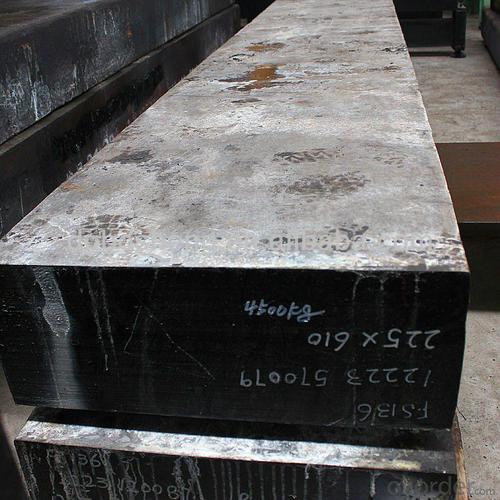
Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
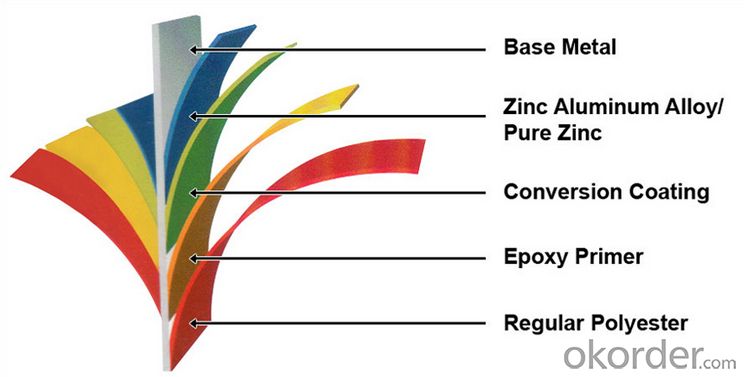
Description of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
1) Automotive bodies: filters, fuel tanks, etc.
2) Construction materials: roofings, welding pipes,
3) Electric and electronic appliances: computer cans, etc.
4) Steel cans: containers, etc.
5) Steel furniture: washing machines, refrigerators, microwaves, etc.
6) Drums
7) Office equipment: printer, recorders, etc.
8) Motors and transformers

Specifications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the thermal conductivity of steel billets?
- The thermal conductivity of steel billets is primarily influenced by several factors. Firstly, the chemical composition of the steel plays a significant role in determining its thermal conductivity. Elements such as carbon, manganese, and silicon can affect the crystal structure and the arrangement of atoms within the steel, which in turn influences its ability to conduct heat. Generally, steels with a higher carbon content have lower thermal conductivity due to the increased presence of impurities and the formation of non-conductive carbides. Secondly, the microstructure of the steel also affects its thermal conductivity. Heat conduction in steel occurs through the movement of lattice vibrations, known as phonons. The presence of grain boundaries, dislocations, and other defects within the microstructure can impede the phonon movement, resulting in reduced thermal conductivity. Conversely, a more uniform and fine-grained microstructure tends to enhance thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the temperature of the steel billet can significantly impact its thermal conductivity. As the temperature increases, the thermal conductivity of steel generally decreases due to the increased scattering of phonons by lattice vibrations and the accompanying rise in thermal resistance. Another factor that influences the thermal conductivity of steel billets is their physical dimensions, particularly their cross-sectional area and length. The larger the cross-sectional area, the higher the thermal conductivity, as there is more space available for the heat to transfer through. Similarly, longer billets tend to have lower thermal conductivity due to the increased distance over which heat must be conducted. Lastly, the presence of impurities and alloying elements in the steel can also affect its thermal conductivity. For example, alloying elements like nickel, chromium, and copper can alter the crystal structure and lattice vibrations, thereby influencing the thermal conductivity of the steel billet. In summary, the main factors affecting the thermal conductivity of steel billets include the chemical composition, microstructure, temperature, physical dimensions, and the presence of impurities and alloying elements. Understanding these factors is crucial in various industrial applications where heat transfer and thermal management play a critical role.
- Q: How are steel billets measured and classified?
- Steel billets are measured and classified based on their dimensions and chemical composition. The dimensions of a steel billet are typically measured in terms of length, width, and height. These measurements are important for determining the size and shape of the billet, which in turn affects its usability in various applications. Additionally, steel billets are classified based on their chemical composition. This is determined by analyzing the percentage of various elements present in the steel, such as carbon, manganese, silicon, and sulfur. The chemical composition of a billet is crucial in determining its mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, hardness, and ductility. The classification of steel billets is typically done according to international standards set by organizations such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for measuring and classifying steel billets, ensuring consistency and quality across the industry. In terms of measurement, steel billets are typically measured using calipers or precision measuring instruments to obtain accurate dimensions. The length is measured from end to end, while the width and height are measured at their widest points. These measurements are often recorded in millimeters or inches, depending on the regional standards. After measuring the dimensions and analyzing the chemical composition, steel billets are classified into various grades or specifications. These classifications help in identifying the suitable applications and industries where the billets can be used. For example, there may be specific grades of steel billets that are suitable for construction purposes, while others are more suitable for manufacturing automotive parts or machinery. In conclusion, steel billets are measured and classified based on their dimensions and chemical composition. The dimensions of the billets are measured in terms of length, width, and height, while the chemical composition is determined by analyzing the percentage of various elements present in the steel. These measurements and classifications are essential for determining the usability and quality of the steel billets in different applications and industries.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of machined parts?
- Steel billets are an essential raw material in the production of machined parts. They are typically used as the starting point for creating various components and products through machining processes such as turning, milling, drilling, and grinding. Firstly, steel billets are heated to a specific temperature to make them more malleable. This process, known as forging, allows the billets to be shaped and manipulated into the desired form. The heated billets are then placed onto a cutting machine, where they are cut into smaller sections called blanks or workpieces. After the billets have been cut, the blanks are further processed using different machining techniques. For example, turning involves rotating the workpiece while removing excess material with cutting tools to create cylindrical shapes like shafts or rods. Milling involves using rotary cutters to remove material from the workpiece, typically to create complex shapes or features. Drilling is another common machining process where holes are created in the billet or workpiece using a drill bit. This is often required to accommodate screws, bolts, or other fasteners in the final product. Grinding, on the other hand, is used to achieve a smooth and precise surface finish on the machined parts. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in the production of machined parts. They provide a solid and durable foundation that can be shaped and transformed into various components through the application of different machining techniques. Without steel billets, the manufacturing of machined parts would not be possible, as they serve as the starting point for creating the final products that we use in numerous industries.
- Q: What are the main differences between hot rolled and cold rolled steel billets?
- The main differences between hot rolled and cold rolled steel billets lie in the manufacturing process and resulting properties. Hot rolled steel billets are created by heating the steel and then rolling it at high temperatures, which leads to a rougher surface finish and less precise dimensions. On the other hand, cold rolled steel billets undergo a process of rolling at room temperature, resulting in a smoother surface finish and tighter dimensional tolerances. Moreover, hot rolled steel billets are generally more ductile and have a higher carbon content, while cold rolled steel billets are typically harder and have improved strength due to the strain hardening during the cold rolling process.
- Q: Are steel billets subject to any heat treatment processes?
- Indeed, heat treatment processes can be used on steel billets. Heat treatment is a regulated procedure that involves heating and cooling metals in order to modify their physical and mechanical properties. Steel billets, which are semi-finished steel products with a square or rectangular shape, can undergo different heat treatment processes depending on the desired properties for the final product. One commonly used heat treatment process for steel billets is annealing. Annealing consists of heating the billets to a specific temperature and gradually cooling them to relieve internal stresses and enhance their ductility and toughness. This process is typically employed to soften the steel and make it more malleable for subsequent manufacturing processes. Another heat treatment process for steel billets is quenching and tempering. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the heated steel billets in a liquid medium, such as oil or water, to achieve high hardness and strength. However, this process results in a hard but brittle material. To reduce the brittleness, the quenched billets are then tempered by reheating them to a lower temperature and slowly cooling them. Tempering improves the toughness and ductility of the steel while maintaining a certain level of hardness. Additional heat treatment processes that can be applied to steel billets include normalizing, which involves heating the steel above its critical temperature and then cooling it in still air to refine the grain structure, and stress relieving, which is performed to reduce residual stresses in the billets after extensive machining or welding. Overall, heat treatment processes can significantly improve the mechanical properties of steel billets, making them more suitable for various applications in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for stainless steel billets?
- There are several surface finishes available for stainless steel billets, depending on the desired aesthetic appearance and functional requirements. Some of the most common surface finishes for stainless steel billets include: 1. Mill Finish: This is the standard finish produced by the steel mill during the manufacturing process. It has a dull appearance with visible oxidation marks and can vary in smoothness. 2. Hot Rolled: This finish is achieved by heating the stainless steel billet and then rolling it through a series of rollers. It results in a rougher surface with visible scale and a characteristic orange peel texture. 3. Cold Rolled: This finish is obtained by subjecting the stainless steel billet to cold rolling, which reduces its thickness and improves its surface smoothness. It has a slightly reflective appearance and is often used for applications requiring a smooth finish. 4. Brushed Finish: Also known as satin finish, this surface finish is achieved by mechanically brushing the stainless steel billet with abrasive materials. It creates a consistent linear pattern, giving the steel a matte appearance. 5. Polished Finish: This finish involves polishing the stainless steel billet using abrasives to create a smooth and reflective surface. The level of polish can vary from a low-gloss satin finish to a mirror-like, highly reflective finish. 6. Bead Blasted Finish: In this finish, the stainless steel billet is bombarded with tiny glass or ceramic beads under high pressure, which creates a uniform matte texture. It is commonly used for architectural and decorative applications. 7. Electropolished Finish: This surface finish is achieved by immersing the stainless steel billet in an electrolyte bath and applying an electric current. It removes a thin layer of material, resulting in a smooth, reflective surface with improved corrosion resistance. These are just a few examples of the different surface finishes available for stainless steel billets. Each finish has its own unique characteristics and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning.
- Q: Are steel billets used in the production of musical instruments?
- Yes, steel billets are commonly used in the production of musical instruments. They are often used to create various components such as keys, valves, and rods, which are essential parts of instruments like saxophones, trumpets, and trombones.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the transportation aftermarket?
- Steel billets have various potential applications in the transportation aftermarket. They can be used for manufacturing various components such as engine parts, suspension systems, chassis, and body structures. Steel billets offer excellent strength, durability, and reliability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications in the transportation industry. Additionally, their versatility allows for customization and adaptability to meet specific requirements. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in enhancing the performance, safety, and efficiency of vehicles in the transportation aftermarket.
- Q: Does anyone know how much it costs to refine a ton of steel? What are the expenses involved?
- Electricity, water, wages, raw materials, raw materials loss, charges, oxygen, according to their own circumstances, as well as freight and other expenses, now the steel profits are not as good as before, a ton of net profit is about 100 yuan
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet cutting?
- There are various techniques for cutting steel billets, each offering unique advantages and applications. Some of the most prevalent methods are as follows: 1. Sawing: Sawing involves the use of a saw blade to cut steel billets. It can be performed either manually or with the aid of a machine. Sawing is a versatile approach that can be applied to billets of various sizes and shapes, although it may not be suitable for thicker billets. 2. Flame cutting: Also known as oxy-fuel cutting, flame cutting entails heating the steel billet to its ignition temperature using a torch, and then introducing oxygen to create a chemical reaction that cuts through the metal. This method is commonly employed for thicker billets and allows for both straight and beveled cuts. 3. Plasma cutting: Plasma cutting employs a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and eliminate the steel. It is a versatile technique suitable for cutting steel billets of various thicknesses, providing high-quality cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. 4. Water jet cutting: This method involves using a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through the steel billet. Water jet cutting is particularly effective for cutting intricate shapes and can deliver precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. Furthermore, it is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. 5. Laser cutting: Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to melt and vaporize the steel billet, resulting in a narrow cut. This method is highly precise and capable of producing intricate cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. Laser cutting is commonly used for cutting thin to medium thickness billets and is especially favored in industries that require high precision and speed. In conclusion, the methods of steel billet cutting encompass sawing, flame cutting, plasma cutting, water jet cutting, and laser cutting. Each method possesses its own strengths and is appropriate for different applications, depending on factors such as billet thickness, desired precision, and material type.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP Standard 125mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































