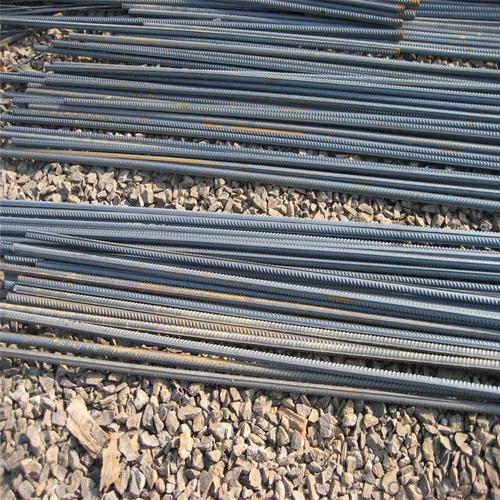
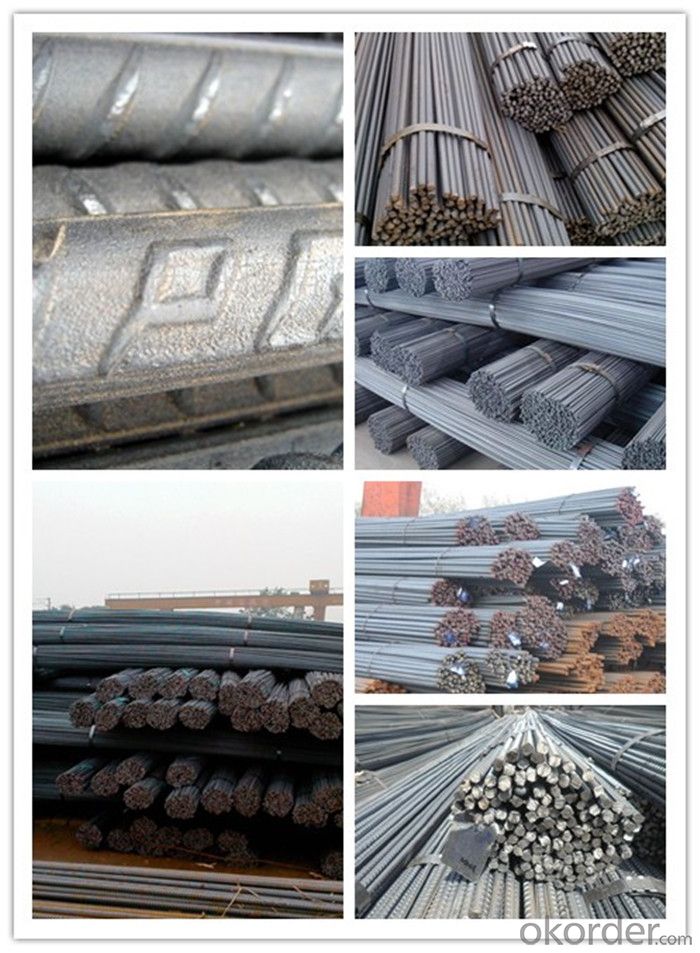
Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bars in Stock
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bars in Stock
Description of Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bar:
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm Hrb500 deformed steel bars
10m- 40mm Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bar
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
2, Produce Process: hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black Polish Bright
5, Quality Assurance: You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bars:
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Product Show of Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bars:
Company Information:
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
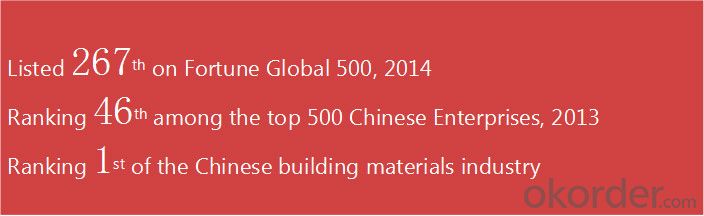
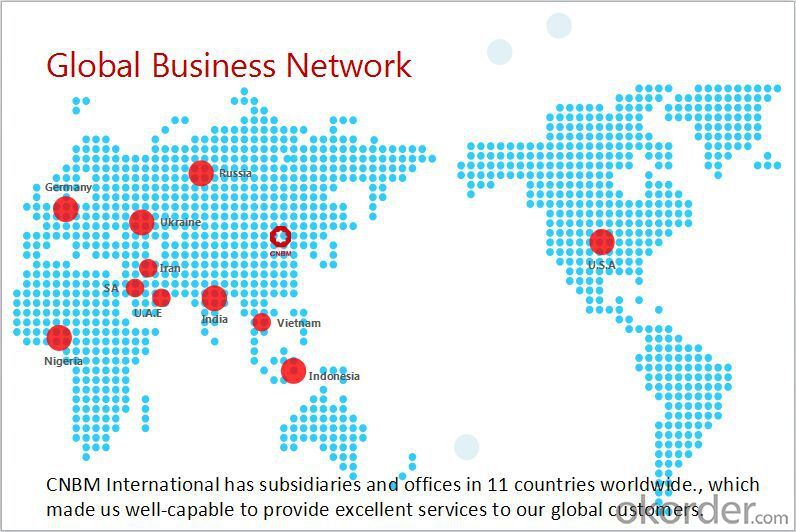
FAQ:
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the properties of high-temperature tool steel?
- High-temperature tool steel is known for its exceptional heat resistance, hardness, and wear resistance. It has the ability to retain its strength even at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for applications in high-temperature environments. Additionally, it exhibits excellent toughness, allowing it to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation. High-temperature tool steel also has good dimensional stability and can maintain its shape even under extreme conditions.
- Q: How does special steel perform in terms of chemical resistance?
- Special steel typically performs very well in terms of chemical resistance. Its composition and properties make it highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, allowing it to withstand exposure to various chemicals without significant degradation. Additionally, special steel can be specially alloyed or treated to enhance its chemical resistance even further, making it an excellent choice for applications in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine environments.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface hardening for special steel?
- There are several methods of surface hardening for special steel, including carburizing, nitriding, induction hardening, flame hardening, and laser hardening.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the medical device manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the medical device manufacturing industry. Special steel, such as stainless steel, is often used in the production of medical devices due to its corrosion resistance, high strength, and biocompatibility. It is commonly used for surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical equipment where durability and hygiene are crucial.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the renewable energy aftermarket industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the renewable energy aftermarket industry by enhancing the efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy systems. One of the primary applications of special steel in this industry is in the manufacturing of wind turbine components. Wind turbines require high-strength and corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the harsh environmental conditions and generate electricity efficiently. Special steel alloys, such as high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel and stainless steel, offer superior mechanical properties, fatigue resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for wind turbine tower structures, rotor blades, and other critical components. By using special steel in wind turbine manufacturing, the renewable energy aftermarket industry can benefit from increased turbine lifespan, reduced maintenance costs, and improved energy output. The strength and durability of special steel enable taller and larger wind turbine towers, allowing for the installation of turbines in areas with lower wind speeds. This expansion of suitable locations helps to maximize the energy production potential, making wind energy a more viable and widespread renewable energy source. Furthermore, special steel also contributes to the renewable energy aftermarket industry through its application in solar power systems. Solar panels require robust mounting structures to support the weight of the panels, withstand wind and snow loads, and ensure optimal sun exposure. Special steel, with its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is commonly used in these mounting structures, providing long-lasting and reliable support for solar panels. In addition to wind and solar energy, special steel finds applications in other renewable energy systems such as hydroelectric power plants and geothermal systems. These industries benefit from the corrosion resistance and resistance to extreme temperatures offered by special steel, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the equipment. Overall, special steel significantly contributes to the renewable energy aftermarket industry by enabling the production of reliable, durable, and efficient renewable energy systems. Through its use in wind turbines, solar panels, and other renewable energy technologies, special steel helps to enhance the performance and longevity of these systems, ultimately driving the growth and adoption of renewable energy sources worldwide.
- Q: What are the limitations of special steel in certain applications?
- Special steel, although highly versatile and durable, does have certain limitations in certain applications. One limitation of special steel is its high cost. Special steel is typically more expensive to produce compared to regular steel due to the addition of various alloying elements. This can make it less economically viable for certain applications where cost is a significant factor, especially in large-scale projects or industries with tight budgets. Another limitation is its susceptibility to corrosion. While special steel is generally more resistant to corrosion compared to regular steel, it is still not completely immune to the effects of corrosion. In environments with high levels of moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, special steel may still corrode over time if not properly protected or maintained. Special steel also has limitations in terms of formability and workability. Due to its higher strength and hardness, special steel can be more challenging to shape, bend, or weld compared to regular steel. This can limit its use in applications that require complex or intricate designs, as well as those that involve extensive fabrication or assembly processes. Furthermore, special steel may have certain limitations in terms of availability and supply chain. Not all types of special steel may be readily available in the market, especially in remote or less developed regions. This can make it difficult to source the required special steel for specific applications, leading to potential delays or compromises in project execution. Lastly, the specialized properties of special steel may not always be necessary or advantageous for certain applications. In some cases, regular steel or alternative materials may be more suitable and cost-effective, especially if the specific properties of special steel are not required for the intended use. Overall, while special steel offers numerous benefits and advantages, it is important to consider its limitations in certain applications. Careful evaluation of the specific requirements, cost-effectiveness, and availability of special steel is essential to ensure its successful and optimal use in any given situation.
- Q: What are the main characteristics of alloy steel forgings?
- Alloy steel forgings possess a multitude of desirable qualities that make them highly sought-after in diverse industries. Firstly, their exceptional strength and durability are widely recognized. By incorporating various alloying elements like chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium, the mechanical properties of the steel are enhanced, resulting in resistance to wear, fatigue, and corrosion. Another notable characteristic of alloy steel forgings is their remarkable versatility. These forgings can be tailored to meet specific requirements in terms of shape, size, and performance. This adaptability enables the production of intricate and complex components, often utilized in critical applications such as aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas industries. Furthermore, alloy steel forgings exhibit excellent heat resistance, maintaining their structural integrity even under extreme temperature fluctuations. This attribute proves highly advantageous in applications where components are exposed to high temperatures or rapid temperature changes, like gas turbines, boilers, and heat exchangers. Moreover, alloy steel forgings offer superior machinability and weldability, simplifying the manufacturing process. This quality facilitates precise shaping, forming, and machining, enabling manufacturers to achieve intricate designs and tight tolerances. Lastly, alloy steel forgings are renowned for their cost-effectiveness. Despite their exceptional properties, these forgings can be produced in large quantities, resulting in economies of scale. This makes them a cost-efficient choice for industries seeking a balance between performance, durability, and affordability. In conclusion, the key characteristics of alloy steel forgings include outstanding strength, durability, versatility, heat resistance, machinability, weldability, and cost-effectiveness. These qualities establish alloy steel forgings as the preferred choice for applications requiring high-performance components that can withstand challenging conditions.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the cement manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the cement manufacturing industry. It is commonly used in the construction of cement plant equipment, such as kilns, crushers, and mills, due to its high strength, heat resistance, and durability. Special steel alloys are particularly suitable for applications that involve high temperatures and abrasive materials, making them an ideal choice for various components in the cement manufacturing process.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to reducing product defects?
- Special steel contributes to reducing product defects by offering enhanced properties such as increased strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. These properties ensure that the steel components used in various products, especially in critical applications, are less prone to wear, breakage, or malfunction. By using special steel, manufacturers can create more reliable and high-quality products, which ultimately leads to a reduction in defects and improves overall product performance.
- Q: How is high-strength steel used in the automotive industry?
- High-strength steel is extensively used in the automotive industry for various applications. It is commonly used for manufacturing car frames, body panels, and structural components due to its exceptional strength, durability, and lightweight properties. This type of steel enhances the overall safety and performance of vehicles while reducing their weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. High-strength steel also provides enhanced protection in case of accidents by effectively absorbing and distributing energy during collisions.
Send your message to us
Hrb500 Deformed Steel Bars in Stock
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



































