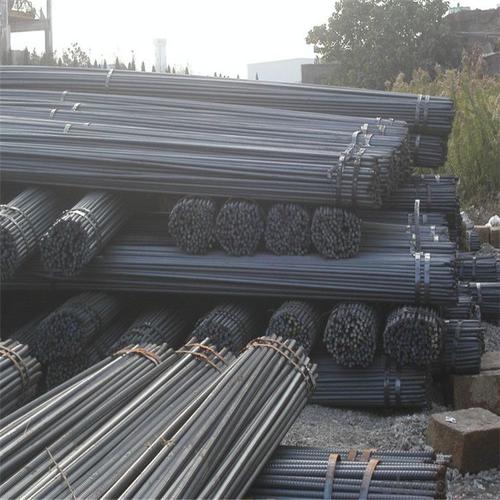
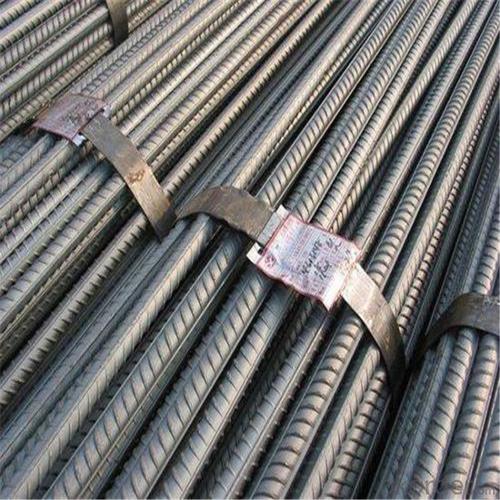
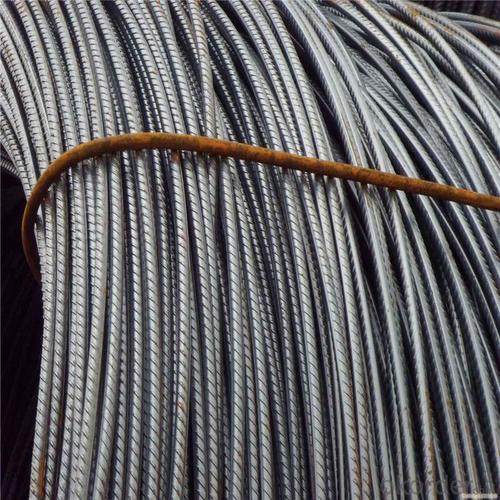
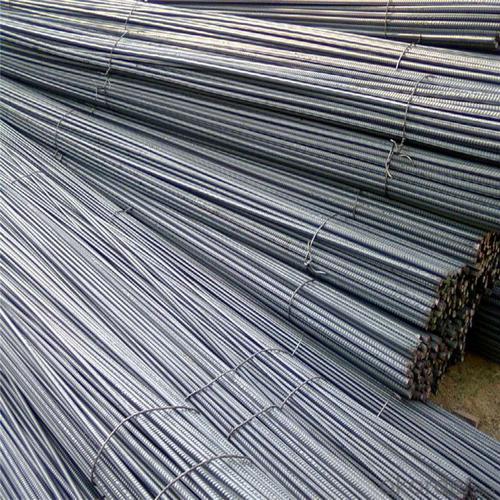
HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
Description of HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
10m- 40mm HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
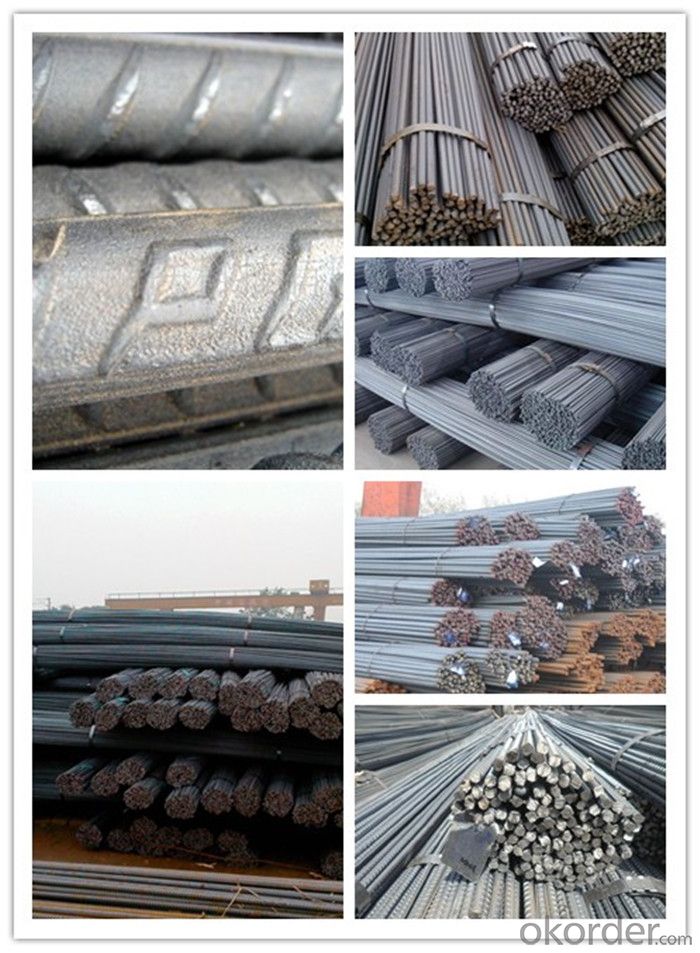
Products Show of HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
Company Information
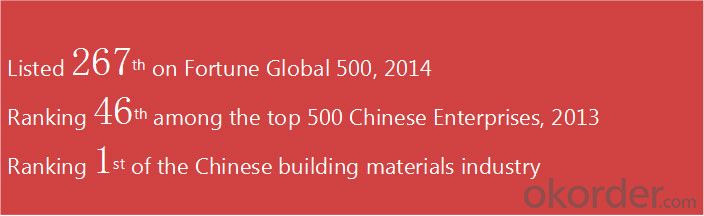
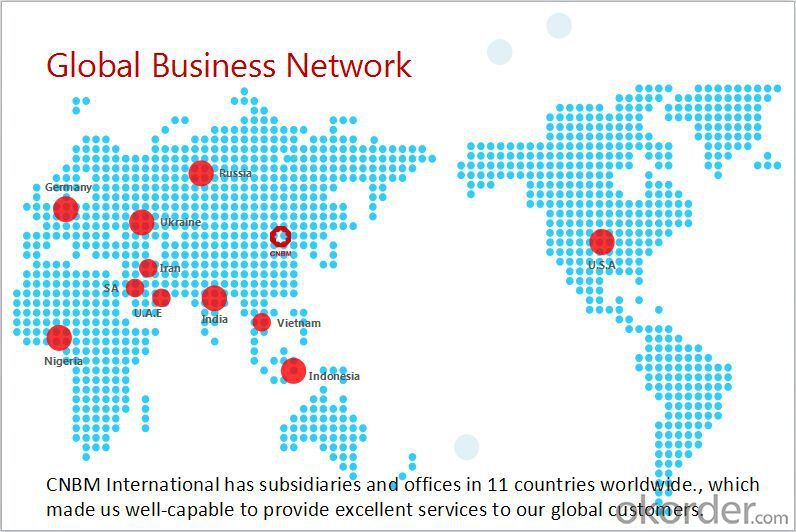
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: How is special steel used in the mining industry?
- Special steel is widely used in the mining industry due to its exceptional properties such as high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. It is utilized in various applications including the manufacturing of drilling tools, crushing equipment, conveyor systems, and structural components for mining machinery. Additionally, special steel is used in the production of wear-resistant plates and liners, which protect mining equipment from abrasion and extend their lifespan. This type of steel plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and safety of mining operations.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the overall economy?
- Special steel contributes to the overall economy in several ways. Firstly, it plays a crucial role in various industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing, where it is used for producing high-performance components and structures. This fosters innovation, enhances productivity, and drives economic growth. Additionally, the production and processing of special steel create employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, stimulating job growth and income generation. Moreover, special steel exports contribute to trade balance and foreign exchange earnings, further bolstering the economy. Overall, the utilization of special steel in diverse sectors strengthens industrial competitiveness, supports economic development, and fuels economic prosperity.
- Q: What are the different quality control measures for special steel production?
- There are several quality control measures for special steel production, including thorough material inspections, precise chemical composition analysis, stringent dimensional and shape control, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle inspections, and rigorous mechanical property evaluations. Additionally, heat treatment processes and surface treatments are closely monitored to ensure the desired properties and surface finish of the special steel. Continuous monitoring and quality checks are essential throughout the production process to maintain the highest standards and meet customer requirements.
- Q: How does special steel perform in molding applications?
- Due to its exceptional properties and performance, special steel is highly favored in molding applications. Firstly, its excellent hardness and wear resistance ensure that it remains undamaged and maintains its shape even under high pressure and temperature during the molding process. Additionally, special steel's superb thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer, resulting in uniform heating and cooling of the mold. This leads to consistent and high-quality molded products and reduces cycle times, thus enhancing productivity. Furthermore, special steel's superior corrosion resistance prevents any chemical reactions or rusting, ensuring its durability and longevity even when exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. When it comes to machinability, special steel is easily workable, enabling precise and intricate mold designs. This facilitates the production of detailed molded products with high accuracy and dimensional stability. Lastly, special steel's excellent strength and toughness make it highly resistant to cracking or fracturing under high stress conditions. Consequently, this guarantees the longevity and reliability of the mold, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Overall, the exceptional properties of special steel, including hardness, wear resistance, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, machinability, and strength, make it an ideal choice for molding applications. It ensures high-quality and consistent molded products, increased productivity, and extended lifespan for the molds.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the medical device manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the medical device manufacturing industry. Special steel alloys, such as stainless steel or titanium, are commonly used in medical device manufacturing due to their excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and strength characteristics. These alloys are specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements and regulations of the medical industry, making them ideal for producing safe and durable medical devices.
- Q: What are the different surface finishing techniques for special steel parts?
- Special steel parts can undergo various surface finishing techniques to enhance their appearance, protect against corrosion, and improve overall performance. Some commonly utilized methods include: 1. Achieving a smooth and glossy surface on the steel part through polishing, using abrasives. This technique not only enhances aesthetics but also enhances resistance against corrosion. 2. Plating involves depositing a layer of metal onto the steel part's surface, with options such as chrome, nickel, and zinc. This technique provides additional protection against corrosion, improves wear resistance, and can offer desired color or finish. 3. Powder coating entails electrostatically applying a dry powder to the steel part's surface, followed by heat curing. The melted powder forms a durable and visually appealing coating that provides excellent resistance against corrosion, impact, and chemicals. 4. Anodizing, primarily used for aluminum but applicable to certain special steel parts, creates a controlled oxide layer on the surface. This enhances corrosion resistance, improves appearance, and can even provide insulation. 5. Employing a chemical process known as passivation removes free iron and contaminants from the steel part's surface. This process helps prevent corrosion and enhances resistance against staining or discoloration. 6. Heat treatment involves altering the physical and mechanical properties of the steel part by subjecting it to heating and cooling. This process improves hardness, strength, toughness, and provides desired surface finishes. 7. Through electropolishing, an electrochemical process, a thin layer of metal is removed from the steel part's surface. This technique eliminates surface imperfections, smoothens the part, and enhances corrosion resistance. Choosing the appropriate surface finishing technique is crucial, taking into consideration the specific requirements of the special steel part, including its function, desired appearance, and the environmental conditions it will encounter.
- Q: How is martensitic steel used in knife making?
- Martensitic steel is commonly used in knife making due to its excellent hardness, strength, and ability to hold a sharp edge. This type of steel undergoes a heat treatment process called quenching, which transforms its structure to be very hard and brittle. Knives made from martensitic steel are highly durable and resistant to wear and corrosion, making them ideal for various cutting tasks.
- Q: What are the different annealing techniques used for special steel?
- There are several annealing techniques used for special steel, including full annealing, spheroidizing annealing, and stress relieving annealing. Full annealing involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then slowly cooling it, which helps to refine the grain structure and reduce internal stresses. Spheroidizing annealing is used to soften the steel and improve machinability by forming spherical carbides within the microstructure. Stress relieving annealing is performed to reduce residual stresses in the steel, typically after significant machining or welding operations. These different techniques allow for the customization of special steel properties to meet specific application requirements.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to reducing production costs?
- Special steel contributes to reducing production costs in several ways. Firstly, special steel has higher strength and durability compared to regular steel, which means that it can be used to make lighter and more efficient components. This leads to reduced material usage and lower costs. Additionally, special steel has superior corrosion resistance, which prolongs the lifespan of machinery and equipment, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Moreover, special steel can be customized to specific requirements, allowing for more precise manufacturing processes, minimizing waste, and optimizing production efficiency. Overall, special steel helps in minimizing material costs, maintenance expenses, and maximizing productivity, leading to significant reductions in production costs.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in marine applications?
- Special steel used in marine applications must meet certain requirements to ensure its durability and performance in the harsh marine environment. These requirements typically include high corrosion resistance to withstand exposure to saltwater, excellent strength and toughness to withstand extreme forces and impacts, good weldability for ease of fabrication and maintenance, and low magnetic permeability to avoid interference with electronic equipment. Additionally, the steel must be able to withstand fluctuating temperatures and be resistant to fatigue and stress corrosion cracking to ensure long-term reliability in marine applications.
Send your message to us
HRB400 High Tensile Rebars for Building Material
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































