Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
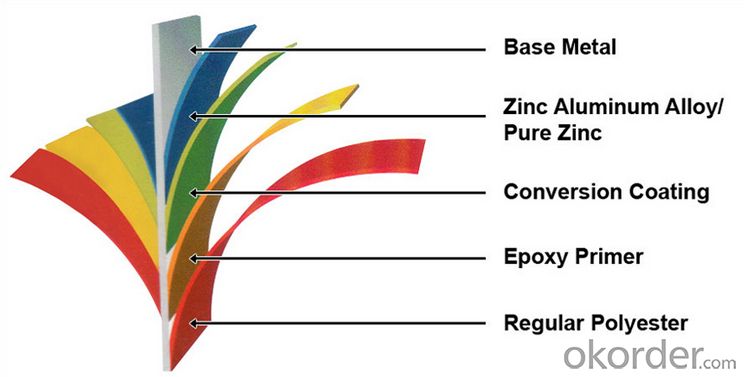
Description of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: How are steel billets labeled for identification purposes?
- Steel billets are labeled for identification purposes using a combination of alphanumeric codes and markings. These labels provide crucial information about the steel billet's composition, size, and other important details. The most common method of labeling steel billets involves stamping or engraving the required information directly onto the surface of the billet. This can include details such as the grade of steel, heat number, lot number, and the manufacturer's symbol or logo. These markings are typically made using industrial-grade ink or through a process called electrochemical etching, which ensures durability and legibility even in harsh environments. Additionally, steel billets may also have identification tags or labels attached to them, providing further information that cannot be easily engraved or stamped. These tags or labels may include barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags, which can be scanned or read using specialized equipment to quickly access the relevant information. By using these labeling methods, steel billets can be easily identified, tracked, and traced throughout their lifecycle, ensuring quality control, inventory management, and efficient production processes in the steel industry.
- Q: What are the safety measures involved in handling steel billets?
- To ensure the well-being of workers and prevent accidents while handling steel billets, it is necessary to adhere to several important safety measures. These measures include the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), proper training, regular equipment inspection, secure storage, adequate lighting, maintaining floor conditions, clear communication, and emergency preparedness. 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers must wear appropriate PPE, such as safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and helmets. This equipment provides protection against potential hazards like sharp edges, flying debris, and falling objects. 2. Training: Workers involved in handling steel billets should receive proper training on safe lifting techniques, handling procedures, and the use of equipment like cranes or forklifts. This knowledge helps minimize the risk of musculoskeletal injuries and accidents caused by improper handling. 3. Equipment Inspection: It is crucial to regularly inspect equipment like cranes, hoists, and lifting slings to ensure their proper functioning. Any defects or malfunctions should be promptly reported and repaired to prevent accidents. 4. Secure Storage: Steel billets should be stored securely and in an organized manner to prevent falls or tipping over. Proper racking systems and storage areas should be used to ensure stability and prevent accidents due to falling objects. 5. Adequate Lighting: Good lighting is essential in the working area to ensure clear visibility and prevent accidents caused by tripping or colliding with objects. 6. Floor Conditions: The floor should be kept clean and free from hazards such as oil spills or debris, which can cause slips, trips, or falls. Regular cleaning and maintenance are necessary to maintain a safe working environment. 7. Communication: Clear communication among workers involved in handling steel billets is crucial to prevent accidents. Coordination through signals, hand gestures, or the use of radios or other communication devices can help avoid collisions or accidents. 8. Emergency Preparedness: Adequate emergency preparedness measures, like fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and evacuation plans, should be in place. Workers should be trained in emergency procedures to ensure a swift and safe response in case of an incident. By following these safety measures, the risks associated with handling steel billets can be minimized, creating a safer work environment for all involved.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of marine gear?
- The unique characteristics and properties of steel billets are crucial in the manufacturing of marine gear. Marine gear, which includes propeller shafts, gears, and bearings, requires high strength, resistance to corrosion and wear. To start the manufacturing process, steel billets are used as the starting material. These semi-finished metal forms are typically made from carbon or alloy steel and are shaped into long, rectangular bars. The specific marine gear components are created through further processing of these billets. The strength of steel billets is ideal for marine gear manufacturing as it allows them to withstand heavy loads and intense pressures in marine environments. This ensures the durability and reliability of the gear components, minimizing failures and enhancing safety. Corrosion resistance is also crucial in marine gear manufacturing. Steel billets can be made from stainless steel, which contains chromium and other alloying elements that form a protective layer on the surface. This protective layer prevents rust and corrosion caused by exposure to saltwater, ensuring the longevity and performance of the components in harsh marine conditions. Additionally, steel billets can be heat-treated to improve their mechanical properties such as hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. This involves heating the billets to specific temperatures and then cooling them rapidly or slowly, depending on the desired properties. Heat-treated steel billets provide the necessary hardness and wear resistance required for gears, shafts, and bearings to withstand the constant friction and stress in marine applications. In conclusion, steel billets play a significant role in marine gear manufacturing by providing the required strength, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. They serve as the foundation material for creating durable and reliable components that can withstand the challenging conditions of the marine environment.
- Q: What are the main factors that affect the international trade of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that affect the international trade of steel billets. 1. Economic factors: The state of the global economy plays a crucial role in determining the demand and supply of steel billets. Economic growth and stability in major importing and exporting countries impact the overall demand for steel products, including billets. A strong economy usually leads to increased construction and infrastructure projects, which in turn boosts the demand for steel billets. 2. Government policies and regulations: Trade policies, import/export regulations, and tariffs imposed by governments significantly impact the international trade of steel billets. Governments can impose trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, to protect domestic steel industries or address national security concerns. These policies can directly affect the competitiveness and cost of steel billets in the international market. 3. Currency exchange rates: Exchange rates between currencies can influence the competitiveness of steel billets in international markets. If the currency of a steel billet exporting country strengthens against the currency of the importing country, it becomes more expensive for the importing country to purchase steel billets. This can impact the demand and prices of steel billets in international trade. 4. Technological advancements: Technological advancements in steel production and manufacturing processes can affect the international trade of steel billets. Improvements in production efficiency, quality control, and the development of new steel grades can give certain countries a competitive advantage in the global market. Innovative manufacturing techniques can lead to cost reductions and improved product quality, making steel billets more attractive to international buyers. 5. Environmental and sustainability considerations: Increasingly, environmental regulations and sustainability concerns are becoming important factors in international trade. Countries with stricter environmental regulations may require steel billet exporters to meet certain standards or obtain certifications, which can affect their competitiveness in the international market. Additionally, the demand for sustainable and low-carbon steel products is growing, which can influence the trade of steel billets. 6. Political stability and geopolitical factors: Political stability and geopolitical tensions can also impact the international trade of steel billets. Political instability, conflicts, or trade disputes between countries can disrupt supply chains, affect market access, and create uncertainties in the international trade of steel billets. These factors can lead to disruptions in trade flows and impact the prices and availability of steel billets in the global market. Overall, the international trade of steel billets is influenced by a combination of economic, regulatory, technological, environmental, and geopolitical factors. Understanding and monitoring these factors is crucial for stakeholders in the steel industry to navigate the complexities of the global market and make informed decisions.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the corrosion resistance of alloy steel billets?
- The main factors affecting the corrosion resistance of alloy steel billets are the composition of the alloy, the presence of impurities, the surface treatment, and the environmental conditions in which the billets are exposed to.
- Q: What are the advantages of using steel billets in construction?
- There are several advantages of using steel billets in construction: 1. Strength and Durability: Steel billets are known for their high strength and durability, making them ideal for construction purposes. They can withstand heavy loads and extreme weather conditions, ensuring the longevity and stability of the structure. 2. Versatility: Steel billets can be molded and shaped into various forms, allowing for flexibility in design and construction. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from beams and columns to framing and foundations. 3. Cost-effectiveness: Despite the initial cost of steel billets being higher than other construction materials, their long-term benefits outweigh the investment. Steel is low maintenance, doesn't require frequent repairs or replacements, and offers excellent fire resistance, reducing insurance costs. 4. Sustainability: Steel is a highly sustainable material due to its recyclability. Steel billets can be recycled and reused without losing their properties, reducing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing environmental impact. 5. Speed of construction: Steel billets are pre-fabricated, meaning they are manufactured off-site and then transported to the construction site. This significantly reduces construction time and allows for faster completion of projects. 6. Resistance to pests and rot: Unlike wood, steel billets are not susceptible to termites, pests, or rot. This eliminates the need for chemical treatments or regular inspections, saving both time and money. 7. Design flexibility: Steel billets offer a wide range of design possibilities, enabling architects and engineers to create unique and aesthetically pleasing structures. The ability to span large distances without the need for additional support columns allows for open floor plans and creative architectural designs. In summary, the advantages of using steel billets in construction include their strength, durability, versatility, cost-effectiveness, sustainability, speed of construction, resistance to pests and rot, and design flexibility. These factors make steel billets an excellent choice for various construction projects, ensuring sturdy and long-lasting structures.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments applied to steel billets?
- There are several surface treatments that can be applied to steel billets. Some common treatments include hot-dip galvanizing, electroplating, powder coating, and painting. These treatments help to protect the steel from corrosion, improve its appearance, and enhance its durability. Additionally, surface treatments can also be used to provide specific characteristics such as increased hardness or improved resistance to wear and tear.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of agricultural equipment?
- Steel billets are a crucial component in the manufacturing of agricultural equipment due to their versatility and durability. These billets, which are essentially semi-finished steel products, serve as the foundation for various agricultural machinery and equipment. Firstly, steel billets are used to create the main structural components of agricultural equipment such as tractors, harvesters, plows, and tillers. These components, such as the chassis, frame, and axles, require a strong and sturdy material to withstand the heavy loads and harsh conditions encountered in agricultural operations. Steel billets provide the necessary strength and resilience to ensure the equipment can withstand the rigors of farming. In addition to the structural components, steel billets are also used to manufacture smaller parts and mechanisms that are integral to the functioning of agricultural machinery. For example, gears, sprockets, shafts, and bearings are commonly made from steel billets. These parts are essential for transmitting power and facilitating the smooth operation of various agricultural equipment. Moreover, steel billets contribute to the longevity and reliability of agricultural equipment. The high strength and durability of steel ensure that the machinery can withstand the demanding agricultural environment, including exposure to moisture, dirt, and extreme temperatures. This durability reduces maintenance requirements and extends the lifespan of the equipment, resulting in cost savings for farmers. Furthermore, steel billets can be easily shaped and molded into complex designs, allowing manufacturers to create customized agricultural equipment tailored to specific farming needs. This flexibility in design enables the production of specialized machinery for various agricultural operations, such as planting, harvesting, irrigation, and livestock management. Overall, steel billets play a vital role in the manufacturing of agricultural equipment by providing the necessary strength, durability, and versatility required for the demanding conditions of modern farming. Their contribution ensures that farmers have access to reliable and efficient machinery, ultimately increasing productivity and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Q: Reasons and treatment methods of billet stripping in continuous casting
- even two cold regions can be uniformly cooled, due to uneven thickness of shell, caused by the inconsistent temperature, the shell shrinkage is still uneven, and also there will be the development of. Therefore, the selection of unqualified mold is the main reason causing the removal. Secondly, the cooling effect of the two cooling zone can not be ignored.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for dimensional accuracy?
- Steel billets are inspected for dimensional accuracy using various methods such as calipers, micrometers, and laser measurement devices. These tools are used to measure the length, width, and height of the billets and ensure they meet the required specifications. Additionally, visual inspections are also conducted to check for any defects or irregularities in the shape and size of the billets.
Send your message to us
Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























