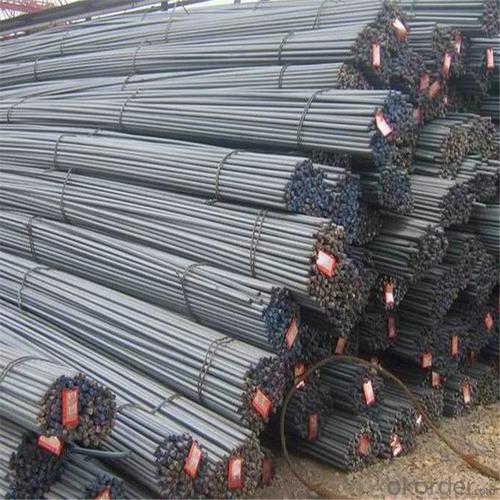
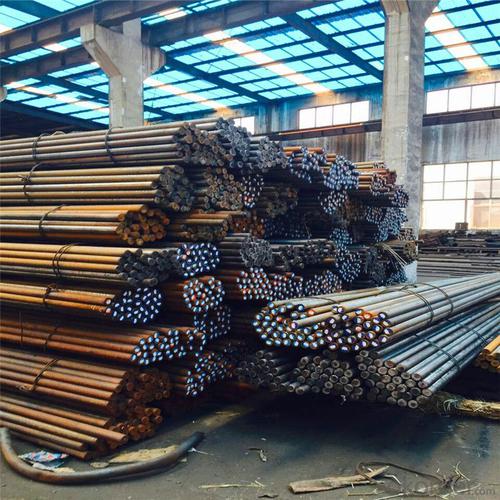
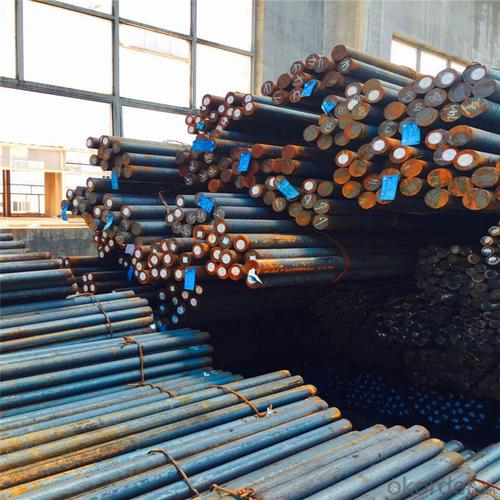
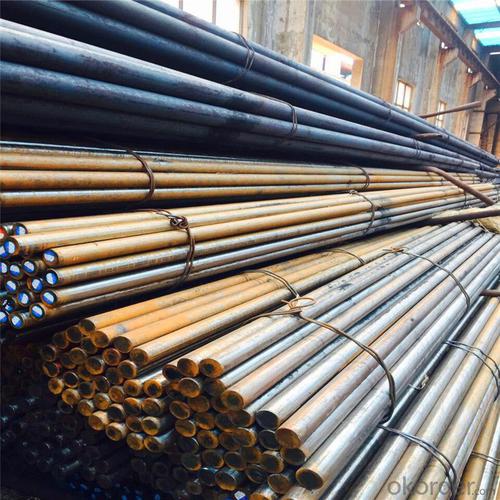
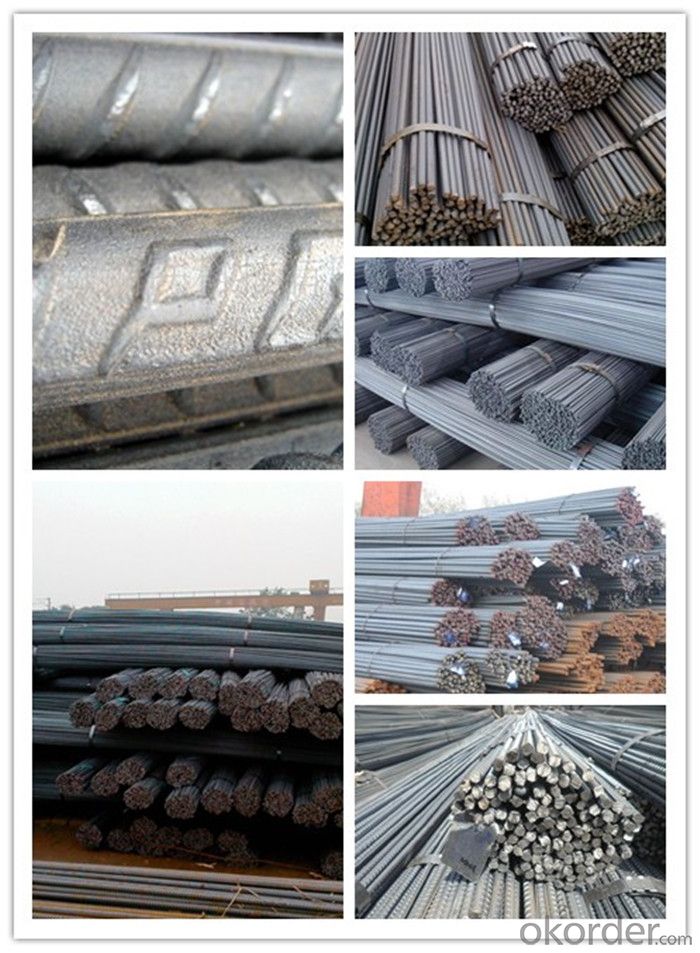
TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
Description of TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
10m- 40mm TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
Company Information
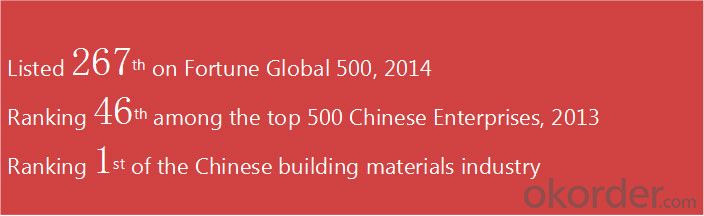
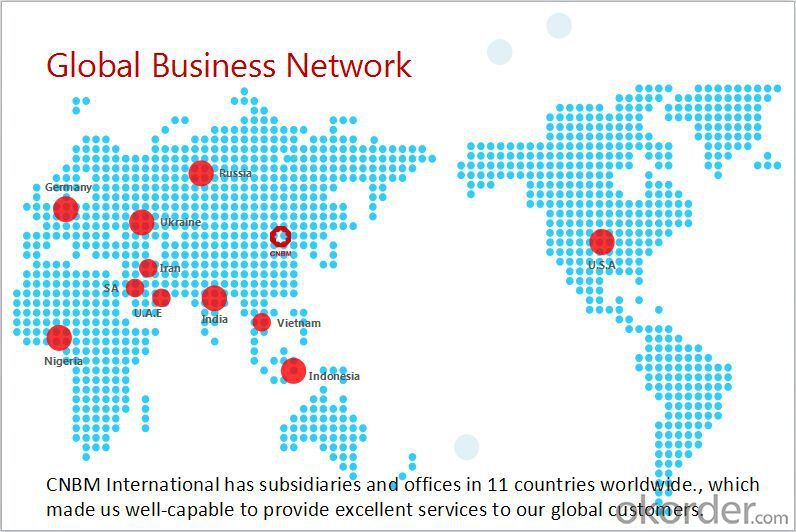
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the different types of coatings for special steel?
- There are various types of coatings available for special steel, including but not limited to, galvanized coatings, powder coatings, epoxy coatings, zinc coatings, and chrome coatings. Each type of coating provides specific benefits such as corrosion resistance, improved aesthetics, enhanced durability, or increased heat resistance, depending on the intended application of the special steel.
- Q: What are the different forging methods used for special steel?
- There are several forging methods commonly used for special steel, including closed die forging, open die forging, and ring rolling. Closed die forging involves shaping the steel between two dies, resulting in precise and intricate shapes. Open die forging involves deforming the steel without any restriction from dies, making it suitable for larger and simpler components. Ring rolling is specifically used for producing seamless rings by rolling a heated metal between two dies. These forging methods help in enhancing the strength, durability, and quality of special steel products.
- Q: How are tungsten alloys used in the defense industry?
- Tungsten alloys are extensively used in the defense industry due to their exceptional strength, high density, and excellent resistance to heat and wear. These alloys are commonly utilized in the manufacturing of armor-piercing ammunition, artillery projectiles, and kinetic energy penetrators. Tungsten alloys are also employed in the production of various defense equipment such as missile components, bomb casings, and tank armor. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions and deliver superior performance makes them invaluable in enhancing the effectiveness and protection capabilities of military applications.
- Q: Can special steel be used for precision instruments?
- Yes, special steel can be used for precision instruments. Special steels, such as high-speed steel or tool steel, possess excellent properties like high hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability. These qualities make them suitable for manufacturing precision instruments that require accuracy and durability, such as surgical tools, measuring equipment, or watch components.
- Q: How is special steel used in the medical supply chain?
- Special steel is used in various ways within the medical supply chain. It is commonly utilized in the production of surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices due to its exceptional properties such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Special steel is crucial in ensuring the quality and safety of these medical supplies, as it can withstand the demanding conditions of surgical procedures and sterilization processes. Additionally, special steel is used in the manufacturing of storage and transportation equipment for medical supplies, ensuring their proper handling and preservation. Overall, special steel plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of medical supplies throughout the entire supply chain.
- Q: What are the applications of special steel in aerospace engineering?
- The aerospace industry heavily relies on special steels for their distinct characteristics and capabilities. These steels are specifically crafted to meet the demanding needs of aerospace engineering, where utmost importance is placed on strength, resistance to corrosion, and tolerance to extreme temperatures. Here are some notable applications of special steel in aerospace engineering: 1. Aircraft engine components: Stainless steels and other special steels are extensively used in the production of aircraft engine components. These steels offer unparalleled strength, resistance to corrosion, and durability at high temperatures, making them perfect for critical parts like turbine blades, compressor discs, and shafts. 2. Landing gear systems: The landing gear of an aircraft undergoes significant stress and impact during takeoff, landing, and taxiing. To withstand these forces, special steels with remarkable strength, toughness, and resistance to fatigue are utilized in the manufacturing of landing gear components such as struts, axles, and shock absorbers. 3. Structural components: Aerospace structures must endure dynamic loads, vibrations, and extreme environmental conditions. Various structural components like wings, fuselage frames, and support structures employ special steels, particularly high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels. These steels offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, ensuring structural integrity while minimizing weight. 4. Fasteners: Special steel fasteners, including bolts, screws, and rivets, play a crucial role in joining different components in aerospace applications. These fasteners are typically made from high-strength steels, providing exceptional tensile and shear strength, as well as resistance to corrosion, to ensure secure and reliable connections. 5. Fuel system components: Special steels with high resistance to corrosion, such as stainless steels, are utilized in the construction of fuel system components like tanks, pipes, and valves. These steels prevent fuel leakage and maintain the system's integrity, even in harsh environments. 6. Electrical connectors: Aerospace electrical systems necessitate reliable and efficient electrical connectors. Special steels, often possessing high electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, are employed in the manufacturing of connectors, guaranteeing optimal performance and longevity. In conclusion, the outstanding properties of special steels make them indispensable in aerospace engineering. Whether it is for critical engine components, landing gear systems, structural applications, fasteners, fuel systems, or electrical connectors, these steels provide the necessary strength, resistance to corrosion, and stability in extreme temperatures, ensuring safe and efficient aircraft operation.
- Q: What are the different defense grades of special steel?
- The different defense grades of special steel typically include grades such as AR200, AR400, AR500, and AR600, which are commonly used for protective armor and structural applications. These grades have varying levels of hardness, strength, and resistance to abrasion, making them suitable for different levels of defense against impacts, wear, and penetration.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the chemical resistance of products?
- Special steel, also known as stainless steel, contributes significantly to the chemical resistance of products due to its unique composition and properties. These steels contain a high percentage of chromium, which forms a thin, passive oxide layer on the surface of the steel. This oxide layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing corrosive substances from coming into direct contact with the steel and causing chemical reactions. The chromium in special steel forms a stable oxide layer that is highly resistant to corrosion, even in harsh chemical environments. This oxide layer is self-repairing, meaning that if it is damaged or scratched, it will quickly reform and continue to protect the steel. Additionally, the presence of other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum further enhances the chemical resistance of special steel. The chemical resistance of special steel extends to a wide range of corrosive substances, including acids, alkalis, and salts. This makes it highly suitable for applications in various industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and marine environments. By using special steel in the manufacturing of products, the risk of chemical degradation and corrosion is significantly reduced. This leads to increased product lifespan, improved performance, and reduced maintenance costs. Furthermore, it ensures that the integrity and safety of the products are maintained, as chemical resistance is crucial in preventing leaks, contamination, and structural failures. In summary, special steel contributes to the chemical resistance of products by forming a protective oxide layer on its surface, which shields it from corrosive substances. Its unique composition and properties make it highly resistant to chemical degradation, ensuring the longevity and reliability of products in various industrial applications.
- Q: What are the different standards and specifications for special steel?
- There are several standards and specifications for special steel, which vary depending on the specific type and application of the steel. Some common standards include AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), EN (European Norm), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards). These standards define the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing processes required for special steel to meet certain quality and performance standards. Additionally, there may be specific specifications for different industries or applications, such as aerospace, automotive, or construction, that further define the requirements for special steel.
- Q: What are the different methods for improving the heat resistance of special steel?
- There are several methods for improving the heat resistance of special steel. These methods include: 1. Alloying: One of the most common methods is to alloy the steel with certain elements that enhance its heat resistance. For example, the addition of chromium, nickel, or molybdenum can significantly improve the steel's ability to withstand high temperatures. 2. Heat treatment: Heat treatment processes such as annealing, quenching, and tempering can be employed to enhance the heat resistance of special steel. These processes help in refining the microstructure of the steel and improving its mechanical properties, including heat resistance. 3. Surface modification: Applying specialized coatings or surface treatments can also improve the heat resistance of special steel. For instance, processes like nitriding, carburizing, or ceramic coating can create a protective layer on the surface of the steel, preventing oxidation and improving its ability to withstand high temperatures. 4. Grain refinement: Controlling the grain size of the steel through processes like grain refinement or recrystallization can enhance its heat resistance. Smaller grain sizes reduce the diffusion of atoms within the material, making it more resistant to high temperatures. 5. Precipitation hardening: Precipitation hardening is a technique where small particles are formed within the steel matrix, strengthening the material and improving its resistance to heat. This method involves a specific heat treatment process that enables the formation of these particles. 6. Controlled cooling: Optimizing the cooling process after heat treatment can also improve the heat resistance of special steel. By controlling the cooling rate, the formation of undesirable phases or microstructural defects can be minimized, ensuring better heat resistance. 7. Material selection: Choosing the right type of special steel with inherently high heat resistance properties is another method for improving heat resistance. For example, stainless steel, tool steel, or superalloys are known for their excellent heat resistance and are often selected for applications where high temperatures are involved. It is worth noting that the selection of the appropriate method or combination of methods for improving heat resistance depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
Send your message to us
TMT Reinforced Bars 10mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



































