Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Dense Castable for Fireside and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Dense Castable for Fireplaces and Industrial Iron and Steel Furnaces
Product Description:
Dense castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by clients. Castables use high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and are made with superfine powder adding technology.
Product Features:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, and also excellent working ability. If should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
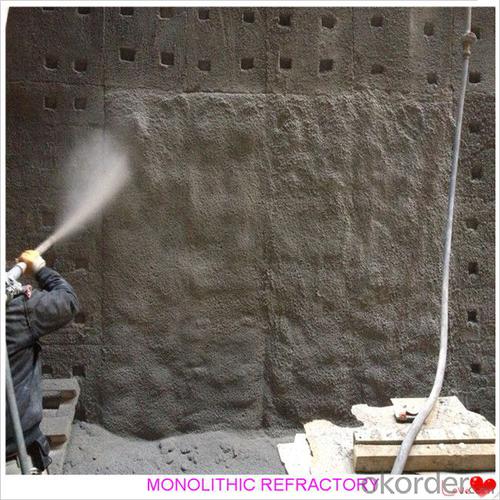
Widely used in various kiln linings, such as boilers, blast furnace hot blast stoves, heating furnaces, ceramic kilns, heat treatment furnaces, incinerators, re-circulating fluidized bed furnaces and chemical industry and construction industry furnaces.
Product Specifications:

Product Images:




FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered by OKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection?
- Monolithic refractories effectively prevent heat loss through convection due to their unique composition and structure. Unlike traditional refractory bricks, which often have gaps and are porous, monolithic refractories are made of a single, seamless structure. This eliminates any possible pathways for hot gases or air to circulate and carry away heat by convection. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have a high thermal conductivity and are often dense, making them excellent conductors of heat. This allows them to rapidly absorb and distribute heat, minimizing the temperature difference between the hot surface and the surrounding environment. By reducing the temperature gradient, monolithic refractories decrease the driving force for convection, resulting in reduced heat loss through this mechanism. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be applied as a continuous lining, conforming to the shape of the equipment or furnace being protected. This seamless application eliminates joints or gaps where hot gases or air could escape and carry away heat. The uniform and uninterrupted lining further decreases the potential for convection heat loss. In summary, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to create a barrier that hinders the movement of hot gases or air, effectively minimizing heat loss through convection. Their dense composition, high thermal conductivity, and seamless application all contribute to their effectiveness in preventing heat loss through this mechanism.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration?
- Monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through several mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made up of high-quality materials that have excellent resistance to slag attack. These materials, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, have a high melting point and can withstand the corrosive nature of the slag. Secondly, monolithic refractories are designed with a dense and compact structure that minimizes the porosity. Slag penetration occurs when the molten slag infiltrates the pores and cracks of the refractory material. By reducing the porosity, monolithic refractories create a barrier that restricts the entry of slag into the refractory lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be chemically bonded to the substrate, forming a strong and impermeable bond. This bond further enhances the resistance to slag penetration by preventing any gaps or weak points where the slag can penetrate. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be designed with a high thermal shock resistance. Slag penetration is often intensified by thermal cycling, where the refractory material undergoes rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories with high thermal shock resistance can withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling, thus reducing the risk of slag penetration. Furthermore, the proper installation and maintenance of monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring their effectiveness against slag penetration. The refractory lining needs to be properly designed, using appropriate thickness and geometry, to provide maximum protection against slag attack. Regular inspection and repair of any damaged or worn-out areas can also prevent slag penetration. In conclusion, monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration through their excellent resistance to slag attack, dense structure, chemical bonding, high thermal shock resistance, and proper installation and maintenance. These factors work together to create a strong and impermeable barrier that protects the underlying substrate from the corrosive effects of slag.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories handle thermal expansion and contraction?
- Thermal expansion and contraction pose challenges that monolithic refractories are specifically designed to tackle. Unlike traditional brick or tile refractories, these materials are composed of a single solid structure. This unique composition allows them to better accommodate the thermal stresses associated with temperature changes. One method employed by monolithic refractories to manage thermal expansion and contraction is their ability to endure high temperatures. These materials are engineered to have a high melting point, enabling them to preserve their structural integrity even in extreme heat conditions. This characteristic prevents them from cracking or disintegrating due to thermal expansion. Additionally, monolithic refractories often contain a binder or bonding agent that holds the refractory particles together. This binder can be formulated to possess a certain level of flexibility, enabling the material to expand and contract without incurring cracks or breaks. This flexibility aids in absorbing the stresses caused by thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring the long-lasting performance of the refractory. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be applied in a manner that allows for expansion and contraction. Installers can leave joints or gaps between sections, which accommodate the movement caused by temperature changes. This technique, referred to as joint design or expansion joint systems, permits the refractory to expand and contract without causing any harm to the overall structure. Overall, monolithic refractories are designed to handle thermal expansion and contraction by withstanding high temperatures, incorporating flexible binders, and employing joint design techniques. These properties enable them to maintain their structural integrity and performance in extreme heat conditions, making them a reliable choice for applications that necessitate resistance to thermal stress.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in blast furnace taphole applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in blast furnace taphole applications due to their unique characteristics and properties. Firstly, monolithic refractories are known for their superior thermal resistance. Blast furnace tapholes are exposed to extremely high temperatures and thermal shocks, making it essential to have a refractory material that can withstand these conditions. Monolithic refractories have high refractoriness, meaning they can maintain their structural integrity even at elevated temperatures, ensuring the taphole remains functional. Secondly, monolithic refractories have excellent erosion and corrosion resistance. In blast furnace taphole applications, the refractory material is constantly exposed to molten metal, slag, and gases that can cause erosion and chemical reactions. Monolithic refractories are designed to resist these aggressive environments, minimizing wear and extending the service life of the taphole. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer good thermal conductivity and insulation properties. This is crucial for blast furnace tapholes as they need to maintain a consistent and controlled flow of molten metal. The refractory material must be able to transfer heat efficiently while also providing insulation to prevent excessive heat loss, ensuring optimal performance and productivity of the blast furnace. Additionally, monolithic refractories are easy to install and repair. Blast furnace tapholes require regular maintenance due to the harsh conditions they are subjected to. Monolithic refractories can be easily shaped and applied, allowing for quick repairs or replacement of damaged areas. This reduces downtime and increases the operational efficiency of the blast furnace. In summary, monolithic refractories are highly suitable for blast furnace taphole applications due to their excellent thermal resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity and insulation properties, as well as ease of installation and repair. These characteristics make them a reliable and effective choice for maintaining the functionality and performance of blast furnace tapholes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the thermal cycling in coke oven applications?
- Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions of thermal cycling in coke oven applications. Thermal cycling refers to the repetitive heating and cooling cycles that occur in these high-temperature environments. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand thermal cycling is their composition. They are typically made from a combination of different refractory materials, such as high-alumina, silica, and magnesia, which provide excellent thermal shock resistance. These materials have low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion properties, allowing them to expand and contract without cracking or spalling under extreme temperature changes. Moreover, monolithic refractories have excellent bonding and adhesion properties, allowing them to form a strong and cohesive structure. This ensures that they can withstand the mechanical stresses caused by the thermal cycling process. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be installed in place through various techniques, such as gunning, casting, or ramming, which further enhances their resistance to thermal cycling. Furthermore, the presence of specialized additives and bonding agents in monolithic refractories improves their resistance to thermal cycling. These additives can enhance the refractory's ability to absorb thermal shock and minimize cracking, thus increasing its durability and longevity in coke oven applications. Overall, monolithic refractories' ability to withstand thermal cycling in coke oven applications can be attributed to their carefully formulated composition, strong bonding properties, and the incorporation of specialized additives. These characteristics make them highly reliable and suitable for the extreme temperature fluctuations experienced in coke oven operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of iron and steel production processes. These refractories are known for their superior thermal properties, high resistance to mechanical stress, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion. One key way that monolithic refractories contribute to the efficiency of iron and steel production is by providing effective insulation. By lining the walls of furnaces and other high-temperature equipment, monolithic refractories prevent heat loss and ensure that the desired temperatures are maintained consistently. This insulation helps to reduce energy consumption, as less heat is wasted, ultimately leading to cost savings. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal shock resistance. In the iron and steel industry, frequent heating and cooling cycles are common, and traditional refractory materials may crack or fail under these conditions. However, monolithic refractories can withstand rapid temperature changes without failure, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the refractory lining. This resistance to thermal shock reduces downtime for repairs and maintenance, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the production process. Moreover, monolithic refractories have strong resistance to chemical corrosion. In iron and steel production, various corrosive substances are present, including molten metal, slag, and gases. The use of monolithic refractories as lining materials helps to protect the underlying structures from chemical attack, preventing erosion and extending the service life of the equipment. This resistance to corrosion reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements, leading to cost savings and increased productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair. Unlike traditional refractories, which are often built brick by brick, monolithic refractories are applied as a single mass. This allows for faster installation and reduces the potential for weak points or joints that might compromise the overall efficiency of the refractory lining. Additionally, when repairs or maintenance are required, monolithic refractories can be easily patched or replaced, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operation. In summary, the use of monolithic refractories in iron and steel production contributes to increased efficiency in several ways. Their excellent thermal insulation properties reduce energy consumption, while their resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion ensures reliable and long-lasting refractory linings. Additionally, their easy installation and repair capabilities further enhance productivity. Overall, monolithic refractories are a vital component in improving the efficiency and sustainability of iron and steel production processes.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of heat-resistant materials used to line high-temperature industrial equipment such as furnaces, kilns, and reactors. Unlike traditional refractories, which are made of pre-formed bricks or shapes, monolithic refractories are a single, solid piece that can be easily shaped and installed. They are composed of various aggregates, binders, and additives, providing excellent thermal insulation and resistance to extreme temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stress. Monolithic refractories offer flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and improved installation efficiency compared to traditional brick refractories.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock?
- Monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock due to their unique composition and structure. They are made from a single, continuous material with no joints or seams, which allows them to expand and contract uniformly under extreme temperature changes. Additionally, monolithic refractories possess excellent thermal conductivity, which enables them to quickly dissipate heat and minimize stress build-up. These properties make them highly resistant to thermal shock and capable of withstanding rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or breaking.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance of ladles and tundishes?
- The performance of ladles and tundishes is significantly improved by monolithic refractories in various ways. Firstly, these vessels are thermally insulated by monolithic refractories, which act as a barrier against heat loss and help maintain the desired temperature. This insulation reduces energy consumption and minimizes heat loss. Secondly, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and erosion. When ladles and tundishes come into contact with molten metal and fluxes, they can be severely corroded and eroded. However, the use of monolithic refractories protects against chemical attacks and extends the lifespan of these vessels. This saves costs associated with frequent repairs or replacements and ensures their integrity and safety. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide superior mechanical strength and structural stability. Ladles and tundishes must withstand the weight of molten metal and the stresses caused during pouring and handling. With high mechanical strength, monolithic refractories can withstand these loads, maintaining their shape and integrity. This reduces downtime and increases productivity in the steelmaking process. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in design and installation. They can be shaped and applied in various configurations, allowing customization to meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes. This flexibility ensures a better fit and improves the overall efficiency of the refractories, ultimately enhancing the performance of the vessels. In conclusion, monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladles and tundishes by providing improved thermal insulation, resistance to chemical corrosion and erosion, increased mechanical strength, and flexibility in design and installation. These benefits contribute to the longevity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of ladles and tundishes in steelmaking operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying furnaces in several ways. Firstly, monolithic refractories offer a high degree of thermal insulation. These refractories have low thermal conductivity, which means they can effectively reduce heat transfer from the furnace to the surrounding environment. This insulation property helps to minimize heat losses, allowing the furnace to maintain a higher temperature for a longer period of time. As a result, the drying process becomes more efficient as the heat is retained within the furnace, reducing the overall energy consumption. Secondly, monolithic refractories have excellent resistance to thermal shock. During the heating and cooling cycles of the furnace, rapid temperature changes can cause stress and cracks in the refractory material. However, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand these thermal shocks and maintain their structural integrity. This durability ensures a longer lifespan of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, the furnace operates at optimal efficiency without the downtime associated with maintenance. Additionally, monolithic refractories provide good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. These properties are crucial in ladle and tundish drying furnaces, as they are exposed to mechanical stresses and abrasive materials such as molten metal and slag. The use of monolithic refractories ensures that the lining can withstand these harsh conditions without undergoing structural damage. This resistance to wear and tear increases the overall efficiency of the furnace, as it can operate for longer periods without interruptions. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer greater design flexibility compared to traditional brick or tile refractories. Their ability to be cast or gunned onto the lining surface allows for easy installation and repair. This flexibility enables the furnace to be customized and adapted to specific requirements, ensuring optimal heat distribution and efficient drying processes. In conclusion, monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish drying furnaces through their thermal insulation, resistance to thermal shock, mechanical strength, and design flexibility. By reducing heat losses, increasing durability, withstanding harsh conditions, and allowing for easy installation and repair, these refractories optimize the performance and energy efficiency of the furnaces.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Dense Castable for Fireside and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords