have a wide range of potential applications in the oil and gas aftermarket. Firstly, steel billets can be used for the manufacturing of various components in the oil and gas industry, such as valves, flanges, and fittings. These components are essential for the operation and maintenance of pipelines, refineries, and drilling facilities. Additionally, steel billets can be used for the production of seamless pipes, which are crucial for transporting oil and gas over long distances. Seamless pipes made from steel billets offer high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for the harsh conditions often encountered in the oil and gas industry. Furthermore, steel billets can be utilized in the manufacturing of downhole tools and equipment. These tools are used during drilling operations to extract oil and gas from the ground. Steel billets provide the necessary strength and toughness required to withstand the extreme pressures and temperatures encountered in downhole environments. Moreover, steel billets can be used for the fabrication of storage tanks and vessels used in the oil and gas industry. These tanks are used for storing crude oil, refined products, and natural gas. Steel billets offer excellent weldability and structural integrity, ensuring the reliability and safety of storage facilities. Furthermore, steel billets can be used for the construction of offshore platforms and structures. These platforms are used for drilling, production, and processing activities in offshore oil and gas fields. Steel billets are favored in this application due to their high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand the harsh marine environment. In summary, the potential applications of steel billets in the oil and gas aftermarket are extensive. From the manufacturing of components, seamless pipes, and downhole tools to the fabrication of storage tanks and offshore platforms, steel billets play a vital role in supporting the operations of the oil and gas industry.
Send your message to us
Z36 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































