Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
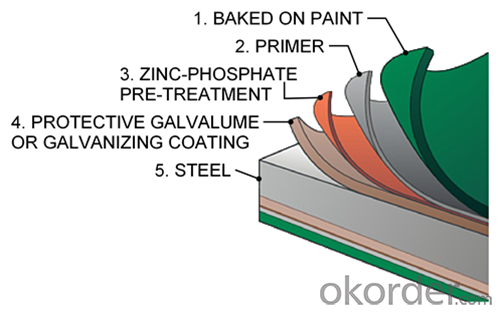
Description of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
Prepainted Rolled steel Coil is a kind of coated steel coil/sheet. With the cold rolled steel of different strength and thickness as substrate, it is produced through applying Al-Zn coat on both faces by hot dip process. In its coating, Al accounts for about 55%, Si 1.6%, while the remaining is Zn. Aluminum zinc coils enjoys both the physical protective feature and durability of Al and the electrochemical protective property of Zn. And its surface has bright silver color and regular embossed-like figure, which are highly decorative. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
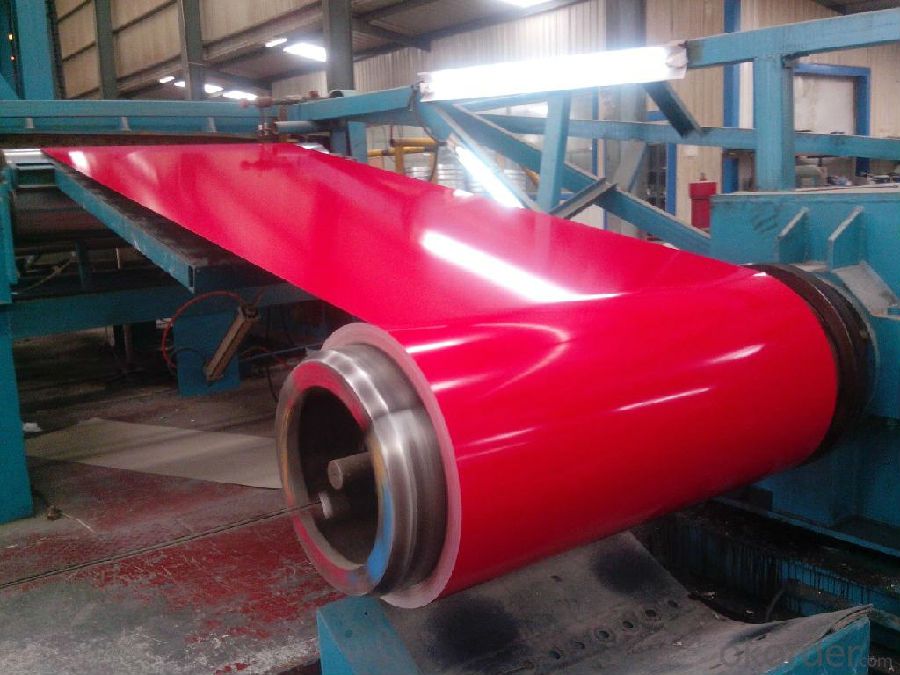

Main Feature of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the zinc protection. When the zinc being worn,
2. Heat resistance: steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; gas tank;road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture constructions :barn; etc.RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; auto parts spare parts etc.
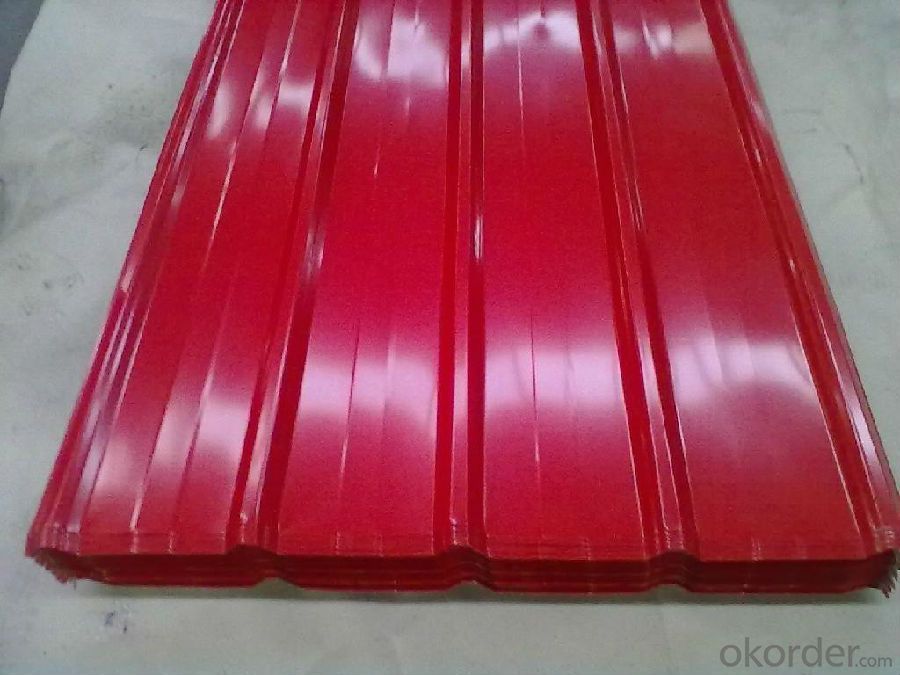

Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
Product | Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.5-3.0mm |
Width | 700-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | AZ30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled,RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 25MT max |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 100 mt for each size each specification. Usually we can offer discount if can buy large QTY once. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
2. How long can we receive the product after ordering?
Our general delivery time is 30 days after confirmation, but so some special orders, we have offer special delivery time
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system ,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4. What is the payment?
We accept T/T, L/C
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of automotive engine components?
- The production of automotive engine components heavily relies on steel billets, which are essential raw materials. These billets are semi-finished steel products, cast into specific shapes and sizes, acting as the foundation for various engine parts including crankshafts, connecting rods, camshafts, and cylinder blocks. To convert steel billets into engine components, a series of processes are undertaken. The initial step involves heating the billets to a high temperature, making them malleable and suitable for forging or machining. Forging, a commonly used technique, involves applying pressure and force to mold the billets into desired forms, like the curved shape of a crankshaft. Once the billets have been shaped through forging, further machining procedures are carried out to refine their dimensions and achieve the desired level of accuracy. Specialized machinery and tools are employed for drilling, milling, turning, and grinding. These machining processes are crucial in meeting the strict tolerances necessary for optimal performance and reliability of engine components. Steel billets are chosen for their exceptional properties, including strength, durability, and heat resistance. These attributes are of utmost importance for engine components, as they endure high pressures, temperatures, and loads during operation. The high tensile strength and ability of steel to withstand extreme conditions make it an ideal material for these critical parts. In conclusion, steel billets hold a significant role in the production of automotive engine components. Through forging and machining, they are transformed into precise and long-lasting parts that contribute to the smooth and efficient operation of engines. The use of steel billets guarantees the overall quality and performance of automotive engines, making them an integral part of the manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the electrical conductivity of steel billets?
- Several key factors primarily influence the electrical conductivity of steel billets. 1. Composition significantly affects the electrical conductivity of steel. The presence of alloying elements, such as carbon, manganese, silicon, and phosphorus, can alter its conductivity properties. 2. Impurities in steel, like sulfur and oxygen, can lower its electrical conductivity. These impurities create barriers to the flow of electric current within the material. 3. The grain structure of steel, influenced by factors like temperature and cooling rate during manufacturing, can impact its electrical conductivity. A fine-grained structure generally results in higher conductivity due to fewer barriers to electron flow. 4. The electrical conductivity of steel billets can be affected by the heat treatment process. Annealing or quenching, for example, can modify the material's microstructure and consequently impact its conductivity. 5. Temperature plays a significant role in the electrical conductivity of steel billets. As temperature increases, conductivity decreases due to increased thermal vibrations that hinder electron flow. 6. The surface condition of steel billets, including the presence of oxides, scale, or contaminants, can influence their electrical conductivity. A clean and smooth surface promotes better conductivity by reducing barriers to electron flow. 7. Mechanical stress or strain in steel billets can affect their electrical conductivity. Processes like rolling, forging, or bending can alter the material's crystal structure and introduce dislocations, which impact conductivity. In conclusion, the electrical conductivity of steel billets is a complex property influenced by factors such as composition, impurities, grain structure, heat treatment, temperature, surface conditions, and mechanical stress. Understanding and controlling these factors is crucial for achieving the desired electrical conductivity in steel billets for various applications.
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for surface finish?
- To ensure quality and compliance with industry standards, various methods and techniques are employed to inspect the surface finish of steel billets. Visual inspection is a common approach, where trained inspectors carefully examine the billet's surface for any defects, such as scratches, pits, cracks, or irregularities. This examination is typically conducted under appropriate lighting conditions to enhance defect visibility. Another method employed is non-destructive testing (NDT), which encompasses techniques like magnetic particle inspection (MPI) and liquid penetrant inspection (LPI). MPI involves the application of a magnetic field to the billet, followed by the use of a magnetic particle suspension to reveal surface defects by adhering to them. On the other hand, LPI involves the application of a liquid penetrant solution to the billet's surface, which is subsequently removed and followed by the application of a developer to highlight any defects. Ultrasonic testing (UT) is also commonly utilized to inspect the surface finish of steel billets. UT employs high-frequency sound waves transmitted through the billet, with any reflected waves analyzed to detect surface or subsurface defects. This method provides detailed information about the surface condition and can even detect minute flaws. Additionally, surface profilometers can be employed to measure the roughness of the billet's surface. These devices utilize a stylus or laser to measure height variations on the surface, thereby providing data on roughness and texture. In summary, a combination of visual inspection, NDT techniques, and surface profilometry is employed to conduct thorough inspections of steel billets' surface finish. These inspections play a crucial role in ensuring that the billets meet the required surface finish standards and are suitable for further processing or manufacturing.
- Q: What are the different surface defects in steel billets?
- Steel billets can have various types of surface defects, which can occur during manufacturing or due to handling and transportation. Some common defects include scale, cracks, lamination, pitting, slivers, rolled-in scale, and surface scratches. Scale forms as a rough, flaky coating during heating and rolling, affecting the billet's appearance. Cracks can be caused by improper cooling, excessive pressure, or stress during handling, compromising the billet's strength. Lamination defects occur when non-metallic layers weaken the billet. Pitting is the formation of small cavities due to corrosion or exposure to corrosive environments. Slivers are thin, protruding pieces caused by improper cutting or shearing. Rolled-in scale refers to embedded scale, requiring additional cleaning. Surface scratches are shallow marks that can affect aesthetics and may need further treatment. Proper identification, handling, and treatment of these defects are essential to ensure the quality of the steel billets. Regular inspection and appropriate techniques can minimize defects and enhance the billets' overall quality.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of reinforcement bars?
- Rebar production relies heavily on steel billets, which are integral components. These billets, resembling rectangular or square semi-finished steel products, act as the initial stage in the manufacturing process. To create rebar, the steel billets are first heated to a temperature surpassing their recrystallization point in a furnace. This procedure, known as hot rolling, involves passing the heated billets through a series of rollers. These rollers gradually decrease the billets' cross-sectional area while elongating the material. Consequently, the billets transform into long, slender bars possessing the desired mechanical properties and dimensions. Throughout the hot rolling process, the steel billets experience significant plastic deformation. This deformation leads to the realignment of grains within the material, resulting in a more uniform and compact structure. This refined microstructure enhances the strength and durability of the rebar, thereby making it ideal for construction projects necessitating high tensile strength, such as reinforced concrete structures. The size and shape of the steel billets employed in rebar production vary according to specific end-product requirements. It is crucial to note that the quality of the billets plays a vital role in determining the rebar's overall quality. Therefore, manufacturers must meticulously select and inspect the billets to ensure they meet the required specifications and standards. In conclusion, steel billets are indispensable in rebar production as they undergo transformation through the hot rolling process, resulting in the desired shape and dimensions. The resulting rebar exhibits enhanced strength and durability, rendering it suitable for reinforcing concrete structures and ensuring their structural integrity.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of power transmission equipment?
- Power transmission equipment relies heavily on steel billets, which are indispensable for their production. Gears, shafts, and couplings, vital components of power transmission equipment, necessitate materials that possess both high strength and durability to endure the forces and stresses involved in transmitting power. Steel billets, categorized as semi-finished steel products, play a pivotal role in meeting these requirements. Primarily, steel billets serve as the raw material for forging or casting processes, enabling the creation of diverse power transmission equipment components. Through forging, billets are subjected to high temperatures and shaped under immense pressure, resulting in a robust and compact material with exceptional mechanical properties. On the other hand, casting involves pouring molten steel into molds to form intricate shapes. In this process, steel billets are melted and cast into molds to fabricate complex components like gears or shafts. Moreover, the composition and quality of steel billets are meticulously controlled to ensure the final product aligns with the specific demands of power transmission equipment. Steel billets are manufactured using various steel grades, each possessing distinct properties such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance. The selection of the appropriate steel grade relies on the particular application and operating conditions of the power transmission equipment. For example, a gear employed in heavy-duty industrial machinery may require a higher strength steel billet compared to a gear used in a smaller-scale application. Additionally, steel billets can undergo further processing, such as heat treatment, to enhance their mechanical properties. Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering have the potential to bolster the hardness, toughness, and overall performance of the billets. This guarantees that the final power transmission equipment possesses the necessary strength and durability to withstand the challenges associated with power transmission. In conclusion, steel billets play a paramount role in the production of power transmission equipment due to their strength, durability, and flexibility. They act as the raw material for forging or casting processes, facilitating the creation of intricate components. Meticulous selection of steel grade and utilization of heat treatment processes ensure that the final product meets the specific requirements of power transmission equipment, solidifying the integral role of steel billets in the manufacturing process.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of electrical appliances?
- Steel billets are used in the manufacturing of electrical appliances as they serve as a raw material for various components. These billets are transformed into sheets, wires, or rods which are then used to create the outer casings, frames, or conductive elements of the appliances. The strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for ensuring the longevity and safety of electrical appliances.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of automotive parts?
- Steel billets are commonly used in the production of automotive parts as they serve as the raw material for forging, rolling, or extruding processes. These billets are heated and shaped into various forms such as rods, bars, or sheets to create components like engine parts, suspension systems, and body frames. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for manufacturing automotive parts, ensuring safety and performance in vehicles.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of industrial furnaces?
- Steel billets are an essential component in the production of industrial furnaces. These billets, which are semi-finished steel products, serve as the raw material for manufacturing various furnace components. To begin with, steel billets are used to fabricate the furnace shell or casing, which provides the structural integrity and containment for the furnace. The billets are shaped and welded together to form a sturdy and durable outer shell that can withstand the high temperatures and harsh conditions within the furnace. Moreover, steel billets are used to construct the furnace doors and access panels. These components need to be strong and resistant to deformation and warping caused by the intense heat generated inside the furnace. By using steel billets, manufacturers can ensure that the doors and access panels can be opened and closed easily, while maintaining their structural integrity over time. Furthermore, steel billets are also utilized in the production of furnace grates and supports. These components are responsible for holding and supporting the materials being heated inside the furnace. By using steel billets, manufacturers can create robust and heat-resistant supports that are capable of withstanding heavy loads and high temperatures for extended periods. In addition, steel billets are often used in the fabrication of heat exchangers within industrial furnaces. Heat exchangers are vital for transferring heat from the combustion chamber to the materials being processed. The use of steel billets ensures that the heat exchangers have excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand the corrosive effects of the furnace environment. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in the production of industrial furnaces by providing the necessary strength, durability, and heat-resistant properties required for their various components. Without steel billets, it would be challenging to manufacture furnaces capable of withstanding the extreme conditions encountered in industrial processes.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet forging machines?
- There are several different types of steel billet forging machines available in the market today. These machines are designed to efficiently shape and form steel billets into desired shapes and sizes. Here are some of the common types of steel billet forging machines: 1. Hydraulic Forging Press: This type of machine uses hydraulic power to exert force on the steel billet, allowing it to be forged into the desired shape. Hydraulic forging presses are known for their high force capabilities and versatility in handling different sizes of billets. 2. Mechanical Forging Press: Mechanical forging presses use mechanical power, such as flywheels or eccentric mechanisms, to exert force on the billet. These machines are known for their reliability and precision, making them suitable for high-volume production. 3. Screw Press: Screw presses utilize a rotating screw mechanism to apply force on the steel billet. They are characterized by their high-speed operation and efficient energy usage. Screw presses are commonly used for forging small to medium-sized billets. 4. Hammer Forging Machine: Hammer forging machines use a hammering action to shape the steel billet. There are various types of hammer forging machines, including steam hammers, air hammers, and hydraulic hammers. These machines are known for their high impact force, making them suitable for heavy-duty forging. 5. Upsetter: Upsetters, also known as upsetting machines, are specifically designed for forging the ends of steel billets. They use a vertical or horizontal ram to apply pressure on the billet, causing it to increase in diameter and length. Upsetters are commonly used for producing forged components with thickened ends. 6. Radial Forging Machine: Radial forging machines employ a rotating roller to apply radial force on the steel billet. This force causes the billet to increase in diameter while maintaining its original length. Radial forging machines are often used for producing seamless rings and other cylindrical components. It's important to note that the choice of the most suitable steel billet forging machine depends on factors such as the size and shape of the billet, desired production volume, and specific requirements of the final product. Each type of machine has its own advantages and limitations, so it is crucial to consider these factors when selecting the appropriate forging machine for a given application.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 190mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































