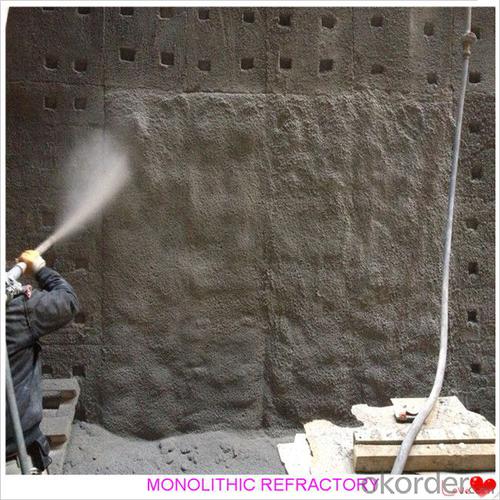
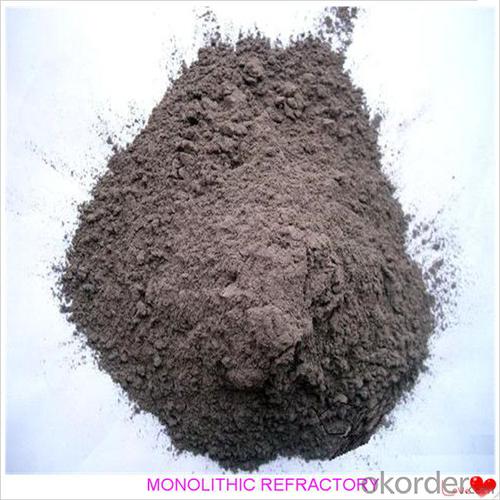
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Portland Cement Castable for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Portland Cement Castable for Fireplaces and Industrial Furnaces
Product Description:
Portland cement castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by clients. Castables use high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and are made with superfine powder adding technology.
Product Features:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, and also excellent working ability. If should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
Widely used in various kiln linings, such as boilers, blast furnace hot blast stoves, heating furnaces, ceramic kilns, heat treatment furnaces, incinerators, re-circulating fluidized bed furnaces and chemical industry and construction industry furnaces.
Product Specifications:

Product Images:




FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered by OKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories impact the quality of iron and steel products?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in influencing the quality of iron and steel products. These refractories are widely used in the lining of furnaces and other high-temperature environments where iron and steel are processed. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide insulation and protect the lining of the furnace from the extreme heat generated during the iron and steel manufacturing process. By maintaining the desired temperature, these refractories ensure the proper and consistent heating of the metal, which is essential for achieving the desired product quality. Without adequate insulation, the heat loss would be significant, leading to inefficient energy consumption and inconsistent product quality. Secondly, monolithic refractories have a significant impact on the overall cleanliness of the iron and steel. During the production process, impurities and slag are formed, which can contaminate the metal if not properly managed. Refractories with high resistance to slag penetration and corrosion prevent these impurities from infiltrating the metal, ensuring a cleaner and purer final product. Furthermore, monolithic refractories also contribute to the mechanical strength and durability of the furnace lining. The lining needs to withstand the harsh conditions and repeated thermal shocks encountered during the iron and steel production process. A strong and well-designed refractory lining can resist cracking, spalling, and erosion, extending the life of the furnace and minimizing the risk of downtime. In conclusion, monolithic refractories have a profound impact on the quality of iron and steel products. They provide thermal insulation, prevent contamination, and ensure the mechanical integrity of the furnace lining. By choosing the appropriate refractory material and maintaining it properly, manufacturers can optimize their production processes, increase product quality, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional brick refractories?
- There are several differences between monolithic refractories and traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are composed of a single, homogeneous material, whereas traditional brick refractories are made up of individual bricks that are pieced together. This variance in construction allows monolithic refractories to possess a more uniform and consistent structure, which can enhance their performance and durability. Secondly, installing monolithic refractories is typically easier compared to traditional brick refractories. Due to their composition, they can be poured or sprayed into place, eliminating the need for precise bricklaying and mortar application. This simplified installation process saves time and labor during construction or repair projects. Furthermore, monolithic refractories often exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock when compared to traditional brick refractories. The homogeneous structure of monolithic refractories enables them to expand and contract more uniformly under thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracking and failure. This characteristic makes monolithic refractories more suitable for applications with rapid temperature changes, such as in furnaces or kilns. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to chemical attacks and erosion. Traditional brick refractories may have joints and gaps between bricks, which can become vulnerable to chemical reactions or erosion over time. Conversely, monolithic refractories possess a seamless structure that minimizes the risk of chemical penetration and erosion, enhancing their longevity and performance. In conclusion, monolithic refractories provide advantages in terms of uniformity, ease of installation, thermal shock resistance, and chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. These disparities make monolithic refractories the preferred choice for numerous industrial applications that involve high temperatures and harsh environments.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in aluminum holding furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in aluminum holding furnace applications due to their high thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and superior mechanical strength. They can withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments found in these furnaces, ensuring long-lasting and efficient operations. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, making them a preferred choice in aluminum holding furnace applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production. These refractories are a type of heat-resistant material that is used to line the walls and floors of furnaces and other high-temperature equipment. One of the primary ways monolithic refractories help in reducing energy consumption is through their excellent thermal insulation properties. These materials have low thermal conductivity, which means they can effectively reduce heat loss from the furnace or equipment. By minimizing heat loss, monolithic refractories help maintain a high and consistent temperature inside the furnace, resulting in improved energy efficiency. This allows for better utilization of the heat generated, reducing the need for additional energy input and ultimately leading to energy savings. Moreover, monolithic refractories have high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. This means they can withstand the extreme temperatures and rapid temperature changes commonly encountered in iron and steel production processes. By having a durable and reliable lining, these refractories help prevent heat leakage and ensure that the heat is efficiently transferred to the desired areas, reducing energy wastage. Additionally, monolithic refractories also contribute to energy reduction through their ability to resist chemical attack and erosion. In iron and steel production, the lining of furnaces and equipment is exposed to various aggressive substances, such as molten metal, slag, and gases. Monolithic refractories have excellent resistance to these corrosive elements, extending their lifespan and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This not only saves energy that would be required for maintenance but also avoids production interruptions and associated energy losses. In summary, monolithic refractories assist in reducing energy consumption in iron and steel production by providing effective thermal insulation, withstanding extreme temperatures, and resisting chemical attack. By optimizing heat management and extending equipment durability, these refractories significantly contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings in the industry.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for blast furnace applications?
- To withstand the harsh conditions and high temperatures within a blast furnace, monolithic refractories used in these applications have specific requirements. These requirements encompass thermal stability, high strength, chemical resistance, erosion and abrasion resistance, low porosity, dense structure, and easy installation. Firstly, monolithic refractories must possess excellent thermal stability to endure the extreme temperatures encountered in blast furnaces. They should be able to resist thermal shock and maintain their physical and chemical properties even at high temperatures. Secondly, blast furnace conditions subject refractory linings to significant pressure and mechanical stress. As a result, monolithic refractories need to possess high strength and resistance to mechanical wear in order to withstand the weight of the burden and the movement of materials inside the furnace. Furthermore, blast furnace environments are highly corrosive due to the presence of molten metals, slag, and gases. Therefore, monolithic refractories should exhibit exceptional chemical resistance to prevent chemical reactions with these substances, which could lead to refractory degradation. Additionally, the materials being processed in a blast furnace can cause erosion and abrasion, resulting in wear of the refractory lining. Monolithic refractories used in blast furnaces should be able to withstand these erosive and abrasive forces, ensuring a longer service life. Moreover, blast furnace refractories should have low porosity to minimize the penetration of molten materials and gases. This is crucial as their penetration can cause refractory spalling and damage. Additionally, low porosity helps maintain the refractory lining's thermal stability and overall performance. Furthermore, the refractory lining in a blast furnace should have a dense structure to prevent the penetration of molten slag and metal, which could lead to refractory failure. A dense structure also aids in the refractory's heat insulation properties. Lastly, blast furnace refractories need to be easily installed and repaired due to frequent maintenance and repair requirements. Monolithic refractories offer the advantage of easy installation as they can be cast, gunned, or sprayed onto the refractory surface. This allows for quick repairs and reduced downtime. Overall, meeting these specific requirements ensures the durability and efficiency of the refractory lining, ultimately leading to improved blast furnace performance.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace applications due to their exceptional thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. These refractories are designed to withstand high temperatures, rapid temperature changes, and harsh operating conditions commonly found in reheating furnaces. One of the key advantages of monolithic refractories in reheating furnace applications is their ability to provide a seamless lining. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require extensive installation and joints, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This eliminates the risk of thermal stress and cracking at joints, ensuring a more reliable and durable lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties, which help to conserve energy and reduce heat loss in the reheating furnace. This not only improves the overall efficiency of the furnace but also reduces operational costs. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit high mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand the mechanical stress and abrasion caused by the movement of the furnace charge. They also have good resistance to chemical attack from gases, slags, and molten metals commonly encountered in reheating furnace operations. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be easily repaired or patched, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous furnace operation. Their ability to be easily shaped and molded to fit various furnace geometries also makes them highly versatile and adaptable to different reheating furnace designs. Overall, monolithic refractories offer exceptional performance in reheating furnace applications by providing superior thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Their seamless lining, thermal insulation properties, and resistance to mechanical and chemical stress make them an ideal choice for ensuring reliable and efficient furnace operation.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are extensively used in the iron and steel industry for various applications due to their superior performance and versatility. These refractories are composed of a single, uniform material and are designed to be used as a seamless lining in high-temperature environments. In the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in different stages of the manufacturing process. One of the primary applications is in the blast furnace, where monolithic refractories are used to line the inside of the furnace. This lining is subjected to extremely high temperatures and harsh chemical reactions. Monolithic refractories provide excellent thermal insulation and resistance to chemical attack, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the blast furnace. Another important application is in the steelmaking process. Monolithic refractories are used to line the ladles and tundish, which are used to transport and pour molten steel. These refractories are specially designed to withstand the high temperatures and corrosive nature of the molten steel, preventing contamination and ensuring the quality of the final product. Moreover, monolithic refractories are also used in various ancillary equipment and structures in the iron and steel industry. They are employed in furnaces, kilns, and other heat treatment systems to provide insulation and maintain high-temperature conditions. Additionally, monolithic refractories are used in the construction of chimneys, exhaust ducts, and other exhaust systems, where they provide thermal insulation and resistance to corrosive gases. Overall, monolithic refractories play a vital role in the iron and steel industry by providing high-temperature insulation, chemical resistance, and durability. They help optimize the production process, improve energy efficiency, and ensure the quality of the final product. With their versatility and excellent performance, monolithic refractories have become an indispensable component in the iron and steel manufacturing industry.
- Q: What are the recommended curing times for monolithic refractories?
- The curing times for monolithic refractories can differ depending on the type of refractory and its specific application. Following the manufacturer's guidelines for curing times is crucial to ensure proper setting and development of the refractory material. For traditional castable refractories, the typical curing time ranges from 24 to 48 hours. During this period, it is important to control temperature and humidity conditions to allow for hydration and hardening of the castable. This curing time is essential to achieve the desired strength and durability of the refractory lining. In contrast, low cement or ultra-low cement castables may need a longer curing time due to their reduced water content. These refractories often require a curing period of 48 to 72 hours to allow for adequate bonding and solidification. For gunning mixes or shotcrete applications, the curing time may be shorter, usually around 8 to 12 hours. This faster curing process is facilitated by adding accelerators to the mix, which promote rapid setting and hardening. It is important to remember that these recommended curing times are general guidelines, and specific recommendations may vary depending on factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and the specific refractory material used. Therefore, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer's instructions or seek guidance from a refractory specialist to ensure optimal curing and performance of the monolithic refractory.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying systems?
- The efficiency of ladle and tundish drying systems can be greatly improved by incorporating monolithic refractories. These refractories play a vital role in the steel industry, specifically in the drying process of ladles and tundishes prior to casting molten steel. One key advantage of monolithic refractories lies in their ability to create a seamless lining devoid of joints or gaps. This characteristic ensures that the lining remains strong and resistant to heat loss during the drying process. By maintaining a uniform and continuous lining, monolithic refractories facilitate faster and more effective drying of ladles and tundishes. Moreover, monolithic refractories possess exceptional thermal insulation properties. They exhibit low thermal conductivity, which enables them to effectively retain heat and prevent its dissipation into the surroundings. This insulation capability promotes better heat retention within ladles and tundishes during drying, ultimately leading to quicker and more energy-efficient drying. Furthermore, monolithic refractories demonstrate superior resistance to thermal shock. The drying process subjects ladles and tundishes to rapid temperature changes, which can induce thermal stress and result in cracks or spalling of the lining. However, monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to thermal shock, ensuring the durability and longevity of the lining. This resistance to thermal shock minimizes the need for frequent repairs or replacements, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of ladle and tundish drying systems. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit good corrosion resistance. They are specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions and corrosive environments that ladles and tundishes encounter during the drying process. This corrosion resistance helps maintain the integrity of the lining, preventing any degradation or damage that could potentially impact the efficiency of the drying systems. In conclusion, the incorporation of monolithic refractories into ladle and tundish drying systems enhances their efficiency by providing a seamless lining, excellent thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock, and corrosion resistance. These properties contribute to faster drying times, energy savings, reduced maintenance needs, and increased equipment longevity.
- Q: What are the recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories are crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here are some key practices to follow: 1. Storage: Monolithic refractories should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. The storage facility should be protected from moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct exposure to sunlight. Ideally, the refractories should be stored on pallets or racks to prevent contact with the ground and minimize the risk of damage. 2. Handling: It is essential to handle monolithic refractories with care to avoid any physical damage. Refractories should be lifted and moved using appropriate lifting equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to prevent excessive stress or strain on the material. Avoid dropping or dragging the refractories, as this can lead to cracks or fractures. 3. Packaging: If the monolithic refractories are supplied in packaging, it is important to inspect the packaging for any signs of damage or moisture before accepting the delivery. Damaged packaging can indicate potential damage to the refractory material. If any anomalies are noticed, it is advisable to inform the supplier immediately. 4. Moisture control: Monolithic refractories are susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to reduced performance and structural integrity. It is crucial to protect the refractories from direct contact with water or excessive humidity during storage and handling. If refractories become wet, they should be dried thoroughly before use to eliminate any absorbed moisture. 5. Stack height: When storing monolithic refractories, it is important to consider the stack height. Excessive stacking can result in pressure on the lower layers, leading to deformation or cracking. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maximum stack height to ensure the refractories' structural integrity. 6. Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the refractory material for any signs of damage or degradation during storage and handling. Look for cracks, spalling, or any other visible abnormalities. If any issues are identified, consult the manufacturer or a refractory expert for guidance on whether the material is still suitable for use. By following these recommended storage and handling practices, you can minimize the risk of damage to monolithic refractories and optimize their performance, ultimately extending their service life and ensuring their effectiveness in high-temperature applications.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Portland Cement Castable for Fireplace and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords