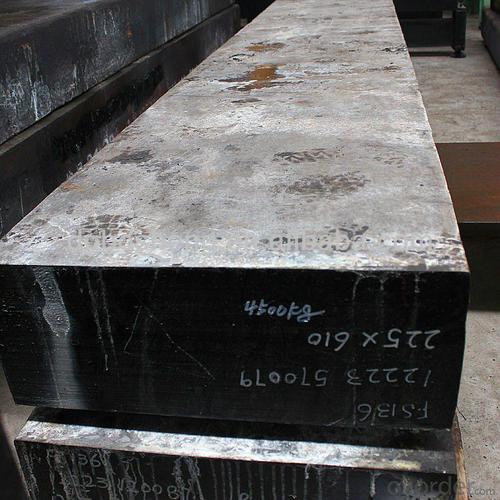
Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
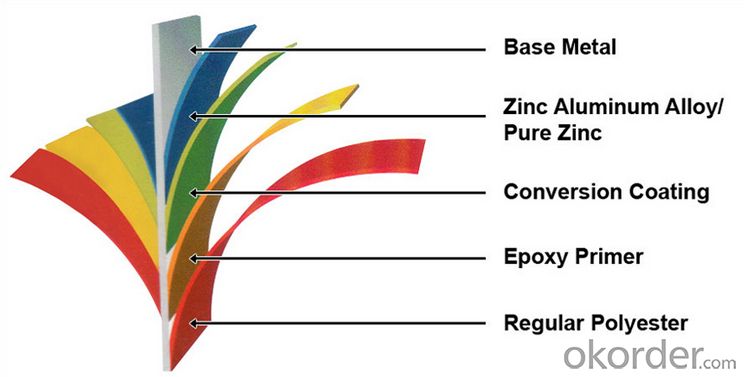
Description of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
1) Automotive bodies: filters, fuel tanks, etc.
2) Construction materials: roofings, welding pipes,
3) Electric and electronic appliances: computer cans, etc.
4) Steel cans: containers, etc.
5) Steel furniture: washing machines, refrigerators, microwaves, etc.
6) Drums
7) Office equipment: printer, recorders, etc.
8) Motors and transformers

Specifications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet cutting processes?
- Various industries utilize several different steel billet cutting processes. Among the most frequently employed methods are: 1. Shearing: This technique entails utilizing a shear machine to cut the steel billet into the desired shape. Shearing is typically chosen for cutting straight lines and is a cost-effective option for smaller billets. 2. Sawing: Another commonly used approach is sawing, which involves utilizing a circular or band saw to cut through the billet. Sawing is suitable for cutting both straight and curved lines, making it more versatile than shearing. 3. Flame cutting: Also known as oxy-fuel cutting, flame cutting involves using a combination of oxygen and a fuel gas (such as acetylene) to heat the steel to its ignition temperature. A high-pressure stream of oxygen is then directed onto the heated area, causing the steel to oxidize and melt away. This process is frequently employed for cutting thicker steel billets. 4. Plasma cutting: Plasma cutting employs a plasma torch to cut through the steel billet. The torch generates a high-temperature plasma arc that melts the metal, while a high-velocity gas stream blows away the molten metal. Plasma cutting is often selected for cutting through thick steel billets or for creating intricate shapes. 5. Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting relies on a high-pressure jet of water mixed with an abrasive material (such as garnet) to cut through the steel billet. The abrasive particles in the waterjet erode the steel, allowing for precise and clean cuts. Waterjet cutting is commonly used for cutting complex shapes or materials that are heat-sensitive. These examples represent just a fraction of the available steel billet cutting processes. The choice of method depends on factors such as billet size, desired shape, precision requirements, and available budget.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of oil and gas industry components?
- Steel billets are an essential raw material used in the manufacturing of various components for the oil and gas industry. These billets, which are semi-finished steel products, play a crucial role in the production of pipes, valves, fittings, and other equipment required for oil and gas extraction, transportation, and processing. One of the primary applications of steel billets in the oil and gas industry is in the production of seamless and welded pipes. These pipes are used extensively for the transportation of oil, gas, and other fluids over long distances. Steel billets are first heated and then passed through a series of rollers to form seamless pipes. In the case of welded pipes, the billets are first formed into a tube shape and then welded along the length to create a strong and durable pipe. Steel billets are also used in the manufacturing of valves, which are crucial components in the oil and gas industry. Valves are used to control the flow of fluids within pipelines and equipment. Billets are machined and shaped to create valve bodies, which are then fitted with various internal components such as seats, discs, and stems. These valves are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring reliable and safe operation in the oil and gas industry. Furthermore, steel billets are utilized in the production of fittings, which are used to connect and join pipes together. Fittings such as elbows, tees, couplings, and flanges are manufactured from billets by machining and shaping them into the required dimensions and configurations. These fittings play a critical role in creating a reliable and leak-free pipeline system for the transportation of oil and gas. In addition to pipes, valves, and fittings, steel billets also find applications in the manufacturing of other equipment used in the oil and gas industry. These include drill bits, pumps, compressors, and various structural components for offshore platforms and refineries. The strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of steel make it an ideal material for these demanding applications, and steel billets serve as the starting point for their production. In conclusion, steel billets are a crucial raw material in the manufacturing of components for the oil and gas industry. Whether it is pipes, valves, fittings, or other equipment, billets are transformed through various processes to create the essential components required for the extraction, transportation, and processing of oil and gas.
- Q: What is the typical composition of steel billets?
- The typical composition of steel billets can vary depending on the specific requirements and intended use. However, in general, steel billets are primarily composed of iron and carbon, with other elements added to enhance certain properties. The carbon content in steel billets is typically around 0.1-0.3%. In addition to iron and carbon, steel billets often contain small amounts of other elements such as manganese, silicon, sulfur, and phosphorus. Manganese helps improve the strength and hardness of the steel while also promoting better heat treatment response. Silicon is commonly added to enhance the steel's fluidity during casting. Sulfur and phosphorus are impurities that need to be minimized as they can negatively affect the steel's machinability and mechanical properties. Furthermore, alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium may also be present in steel billets to impart specific properties. For instance, chromium improves corrosion resistance, nickel enhances toughness and ductility, molybdenum increases high-temperature strength, and vanadium improves wear resistance. Overall, the composition of steel billets is carefully controlled to achieve the desired mechanical, physical, and chemical properties required for the subsequent processing and final applications of the steel.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the production of steel bars?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the production of steel bars. They are semi-finished forms of steel that are typically cast in a square or rectangular shape. These billets serve as the starting material for the production of various steel products, including steel bars. The primary purpose of steel billets is to be further processed and transformed into steel bars through a series of manufacturing steps. Once the steel billets are obtained, they undergo a process known as hot rolling. This involves subjecting the billets to high temperatures and passing them through rolling mills, where they are shaped and elongated into the desired form, such as round bars, square bars, or hexagonal bars. During the hot rolling process, the steel billets are subjected to extreme heat and pressure, causing them to deform and elongate. This process helps to improve the mechanical properties of the steel, such as strength, toughness, and ductility. It also refines the grain structure of the steel, enhancing its overall quality and performance. Steel bars produced from steel billets find wide applications in various industries, such as construction, manufacturing, infrastructure, and automotive. They are widely used as structural components in buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects, as well as in the production of machinery, tools, and equipment. In summary, steel billets play a critical role in the production of steel bars. They serve as the starting material for the manufacturing process, undergoing hot rolling to transform them into the desired shape and size. The resulting steel bars are then used in a wide range of applications due to their enhanced mechanical properties and improved quality.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of defense equipment?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of defense equipment. These billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that are used as raw materials in various manufacturing processes. Defense equipment requires materials that are strong, durable, and can withstand extreme conditions. Steel billets meet these requirements perfectly. One of the primary uses of steel billets in defense manufacturing is in the production of armored vehicles and tanks. These vehicles need to be highly resistant to ballistic threats and provide protection to the soldiers inside. Steel billets, with their exceptional strength and toughness, are an ideal choice for manufacturing the armor plates used in these vehicles. The billets are transformed into thick, hardened steel plates that provide excellent ballistic resistance and can withstand high-velocity impacts. Additionally, steel billets are used in the production of weaponry, such as firearms and missiles. These weapons require materials that can withstand the intense pressure and heat generated during firing or launching. Steel billets, with their high tensile strength and heat resistance, provide the necessary foundation for creating barrels, chambers, and other critical components of these weapons. Moreover, steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of defense equipment by being used in the production of various support structures and infrastructure. This includes military facilities, such as hangars, barracks, and storage facilities, which need to be robust and secure. Steel billets are transformed into beams, columns, and other structural elements that provide strength and stability to these buildings. In summary, steel billets are an essential component in the manufacturing of defense equipment. Their strength, durability, and ability to withstand extreme conditions make them ideal for producing armored vehicles, weaponry, and support structures. By utilizing steel billets, defense manufacturers can ensure the production of high-quality and reliable equipment that meets the stringent requirements of the defense sector.
- Q: How are steel billets manufactured?
- Steel billets, which are essential raw materials for steel products like bars, rods, and wire rods, are produced using a widely used method in the steel industry called continuous casting. This process entails pouring molten steel into a mold that is cooled by water, causing it to solidify into a rectangular or square shape. The molten steel typically originates from a steelmaking furnace like a basic oxygen furnace or an electric arc furnace. Before the casting begins, the mold is heated beforehand to prevent premature solidification of the molten steel. Once prepared, the molten steel is poured into the mold using a ladle or a tundish to regulate the flow and eliminate impurities. When the molten steel enters the mold, it cools rapidly due to the water-cooled mold walls. This rapid cooling results in the outer layer of the steel solidifying and forming a solid shell. The cooling process continues as the steel progresses through the mold, and water is sprayed on it to expedite solidification. Once the solidified steel reaches the end of the mold, it is cut into desired lengths using a cutting torch or a mechanical shear. These solidified steel pieces, known as billets, are then transferred to a cooling bed or a roller table to continue cooling and solidifying. After sufficient cooling, the billets undergo inspection to identify any surface defects or irregularities. Depending on quality requirements, the billets may undergo additional processing, such as heat treatment or surface conditioning, to enhance their mechanical properties and surface finish. In summary, continuous casting enables the efficient and cost-effective production of steel billets, which are crucial raw materials for various downstream steel products.
- Q: Who knows the diamond is?Who knows the diamond is carbon? Is it C60?
- It is also called the diamond diamond, crystal, it is not the molecules themselves, so the formula does not apply to.C said it is only by this kind of carbon elements. While C60 is footballene is another matter, the 60 is because it is a molecular crystal, each molecule consists of 60 carbon.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of electrical transmission equipment?
- Steel billets are often used as raw material in the manufacturing of electrical transmission equipment. They are typically forged or machined to create various components such as brackets, supports, and housings. These billets provide the necessary strength, durability, and dimensional stability required for the equipment to withstand high electrical loads and harsh operating conditions.
- Q: How many tons of billets does it take to produce a ton of thread steel?
- Domestic steel manufacturers, production rate of about 97%, so probably need 1/97%=1.03 tons. The yield was increased, consumption will be reduced.
- Q: What are the properties and characteristics of steel billets?
- Steel billets are semi-finished products that possess several key properties and characteristics. Firstly, they have a rectangular or square cross-section with a relatively large size, typically ranging from 100x100mm to 200x200mm. They are manufactured through the process of continuous casting, which ensures their uniform composition and high quality. Steel billets exhibit excellent strength and hardness, making them suitable for various applications in the manufacturing industry. They have a high resistance to deformation, enabling them to withstand heavy loads and pressures. Additionally, they have good ductility and can be easily shaped or formed into desired products through processes like rolling or forging. Another important characteristic of steel billets is their excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer during processing. They also have a good resistance to corrosion, which makes them suitable for outdoor applications and in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals. Overall, steel billets are versatile and robust materials with a wide range of applications in the construction, automotive, and machinery industries, among others. Their distinctive properties make them a preferred choice for various manufacturing processes, enabling the production of durable and reliable end products.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 130mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































