Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
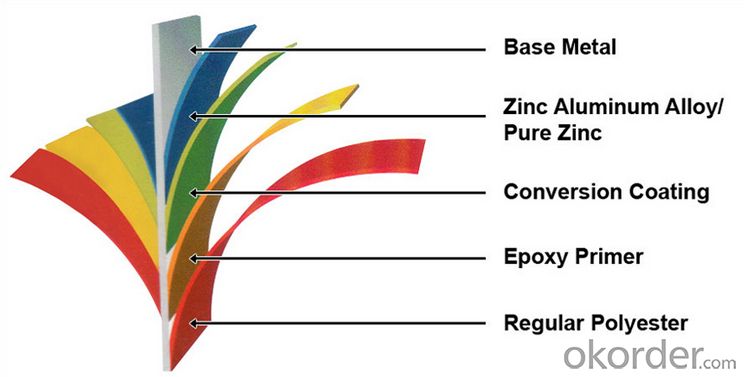
Description of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
1) Automotive bodies: filters, fuel tanks, etc.
2) Construction materials: roofings, welding pipes,
3) Electric and electronic appliances: computer cans, etc.
4) Steel cans: containers, etc.
5) Steel furniture: washing machines, refrigerators, microwaves, etc.
6) Drums
7) Office equipment: printer, recorders, etc.
8) Motors and transformers

Specifications of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: What are the main types of defects found in steel billets?
- The main types of defects found in steel billets include surface defects such as cracks, pits, and scars, internal defects like inclusions, blowholes, and voids, as well as dimensional defects such as improper shape, size, or straightness.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the manufacturing of machinery?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the manufacturing of machinery. Steel billets are semi-finished metal products that are typically hot rolled or forged into various shapes, including bars, rods, or sheets. These billets serve as the raw material for manufacturing machinery components such as gears, shafts, bearings, and structural frames. The use of steel billets in machinery manufacturing offers several advantages. Steel is known for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making it a suitable material choice for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, steel can be easily machined, welded, and formed into complex shapes, allowing for the production of intricate machinery parts. Moreover, steel's high melting point and thermal conductivity make it ideal for applications that involve high temperatures or require heat transfer. Overall, steel billets are widely used in machinery manufacturing due to their excellent mechanical properties, versatility, and reliability.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of construction machinery parts?
- Steel billets are crucial in the production of construction machinery parts. These semi-finished steel products serve as the raw material for shaping various machinery components. To initiate the manufacturing process, steel billets are heated to a high temperature in a furnace. This heating process enhances their malleability and facilitates further shaping. Once heated, the billets are passed through rollers and molds to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. Construction machinery parts such as gears, shafts, axles, and structural components require high strength and durability to withstand heavy-duty applications. Steel billets, made from high-quality steel alloys, possess these desirable properties, making them ideal for manufacturing such parts. After shaping, the billets undergo additional processes such as heat treatment and surface finishing. These treatments enhance their strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Consequently, the overall performance and longevity of the construction machinery parts are improved. The use of steel billets in the manufacturing of construction machinery parts offers several advantages. Firstly, steel is renowned for its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and toughness, which are vital for handling heavy loads and resisting impact and fatigue. Moreover, steel billets can be easily machined and welded, facilitating the precise manufacturing and assembly of complex machinery components. Additionally, steel is a versatile material that can be customized to meet specific requirements. By adjusting the composition and heat treatment processes, manufacturers can tailor the properties of the steel billets to suit the intended application of the construction machinery parts, ensuring optimum performance and durability. In conclusion, steel billets are indispensable in the production of construction machinery parts. Their high strength, durability, and versatility make them essential for manufacturing components that can withstand the demanding conditions of construction sites. By utilizing steel billets, manufacturers can create reliable and long-lasting machinery parts that contribute to the overall efficiency and safety of construction projects.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of electrical components?
- Indeed, the utilization of steel billets in the manufacturing of electrical components is possible. Steel billets, which are considered as intermediate products, are commonly employed in the creation of diverse steel goods, including electrical components. Steel, known for its adaptability, exhibits exceptional strength, durability, and electrical conductivity, rendering it appropriate for electrical applications. Steel billets can undergo further processing and shaping, such as being transformed into bars, rods, or sheets. Subsequently, these forms can be utilized in the production of electrical components like connectors, terminals, wires, and cables. Moreover, steel can undergo coating or plating with other materials to heighten its conductivity or provide resistance against corrosion, thereby further increasing its suitability for the manufacturing of electrical components.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of shipbuilding components?
- Steel billets serve as the primary raw material in shipbuilding, as they are essential for the production of shipbuilding components. These components require a high level of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, all of which can be achieved through the use of steel billets. To produce various shapes and sizes of steel plates, beams, and bars, steel billets are first heated and then passed through a series of rolling processes. These components play a crucial role in the construction of the ship's hull, superstructure, and other structural components. For instance, steel plates are utilized to form the ship's outer shell, while beams and bars provide support and stability. In addition, steel billets can be forged or machined to create specialized shipbuilding components like propeller shafts, rudder stocks, and engine mounts. These components are vital for the ship's propulsion system, steering mechanism, and overall functionality. Moreover, steel billets can be used to manufacture pipes and tubes, which are crucial for the ship's plumbing, ventilation, and fuel systems. The use of steel billets in shipbuilding ensures that the vessels are built to withstand the harsh marine environment, including extreme weather conditions and corrosive seawater. Steel's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an ideal choice for constructing large and sturdy ships. Additionally, steel's weldability allows for efficient assembly and fabrication processes during ship construction. In summary, steel billets are a fundamental component in shipbuilding, providing the necessary strength, durability, and corrosion resistance required for the construction of various ship components. From the hull and superstructure to specialized parts, steel billets are indispensable in the production of shipbuilding components.
- Q: How are steel billets formed into other shapes?
- Steel billets are formed into other shapes through a process called hot rolling or cold rolling. Hot rolling involves heating the steel billet to a high temperature and then passing it through a series of rollers to apply pressure and shape it into the desired form. This process is typically used for larger and more complex shapes such as beams, channels, and angles. On the other hand, cold rolling is performed at room temperature, and it involves passing the steel billet through a series of rollers to gradually reduce its thickness and shape it into sheets, strips, or coils. Cold rolling is commonly used for producing thinner and more precise shapes like plates, foils, and bars. In addition to rolling, steel billets can also be formed into other shapes through processes such as forging, extrusion, and casting. Forging involves applying pressure to the heated billet using a die or hammer to shape it into the desired form. Extrusion involves pushing the heated billet through a die to produce long and continuous shapes like pipes or tubes. Casting involves pouring molten steel into a mold and allowing it to solidify into the desired shape. Overall, the formation of steel billets into other shapes requires various manufacturing processes such as hot rolling, cold rolling, forging, extrusion, or casting, depending on the desired shape and properties of the final product. These processes ensure that steel billets can be transformed into a wide range of shapes for different applications in industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Q: What are the different types of surface defect detection methods for steel billets?
- There are several types of surface defect detection methods for steel billets, including visual inspection, magnetic particle inspection, ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and dye penetrant testing. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and is used depending on the specific requirements and characteristics of the billets being inspected.
- Q: I want to buy a fishing pole, I don't know how to distinguish it. Know what, please reply, thank you, [em10]!
- The tonality of a fishing rod is actually modulated by a different modulus of carbon cloth.Some fishing overall with the 30T following carbon cloth, just use a very small amount of 40T or 46T carbon cloth, called high carbon rod, is actually confuse the public practice of fishing by weighing, hand identification, high carbon rod with real light, hard, two rods in a play, a ratio is obvious.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of construction machinery?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of construction machinery. These cylindrical or square bars of steel are the primary raw material used in the production of various components and parts for construction machinery. Firstly, steel billets are used to create the structural frame of construction machinery. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal material for ensuring the structural integrity of heavy machinery. Steel billets are shaped and welded together to form the sturdy frame, providing the necessary support and stability to the equipment. Additionally, steel billets are used to manufacture critical components such as gears, shafts, and axles. These components require high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear, which can be achieved using steel billets. By machining, forging, or casting steel billets into the desired shape, these components can withstand the heavy loads and harsh operating conditions in the construction industry. Moreover, steel billets are used to produce buckets, blades, and cutting edges for construction machinery. These components are subjected to extreme forces and abrasion during excavation, grading, and other construction activities. Steel billets, with their excellent hardness and toughness, ensure that these components can withstand the demanding conditions and perform effectively. Furthermore, steel billets are essential in the production of hydraulic cylinders and pistons. These components are responsible for generating the force required for lifting, pushing, and pulling heavy loads in construction machinery. Steel billets are machined and shaped to create the cylinder bodies and pistons, ensuring the necessary strength and precision for efficient hydraulic operations. In summary, steel billets are indispensable in the manufacturing of construction machinery. They provide the strength, durability, and wear resistance required for the various components and parts of construction equipment. Steel billets contribute to the overall performance and reliability of construction machinery, ensuring that they can withstand the demanding conditions and heavy workloads encountered in the construction industry.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the manufacturing of storage systems?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of storage systems due to their unique properties and versatility. These billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that are used as raw materials in various manufacturing processes. The primary role of steel billets in the manufacturing of storage systems is to serve as the base material for fabricating different components, such as shelves, frames, supports, and racks. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for these applications, as it can withstand heavy loads and provide long-lasting performance. Steel billets are typically melted and cast into specific shapes, such as square or round, to suit the requirements of the storage system design. These billets undergo further processing, such as hot rolling, to transform them into the desired dimensions and form. This process helps to refine the steel's microstructure, enhancing its mechanical properties and ensuring consistent quality. The versatility of steel billets allows manufacturers to customize storage systems according to specific needs. By shaping and welding steel billets, manufacturers can create storage systems with different configurations, sizes, and load capacities. This flexibility enables the production of storage systems that are tailored to meet various industrial and commercial applications, ranging from warehouses to retail stores. Moreover, steel billets offer excellent resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for storage systems used in both indoor and outdoor environments. This resistance ensures that the storage systems maintain their structural integrity and aesthetics over time, even in harsh conditions. In summary, steel billets play a vital role in the manufacturing of storage systems by serving as the raw material for various components. Their strength, durability, versatility, and corrosion resistance make them an ideal choice for fabricating storage systems that can withstand heavy loads, provide long-lasting performance, and meet specific design requirements.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Square Steel Billet 3SP 80mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































