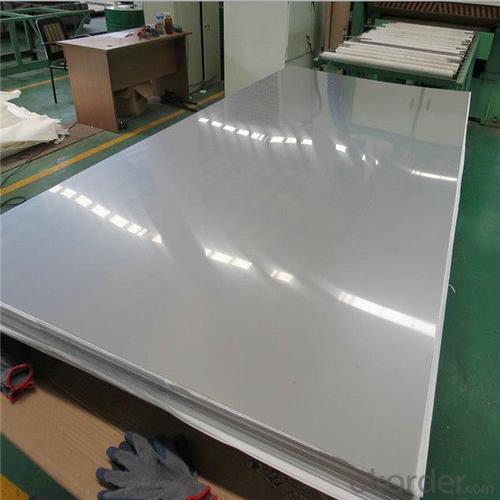
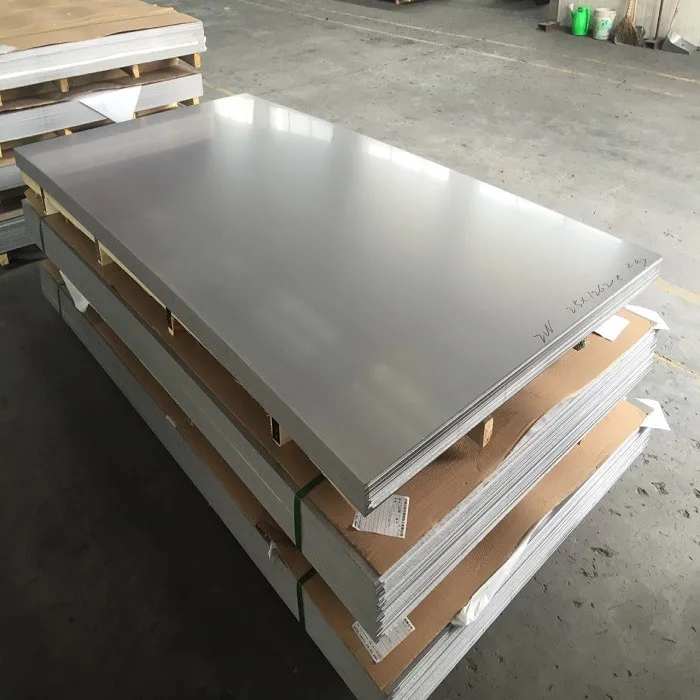
310S Stainless Steel Sheet Price per ton
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
430 201 304 321 316L 310S 2507 317L 904L 2205 Hard Stainless Steel Sheet Price Per Kg
Type | 430 201 304 321 316L 310S 2507 317L 904L 2205 Hard Stainless Steel Sheet Price Per Kg |
Thinckness | Hot rolled: 3.0mm-20mm |
Widthness | 1000-2000mm or as customized |
Length | 1000mm-6000mm |
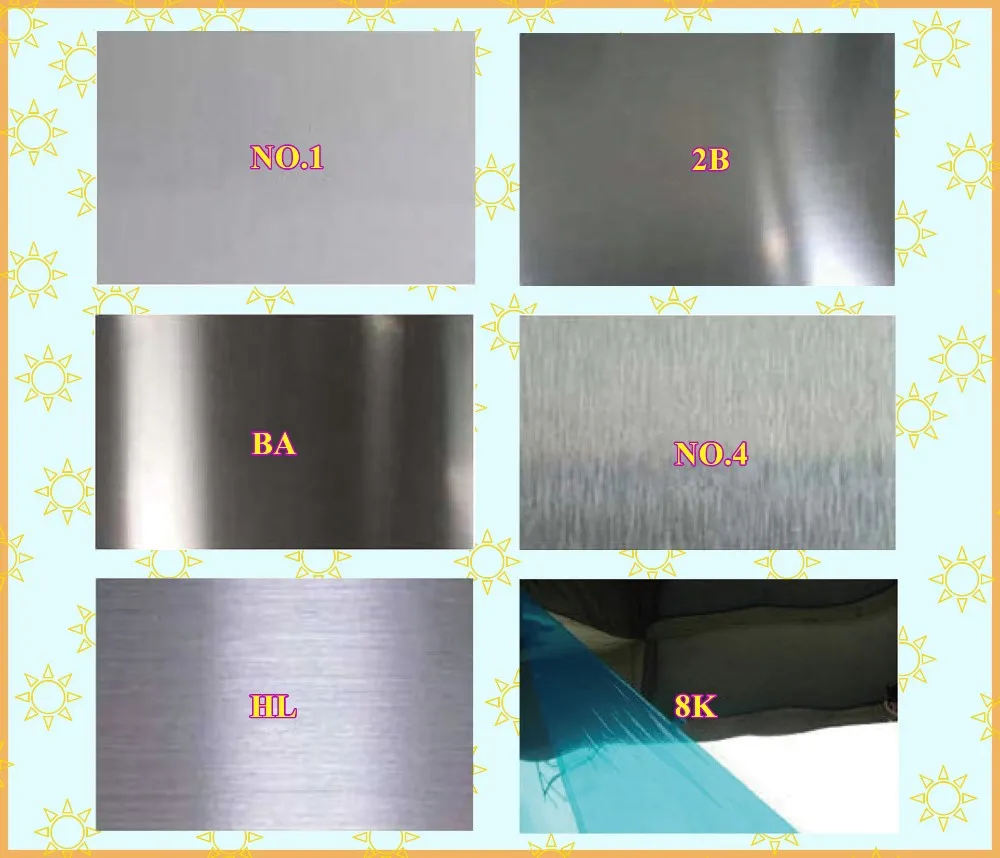
Finish | 2B, BA, HL, Mirror, NO1,NO 4, 8K |
Standard | ASME, ASTM, EN, BS, GB, DIN, JIS |
Material | mainly:201, 202, 304, 304L, 316, 316L,316 300series:301,302,303,304,304L,309,309s,310,310S,316,316L,316Ti,317L,321,3 200series:201,202,202cu,204 400series:409,409L,410,420,430,431,439 |
Application range | Decoration Industry Kitchenwave Building Elevator Upholstery |
Delivery time | 10-15 days subject to the clients' requirement and quantity |
Productivity | 3000 tons/month |
Note | We can produce other standard as the customers’ requirement |
| Surface | Definition | Application |
NO.1 | The surface finished by heat treatment and pickling or processes corresponding there to after hot rolling. | Chemical tank, pipe. |
| 2B | Those finished, after cold rolling, by heat treatment,pickling or other equivalent treatment and lastly by cold rolling to given appropriate luster. | Medical equipment, Food industry,Construction material, Kitchen utensils. |
| NO.3 | Those finished by polishing with No.100 to No.120 abrasives specified in JIS R6001. | Kitchen utensils, Building construction |
| NO.4 | Those finished by polishing with No.150 to No.180 abrasives specified in JIS R6001. | Kitchen utensils, Building construction,Medical equipment. |
| HL | Those finished polishing so as to give continuous polishing streaks by using abrasive of suitable grain size | Building Construction. |
| BA(No.6) | Those processed with bright heat treatment after cold rolling. | Kitchen utensils. Electric equipment,Building construction. |
| Mirror(No.8) | Shinning like a mirror | Building construction |
No. | Grade | Chemical Composition % | ||||||||||
C | Cr | Ni | Mn | P | S | Mo | Si | Cu | N | Other | ||
201 | 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N | ≤0.15 | 16.00-18.00 | 3.50-5.50 | 5.50-7.50 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | ≤0.25 | - |
2205 | 00Cr22Ni5Mo3N,S31803 | ≤0.030 | 21.00-23.00 | 4.50-6.50 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.020 | 2.5-3.5 | ≤1.00 | - | 0.08-0.2 | |
202 | 1Cr18Mn8Ni5N | ≤0.15 | 17.00-19.00 | 4.00-6.00 | 7.50-10.00 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.030 | ≤1.00 | - | ≤0.25 | - | |
204 | 03Cr16Mn8Ni2N | ≤0.030 | 15.00-17.00 | 1.50-3.50 | 7.00-9.00 | 0.15-0.30 | ||||||
301 | 1Cr17Ni7 | ≤0.15 | 16.00-18.00 | 6.00-8.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.065 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
304 | 0Cr18Ni9 | ≤0.07 | 17.00-19.00 | 8.00-10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
304L | 00Cr19Ni10 | ≤0.030 | 18.00-20.00 | 8.00-10.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
310S | 0Cr25Ni20 | ≤0.08 | 24.00-26.00 | 19.00-22.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
316 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | ≤0.08 | 16.00-18.50 | 10.00-14.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | 2.00-3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
316L | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 | ≤0.030 | 16.00-18.00 | 12.00-15.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | 2.00-3.00 | ≤1.00 | - | - | - |
431 | 1Cr17Ni2 | 0.11-0.17 | 16.00-18.00 | 1.50-2.50 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | - | ≤0.80 | - | - | - |
Shows of products
Printing processing
simple process of stainless steel
1.GRINDING
Grinding finish, also called brushed, directional or satin finish. coil or sheet...
2.POLISHING
polished stainless steel sheet uses grinding fluid to polish by polishing equipment on stainless steel ..
3.PVD COLOR COATING
PVD means Physical Vapor Deposition,working in vacuum condiction.....
4.ETCHING
Etching is corrode different kinds of patterns on stainless steel surfaces by chemical methods.
5.EMBOSSING
It is physical rolling on the stainless steel surface, pattern comes from metal roller....

Related Products
Applications
Stainless steel is widely used such as elevator decoration, luxurious doors, outdoor projects, wall decoration, advertisement nameplates, sanitary ware, ceiling, corridor, hotel hall, shop facade,kitchenware, food industry, electronic industry, medical equipment, etc.

Packaging & Shipping
Standard export package with water proof paper, and metal pallet, and angle bar protection, and steel strip or as required
20ft GP: 5.8m(length) x 2.13m(width) x 2.18m(high) about 24-26CBM, 23MTS
40ft GP: 11.8m(length) x 2.13m(width) x 2.18m(high) about 54CBM, 27MTS
40ft HG: 11.8m(length) x 2.13m(width) x 2.72m(high) about 68CBM, 27MTS
MOQ | 1 Ton |
Price Term | FOB CIF |
Payment | L/C at sight or 30% TT as deposit |
Delivery Time | 20-30 days after receiving deposit by T/T or L/C. |
Sample | Samples free and express charges bear by you |
- Q: What are the different types of stainless steel sheet thicknesses available?
- There is a wide variety of stainless steel sheet thicknesses to choose from, each serving different purposes and applications. The most commonly used thicknesses range from 0.4mm to 3.0mm, with increments of 0.4mm. These sheets are typically utilized in general applications such as construction, automotive parts, and household appliances. For more specialized applications, one can find thinner stainless steel sheets with thicknesses ranging from 0.1mm to 0.3mm. These thinner sheets are commonly employed in industries like electronics, telecommunications, and medical equipment manufacturing, where precise and delicate components are necessary. On the other hand, thicker stainless steel sheets, starting from 3.0mm and going up to 20mm or more, are reserved for heavy-duty applications like industrial machinery, shipbuilding, and construction projects that require exceptional structural integrity and durability. It's important to keep in mind that the available stainless steel sheet thicknesses may vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use. Moreover, custom thicknesses can be manufactured to meet the specific requirements of a project.
- Q: Can stainless steel sheets be embossed or textured?
- Certainly, it is possible to emboss or texture stainless steel sheets. This procedure entails employing specialized machinery and techniques to imprint a pattern or design onto the surface of the stainless steel sheet. Embossing generates a raised pattern, whereas texturing produces a textured or brushed appearance on the sheet's surface. These methods are ideal for enhancing the visual appeal of stainless steel sheets, rendering them suitable for a wide range of uses including architectural, decorative, or industrial purposes. Furthermore, embossed or textured stainless steel sheets can offer practical advantages such as enhanced grip or reduced glare.
- Q: How do I prevent galvanic corrosion on stainless steel sheets?
- There are several measures that can be taken to prevent galvanic corrosion on stainless steel sheets: 1. Opt for a suitable stainless steel alloy: Select a grade of stainless steel, such as 316 or 317, which is less susceptible to galvanic corrosion compared to 304 stainless steel. 2. Keep dissimilar metals separate: Avoid direct contact between stainless steel sheets and other metals, particularly those with a higher potential for galvanic corrosion. If contact is necessary, use insulating materials like gaskets or rubber pads to create a barrier between the metals. 3. Apply protective coatings: Use specially designed protective coatings or paints for stainless steel to create a barrier that shields against galvanic corrosion. These coatings act as sacrificial layers, safeguarding the stainless steel from direct contact with corrosive substances. 4. Utilize isolation materials: Install insulating materials, such as plastic washers, insulating tape, or non-conductive gaskets, between stainless steel sheets and other dissimilar metals. This prevents direct electrical contact and subsequent corrosion. 5. Maintain proper upkeep: Regularly clean and inspect stainless steel sheets to remove any contaminants or foreign substances that may contribute to corrosion. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or tools that could damage the protective layer of the stainless steel. 6. Employ electrochemical protection: Implement cathodic protection techniques, such as sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems, to introduce an external source of electrons that counteracts galvanic corrosion. These methods help shift the corrosion potential of the stainless steel sheets to a more passive range. By adhering to these preventive measures, the risk of galvanic corrosion on stainless steel sheets can be significantly reduced. This ensures their longevity and helps maintain their structural integrity.
- Q: Are stainless steel sheets resistant to chemicals and acids?
- Yes, stainless steel sheets are resistant to chemicals and acids. Stainless steel contains a high percentage of chromium, which forms a protective layer on the surface of the metal, making it highly resistant to corrosion and damage from chemicals and acids. This corrosion-resistant property is further enhanced by the addition of other elements such as nickel and molybdenum. Stainless steel sheets are widely used in various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and automotive, where they are exposed to aggressive chemicals and acids. The resistance of stainless steel to chemicals and acids makes it a reliable and durable material for applications that require resistance to corrosion and chemical attack.
- Q: What is the corrosion resistance of stainless steel sheets?
- The high corrosion resistance properties of stainless steel sheets are well-known. This is because the alloy contains chromium, which creates a protective oxide layer on the steel's surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen and moisture from reaching the steel underneath. Consequently, stainless steel sheets exhibit remarkable resistance to rust, staining, and corrosion in different environments, including exposure to water, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The level of corrosion resistance can vary depending on the grade and composition of the stainless steel. In general, higher chromium and nickel content result in better corrosion resistance. Therefore, stainless steel sheets are extensively utilized in industries like construction, automotive, and food processing, where durability and resistance to corrosion are of utmost importance.
- Q: What are the different types of corrosion that stainless steel sheets can resist?
- Compared to other metals, stainless steel sheets possess remarkable corrosion resistance. They can withstand several forms of corrosion, including: 1. Uniform corrosion: This occurs when the entire surface of the stainless steel sheet is exposed to a corrosive environment. However, stainless steel contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which creates a protective oxide layer on the surface, halting further corrosion. 2. Pitting corrosion: Pitting corrosion causes small pits or holes on the stainless steel sheet's surface. Thanks to its high chromium content, stainless steel forms a passive film that prevents pitting corrosion from advancing. 3. Crevice corrosion: This type of corrosion happens in cramped spaces or gaps where stagnant corrosive substances can accumulate. Stainless steel sheets resist crevice corrosion by maintaining their passivity and preventing the buildup of corrosive agents. 4. Stress corrosion cracking (SCC): SCC arises from the combined effects of a corrosive environment and tensile stress. Stainless steel sheets are built to withstand SCC due to their high alloy content and the formation of a protective passive film. 5. Intergranular corrosion: Intergranular corrosion affects the grain boundaries of stainless steel, making it prone to cracking and weakening. However, stainless steel sheets are typically crafted with low carbon content to prevent intergranular corrosion and ensure their durability. In general, stainless steel sheets are highly resistant to various forms of corrosion, making them the preferred choice for multiple applications in industries such as construction, food processing, and marine engineering.
- Q: What is the water absorption rate of stainless steel sheets?
- The water absorption rate of stainless steel sheets is typically very low or negligible. Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and impermeability to liquids, including water. Due to its unique composition and surface properties, stainless steel sheets do not readily absorb water or allow it to penetrate the material. This makes stainless steel a preferred choice for various applications where resistance to moisture is crucial, such as in the food and beverage industry, medical equipment, and outdoor structures.
- Q: Are stainless steel sheets resistant to saltwater corrosion?
- Yes, stainless steel sheets are highly resistant to saltwater corrosion due to their composition, which includes chromium that forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, preventing corrosion when exposed to saltwater.
- Q: Are stainless steel sheets resistant to hydrogen embrittlement?
- Stainless steel sheets are commonly resistant to hydrogen embrittlement. Hydrogen embrittlement refers to the brittleness and susceptibility to cracking caused by the diffusion of hydrogen atoms into the metal structure. Nonetheless, stainless steel has a strong resistance to hydrogen embrittlement due to its distinct composition and microstructure. The presence of chromium in stainless steel produces a protective oxide layer on the surface, acting as a barrier against hydrogen diffusion. Furthermore, stainless steel sheets are often alloyed with elements like nickel and molybdenum, further enhancing their resistance to hydrogen embrittlement. However, it is important to note that certain conditions, such as high temperatures or high levels of hydrogen exposure, can still potentially result in hydrogen embrittlement in stainless steel. Hence, it is crucial to consider the specific application and operating conditions when determining the suitability of stainless steel sheets in relation to hydrogen embrittlement.
- Q: How do you prevent intergranular corrosion in stainless steel sheets?
- To prevent intergranular corrosion in stainless steel sheets, several methods can be employed. First, the selection of the appropriate stainless steel grade is essential. Grades with a low carbon content, such as 304L or 316L, are less susceptible to intergranular corrosion compared to higher carbon grades. This is due to their ability to minimize the formation of chromium carbide precipitates, which are the main cause of intergranular corrosion. Another method is heat treatment. Processes like solution annealing and quenching can help eliminate or reduce the formation of chromium carbide precipitates. By dissolving existing precipitates and promoting the formation of a protective chromium oxide layer on the surface, the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel is restored. Careful attention must also be given to welding techniques when working with stainless steel sheets. Processes like gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) or laser welding, which provide precise control over heat input, are preferred. It is also advisable to use low carbon filler metals or consumables specifically designed for intergranular corrosion resistance to minimize the risk of corrosion. After welding, thorough cleaning of the welded area is crucial to remove any contaminants or oxide scales that could promote corrosion. Acid cleaning followed by passivation helps restore the protective oxide layer and enhances the stainless steel's resistance to intergranular corrosion. Lastly, it is important to avoid sensitization, which occurs when stainless steel is exposed to high temperatures for extended periods. Prolonged exposure to temperatures between 450-850°C (842-1562°F) during fabrication or service should be avoided to prevent sensitization and subsequent intergranular corrosion. By implementing these preventive measures, intergranular corrosion in stainless steel sheets can be effectively minimized, ensuring the longevity and performance of the material in various applications.
Send your message to us
310S Stainless Steel Sheet Price per ton
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords