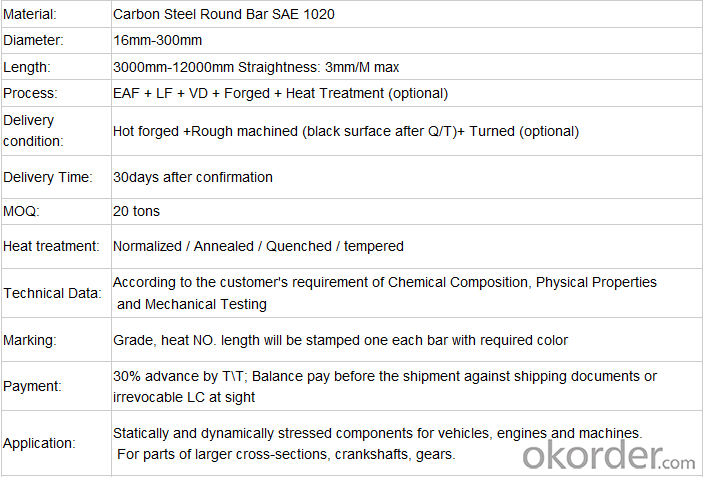
C20 AISI1020 S20C S22C 1020 1023 C22 CK22 1.0402 1.1151 Carbon Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
C20 AISI1020 S20C S22C 1020 1023 C22 CK22 1.0402 1.1151 Carbon Steel Bar
Product information:
Grade:C20 AISI1020 S20C S22C 1020 1023 C22 CK22 1.0402 1.1151 carbon steel bar
Hardness:156HB
Tensile strength:410MPA
Yield strength: 245MPA
elogation:25% Reduction of area:55%
AKV(impact value):54J
Product show

Product detail:
Workshop show

Our service:
-High manufacturing accuracy
-High strength
-Small inertia resistance
-Strong heat dissipation ability
-Good visual effect
-Reasonable price
Chose happens because of quality, then price, We can give you both.Additionally, we can also offer professional products inquiry, products knowledge train(for agents), smooth goods delivery, exellent customer solution proposals.Our service formula: good quality+good price+good service=customer's trust
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem.
If you need the sample, please feel free to let me know. Any question, we will contact you ASAP!
- Q: What are the specific requirements for special steel used in the mining industry?
- Special steel used in the mining industry has specific requirements to ensure its durability, strength, and resistance to harsh conditions. Some of the key requirements for special steel used in the mining industry include: 1. High strength: Special steel used in the mining industry must have high tensile strength to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation under extreme conditions. This enables the steel to endure the pressure, impact, and stress that it may encounter during mining operations. 2. Wear resistance: Mining environments involve abrasive materials, such as rocks and ores, which can cause significant wear on equipment. Special steel used in the mining industry needs to have excellent wear resistance to prevent premature failure and increase the lifespan of mining equipment. 3. Corrosion resistance: Mining operations often take place in highly corrosive environments, such as underground mines or near water bodies. Special steel used in the mining industry should possess high corrosion resistance to withstand exposure to chemicals, moisture, and other corrosive agents. This helps prevent rusting, pitting, and other forms of corrosion that can weaken the steel. 4. Toughness: Mining equipment is subjected to heavy impacts and vibrations, which can lead to fractures if the steel is not tough enough. Special steel used in the mining industry should exhibit excellent toughness, allowing it to absorb energy from impacts and vibrations without fracturing. This ensures the safety and reliability of mining equipment. 5. Heat resistance: Mining operations involve high-temperature environments, such as smelting and refining processes. Special steel used in the mining industry must have good heat resistance to withstand the elevated temperatures without losing its strength or undergoing deformation. 6. Machinability: Special steel used in the mining industry should also have good machinability, allowing it to be easily formed into complex shapes or structures. This facilitates the manufacturing process of mining equipment and components. Overall, the specific requirements for special steel used in the mining industry revolve around strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, toughness, heat resistance, and machinability. Meeting these requirements is crucial for ensuring the reliability, durability, and safety of mining equipment in the demanding mining environments.
- Q: What are the properties of carbon steel?
- Carbon steel is a type of steel that primarily consists of iron and carbon, with trace amounts of other elements. It is known for its strength, durability, and high melting point. Carbon steel is also highly malleable, making it easy to form into various shapes and structures. Additionally, it exhibits good corrosion resistance, although it is not as resistant as stainless steel. Overall, carbon steel is widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical properties.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in construction equipment manufacturing?
- The requirements for special steel used in construction equipment manufacturing are stringent and specific. Here are some key requirements: 1. High strength: Special steel used in construction equipment manufacturing should possess high tensile strength and yield strength to withstand heavy loads and stresses. This ensures the equipment's durability and longevity. 2. Toughness: The steel should have excellent toughness to resist fracture and deformation under impact or dynamic loading conditions. This is crucial for construction equipment operating in challenging environments. 3. Wear resistance: Construction equipment is subjected to abrasive forces, such as digging, scraping, and crushing. Therefore, the special steel should exhibit high wear resistance to prevent premature wear and failure. 4. Corrosion resistance: Construction equipment often operates in harsh environments, such as construction sites, mines, and marine applications. The steel should have good corrosion resistance to prevent rusting and corrosion, which can weaken the equipment's structural integrity. 5. Weldability: Construction equipment manufacturing involves various fabrication processes, including welding. The special steel should have good weldability to ensure proper joining and structural integrity without compromising strength. 6. Heat resistance: In certain construction applications, equipment may be subjected to high temperatures or thermal cycling. Special steel should have good heat resistance to maintain its mechanical properties and structural stability under these conditions. 7. Formability: Construction equipment often consists of complex shapes and structures. The steel should have good formability to allow for easy shaping and fabrication into the desired components without compromising its mechanical properties. 8. Cost-effectiveness: While meeting the above requirements, special steel used in construction equipment manufacturing should also be cost-effective. This means balancing the desired properties with the economic feasibility of production and procurement. Meeting these requirements ensures that the special steel used in construction equipment manufacturing can withstand the demanding conditions, provide long-term durability, and ensure the safety and efficiency of the equipment. Additionally, compliance with industry standards and regulations is essential to guarantee the quality and reliability of the steel used in construction equipment manufacturing.
- Q: How is shock-resistant steel used in the production of impact tools?
- Shock-resistant steel is used in the production of impact tools due to its exceptional ability to withstand high impact forces without deforming or breaking. This steel is specifically designed to absorb and distribute the energy generated during impacts, making it an ideal material for tools such as hammers, wrenches, and chisels. By using shock-resistant steel, manufacturers ensure that their impact tools can endure rigorous use and provide reliable performance, even in demanding applications.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the chemical processing industry?
- The chemical processing industry heavily relies on special steel, which offers a wide range of benefits that enhance the efficiency and safety of various processes. One crucial characteristic of special steel is its high resistance to corrosion, which is vital when dealing with corrosive chemicals. This resistance ensures that equipment and pipelines made from special steel can endure harsh chemical environments without deteriorating, leading to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Moreover, special steel exhibits exceptional strength and durability, enabling it to withstand the high temperatures and pressures commonly encountered in chemical processing. This strength guarantees that equipment like reactors, heat exchangers, and vessels can function effectively under demanding conditions, minimizing the likelihood of failures or accidents. Additionally, special steel possesses excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly advantageous in heat transfer applications. This property facilitates efficient heat exchange between different fluids, thereby enhancing the overall energy efficiency of chemical processes. By enabling effective heat transfer, special steel optimizes the performance of equipment such as condensers, boilers, and evaporators. Furthermore, special steel is frequently utilized in the construction of storage tanks and pipelines for the transportation and distribution of chemicals. Its remarkable resistance to mechanical stress and impact makes it ideal for ensuring the secure containment and transportation of hazardous substances, reducing the risk of leaks or spills that could have severe environmental and safety consequences. In conclusion, the utilization of special steel in the chemical processing industry significantly contributes to the reliability, efficiency, and safety of various processes. Its resistance to corrosion, strength, thermal conductivity, and durability make it an essential material for equipment and infrastructure, guaranteeing the smooth and secure operation of chemical processing plants.
- Q: What are the properties of high-strength tool steel?
- High-strength tool steel possesses several key properties such as excellent hardness, exceptional wear resistance, high toughness, and good dimensional stability. It also exhibits high strength, good machinability, and the ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring heavy-duty cutting and shaping tools.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the medical industry?
- Special steel contributes to the medical industry by providing essential materials for the manufacturing of medical devices and equipment. Its unique properties, such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, make it suitable for various applications, including surgical instruments, implants, prosthetics, and MRI machines. The use of special steel ensures the durability, precision, and safety of medical tools, ultimately improving patient outcomes and advancing medical technologies.
- Q: How does special steel perform in high-temperature oxidation conditions?
- Special steel, also known as heat-resistant or high-temperature steel, is specifically designed to perform exceptionally well in high-temperature oxidation conditions. Oxidation, a chemical reaction between the metal and oxygen at elevated temperatures, can lead to the formation of metal oxides and ultimately result in degradation or failure of the material. However, special steel is formulated with alloying elements that provide superior resistance to oxidation. These alloying elements, such as chromium, aluminum, and silicon, form a protective layer of oxides on the surface of the steel when exposed to high temperatures. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation of the underlying metal. Additionally, the alloying elements can enhance the formation of stable and adherent oxide scales, which further improve the steel's resistance to oxidation. Special steel's excellent performance in high-temperature oxidation conditions can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the alloying elements in the steel composition ensure the formation of a protective oxide layer, which acts as a shield against further oxidation. Secondly, the steel's microstructure is specifically designed to maintain stability and retain its mechanical properties even at elevated temperatures. Furthermore, special steel undergoes rigorous heat treatment processes to enhance its high-temperature oxidation resistance. Heat treatment methods such as annealing, quenching, and tempering optimize the steel's microstructure and eliminate impurities, ensuring its optimal performance in extreme conditions. Overall, special steel demonstrates exceptional resistance to high-temperature oxidation conditions due to its carefully selected alloying elements, tailored microstructure, and optimized heat treatment processes. It provides a reliable and durable solution for various industries that require materials to withstand severe oxidation environments, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in these challenging conditions.
- Q: What are the different standards and specifications for special steel?
- Special steel production and usage is governed by a variety of standards and specifications. These guidelines guarantee that the steel satisfies specific requirements and performance criteria for different purposes. Some of the commonly used standards and specifications for special steel are as follows: 1. AISI/SAE standards: Developed by the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these standards classify special steel types based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. They are widely used across various industries. 2. ASTM standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides standards for special steel materials in construction, manufacturing, and engineering applications. These standards define chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other necessary characteristics for specific grades of special steel. 3. EN standards: The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has established the European Norm (EN) standards for steel products. Covering a wide range of steel grades, these standards specify chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing procedures required for different types of special steel. 4. JIS standards: The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) outline the requirements for various types of steel used in Japan, including special steel. They provide guidelines for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other quality parameters. 5. ISO standards: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standards for steel materials used globally in different industries. These standards ensure compatibility and interchangeability of steel products by defining dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements. 6. MIL-SPEC standards: The United States Department of Defense (DoD) has created military specifications (MIL-SPEC) for special steel used in defense applications. These standards define the requirements for special steel used in military equipment, weapons, and vehicles to ensure reliability and performance under harsh conditions. 7. API standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for special steel utilized in the oil and gas industry. These standards specify materials, dimensions, and other requirements for steel pipes, fittings, and equipment used in oil and gas exploration, production, and transportation. These examples represent only a fraction of the numerous standards and specifications available for special steel. Manufacturers and industries must comply with these standards to guarantee the quality, performance, and safety of special steel products in different applications.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in high-temperature applications?
- To ensure optimal performance and durability in extreme conditions, special steel utilized in high-temperature applications, such as aerospace, power generation, and oil and gas industries, must fulfill specific criteria. Some essential requirements for this type of steel include: 1. Excellent strength and resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures are vital for maintaining structural integrity and preventing failure or deformation under extreme heat. 2. High resistance to oxidation is necessary to prevent the formation of oxides on the steel's surface, which can weaken its structure and compromise its performance. 3. Exceptional creep resistance is essential to prevent excessive deformation or failure over time caused by constant stress at high temperatures. 4. Good thermal stability allows the steel to retain its mechanical properties even after prolonged exposure to high temperatures, ensuring reliable and consistent performance. 5. In addition to oxidation, the steel must also possess good corrosion resistance to protect against various corrosive agents present in the environment, such as acids, alkalis, and salts. 6. High resistance to thermal fatigue is crucial to prevent cracking, fracturing, or failure due to repeated heating and cooling cycles. 7. Low thermal expansion minimizes dimensional changes and maintains dimensional stability under high-temperature conditions, preventing unwanted distortions or misalignments. 8. Good weldability facilitates the fabrication and joining of components, enabling the construction of complex structures and assemblies required in high-temperature environments. By meeting these requirements, special steel used in high-temperature applications can withstand extreme heat, preserve its structural integrity, and deliver reliable performance in demanding conditions.
Send your message to us
C20 AISI1020 S20C S22C 1020 1023 C22 CK22 1.0402 1.1151 Carbon Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























