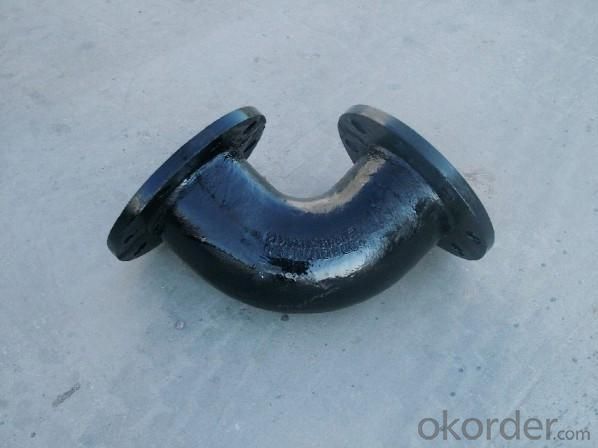
Duct Iron Pipe DI Pipe ISO 2531 Double Socked 90° Bend T Type
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Ductile iron pipe fittings:
Dimensions standard:
ISO2531: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
BS4772: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
EN545: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
Connecting mode:
Flanged
Socketed
Mechanical connection
Loose flanged
Coatings:
Inner lined with cement and outside coated with zinc plus bitumen
Inner and outside coated with epoxy resin
Inner and outside coated with fusion bonded epoxy resin
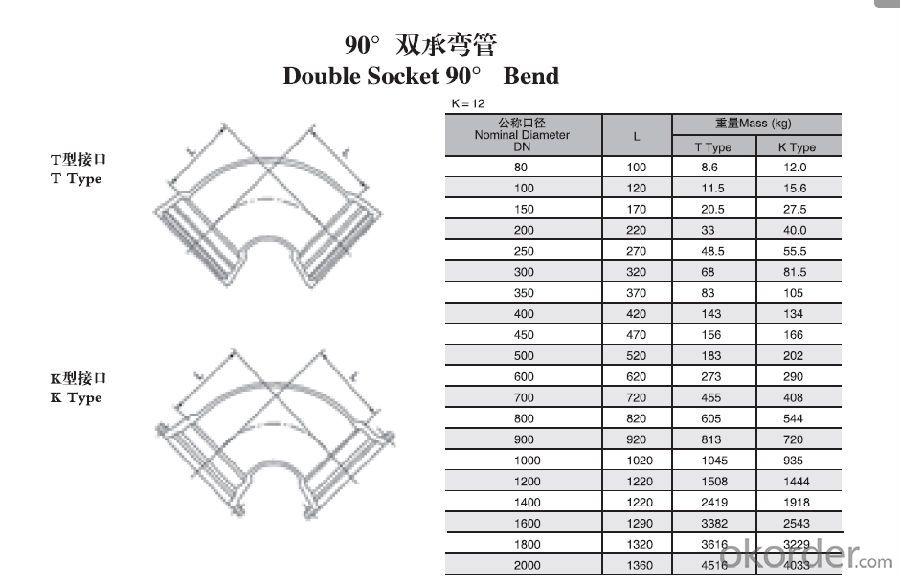
Quality:
ISO 2531 or EN 545 Standard K9 Class, K12 Class
1. ISO 9001 Certificate
2. ISO 2531 & EN 545 Certificate
3. WRAS Potable Water Certificate for FBE Internal Lining
4. WRAS EPDM Rubber Gasket or NBR Rubber Gasket
5. DN80mm - DN2000mm
6. Black Bitumen or Blue FBE / Epoxy Coating
7. Lengh = 6m or cut into 5.6m, 5.7m, 5.8m
8. Client's Brand Customization Allowable
9. Container or Bulk Loading / Shipping
10.Delivery within one Month or According to Client's Order Quantity
11. Support Client or The Third Party Inspection before Shipment

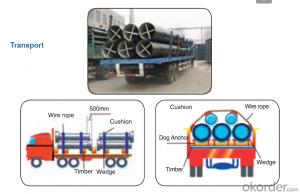
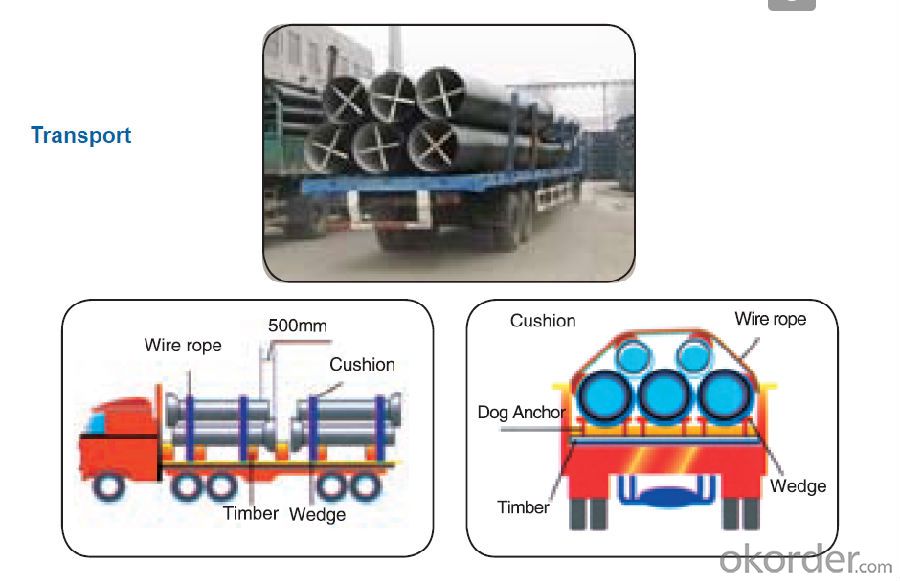
Transport:
- Q: What are the different methods for joining ductile iron pipe?
- There are several methods for joining ductile iron pipe, including mechanical joints, flanged joints, push-on joints, and restrained joints. Mechanical joints use a rubber gasket and a series of bolts and glands to create a secure connection. Flanged joints involve bolting two flanges together with a gasket in between. Push-on joints utilize a rubber gasket and require the pipe to be pushed into the joint. Restrained joints use a combination of mechanical joints and a restraining gland to prevent movement and provide a secure connection.
- Q: Are ductile iron pipes prone to external corrosion?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes are prone to external corrosion.
- Q: Are ductile iron pipes suitable for mining applications?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes are suitable for mining applications. Ductile iron pipes are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for underground mining operations. They can withstand high pressure, heavy loads, and abrasive materials commonly found in mining environments. Additionally, their flexible nature allows for easy installation and maintenance in challenging mining conditions.
- Q: Steel plastic pipe, ductile iron pipe, steel pipe difference
- Spheroidal graphite tube, now application has been relatively small, generally used for conveying water, gas at room temperature, low pressure, large diameter pipelines need to produce concrete pipe base, good corrosion resistance than steel pipe joints, vulnerable to external extrusion and leakage, the price is relatively cheap.
- Q: Are ductile iron pipes suitable for pressure reducing valve stations?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes are suitable for pressure reducing valve stations. Ductile iron pipes are known for their strength and durability, which makes them an ideal choice for applications involving high pressure. Pressure reducing valve stations are designed to regulate and reduce the pressure of a fluid or gas in a pipeline system. Ductile iron pipes can handle the pressure exerted by the fluid or gas, ensuring a reliable and efficient operation of the pressure reducing valve station. Additionally, ductile iron pipes have excellent resistance to corrosion, which is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the pipeline system and preventing leaks or failures. Overall, ductile iron pipes provide the necessary strength, durability, and corrosion resistance required for pressure reducing valve stations.
- Q: Can ductile iron pipes be used in areas with high levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and corrosion potential?
- Before making a decision, it is important to take certain factors into consideration when considering the use of ductile iron pipes in areas with high levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and corrosion potential. Ductile iron pipes display a strong resistance to corrosion, particularly when they are adequately protected with external coatings and linings. This characteristic makes them appropriate for environments with moderate levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and corrosion potential. Nevertheless, in areas with exceedingly high levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and severe corrosion potential, alternative materials such as corrosion-resistant alloys or specially coated pipes may be more suitable. To determine the suitability of ductile iron pipes, conducting a thorough evaluation of the specific conditions in the area is crucial. Factors such as the concentration of hydrogen sulfide gas, the presence of other corrosive elements or chemicals, and the overall corrosiveness of the environment should be taken into account. Furthermore, consulting the local regulations and industry standards is essential to ensure compliance and safety. In conclusion, while ductile iron pipes can withstand moderate levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and corrosion potential, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the specific conditions. In areas with high levels of hydrogen sulfide gas and severe corrosion potential, consulting with experts in the field and considering alternative materials may be required.
- Q: What are the disadvantages of using ductile iron pipe?
- Some of the disadvantages of using ductile iron pipe include its relatively high cost compared to other materials, its susceptibility to corrosion over time, and its heavy weight which can make installation more challenging. Additionally, ductile iron pipe may require more maintenance and repairs due to potential cracking or leaking.
- Q: What are the different methods for restraining ductile iron pipe?
- There exist various techniques for restraining ductile iron pipe to prevent any movement or displacement caused by internal pressure, external forces, or ground movement. The most commonly used approaches include: 1. Thrust blocks: Concrete blocks or structures are positioned at bends, tees, or other directional changes in the pipe. These blocks are designed to resist the forces exerted by flowing water or fluids within the pipe, effectively anchoring it in place. 2. Mechanical restraints: Harnesses or clamps are installed around the pipe and affixed to a fixed structure, such as a wall or concrete anchor. These restraints provide a physical barrier that prevents any movement or shifting of the pipe. 3. Pipe restraints: Devices directly attached to the pipe and anchored to a fixed structure, such as pipe clamps, restraints, or saddles. They are designed to securely hold the pipe in place and resist any movement or displacement. 4. Proper pipe bedding and backfill: It is crucial to properly support and surround the pipe with compacted material to prevent any movement or shifting. This method involves carefully placing and compacting soil or suitable materials around the pipe to provide stability and prevent displacement. 5. Trench walls: The walls of the trench where the ductile iron pipe is installed can also contribute to restraining it. By correctly compacting the soil against the pipe and ensuring proper stability of the trench walls, the pipe can be effectively restrained and prevented from moving. Overall, the various methods for restraining ductile iron pipe aim to ensure its secure placement without any displacement or movement. The choice of method depends on factors such as location, application, and the forces acting on the pipe. It is important to consult with engineers and adhere to industry guidelines and standards to determine the most appropriate method for restraining ductile iron pipe in specific situations.
- Q: Can ductile iron pipes be used in areas with high soil acidity and alkalinity?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes can be used in areas with high soil acidity and alkalinity. Ductile iron is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme pH levels, making it suitable for such environments.
- Q: What are the different types of linings available for ductile iron pipe?
- Ductile iron pipes offer various linings with distinct advantages and applications. 1. Cement mortar lining: The most commonly used lining for ductile iron pipes is cement mortar. It involves applying a layer of cement mortar to the pipe's interior surface. This lining excels in resisting corrosion and chemical attacks, making it suitable for potable water distribution, wastewater conveyance, and industrial pipelines. Additionally, it improves flow efficiency by reducing friction and turbulence within the pipe. 2. Polyethylene lining: Ductile iron pipes often utilize polyethylene linings when corrosion resistance is a primary concern. This lining consists of a layer of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), either extruded or sprayed onto the inner surface of the pipe. Polyethylene lining provides exceptional resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical attacks, making it ideal for transporting aggressive fluids such as saltwater, chemicals, or industrial waste. 3. Polyurethane lining: For applications requiring protection against abrasive wear, polyurethane linings are commonly employed in ductile iron pipes. This lining is created by spraying or pouring a layer of polyurethane onto the inner surface of the pipe. Polyurethane lining offers excellent resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemical attacks. It is suitable for conveying abrasive slurries, mining applications, and other high-wear environments. 4. Epoxy lining: To safeguard against corrosion and chemical attacks, epoxy linings are applied to ductile iron pipes. This lining is typically formed by applying a layer of epoxy resin to the pipe's inner surface using centrifugal casting or electrostatic spraying. Epoxy lining demonstrates outstanding adhesion and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various applications like potable water distribution, wastewater treatment, and industrial pipelines. 5. Zinc lining: Ductile iron pipes employ zinc linings to provide cathodic protection against corrosion. This lining involves applying a layer of zinc to the pipe's inner surface through hot-dip galvanizing or electroplating. Zinc lining acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding preferentially to the iron pipe and shielding it from corrosion. It is commonly used in highly corrosive environments like seawater or acidic soils. Ultimately, the selection of a lining for ductile iron pipes relies on the specific requirements of the application, including the transported fluid, desired corrosion resistance, and potential for abrasive wear. Seeking guidance from industry experts and considering factors like cost, longevity, and maintenance requirements aids in determining the most suitable lining option for a particular project.
Send your message to us
Duct Iron Pipe DI Pipe ISO 2531 Double Socked 90° Bend T Type
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords