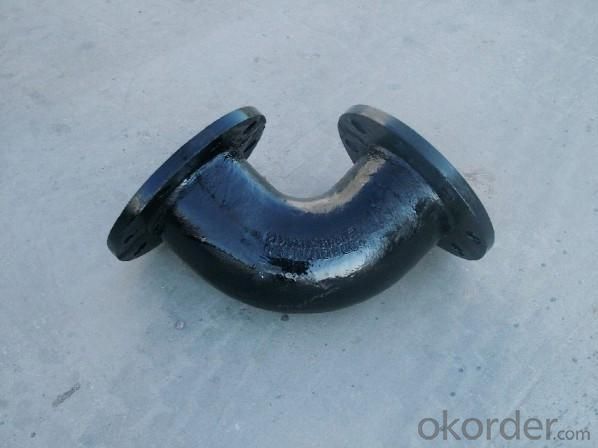
Duct Iron Pipe DI Pipe ISO 2531 DN 80-2000mm Double Socked 90° Bend
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Ductile iron pipe fittings:
Dimensions standard:
ISO2531: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
BS4772: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
EN545: 50-1000mm, PN10/16
Connecting mode:
Flanged
Socketed
Mechanical connection
Loose flanged
Coatings:
Inner lined with cement and outside coated with zinc plus bitumen
Inner and outside coated with epoxy resin
Inner and outside coated with fusion bonded epoxy resin
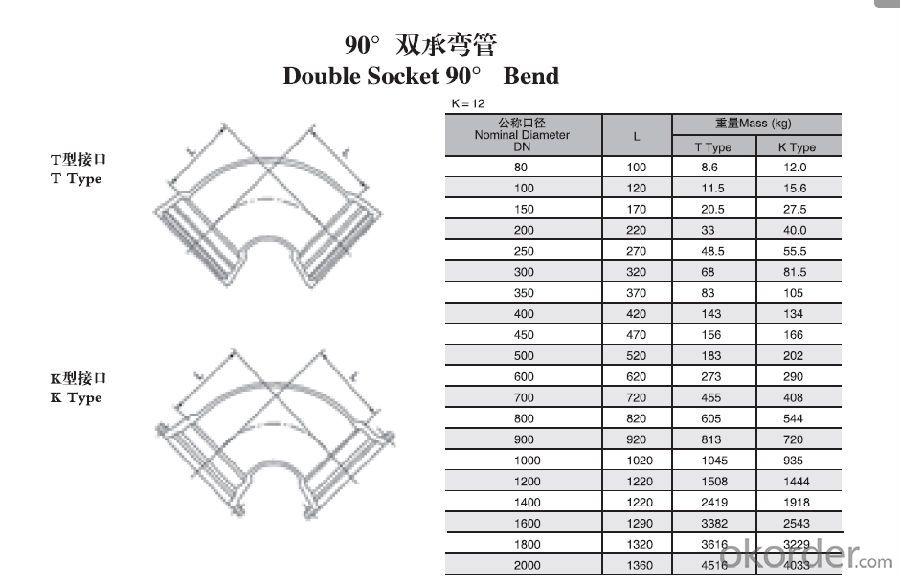
Quality:
ISO 2531 or EN 545 Standard K9 Class, K12 Class
1. ISO 9001 Certificate
2. ISO 2531 & EN 545 Certificate
3. WRAS Potable Water Certificate for FBE Internal Lining
4. WRAS EPDM Rubber Gasket or NBR Rubber Gasket
5. DN80mm - DN2000mm
6. Black Bitumen or Blue FBE / Epoxy Coating
7. Lengh = 6m or cut into 5.6m, 5.7m, 5.8m
8. Client's Brand Customization Allowable
9. Container or Bulk Loading / Shipping
10.Delivery within one Month or According to Client's Order Quantity
11. Support Client or The Third Party Inspection before Shipment

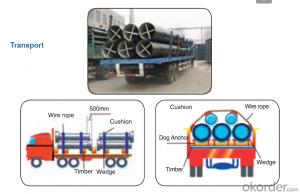
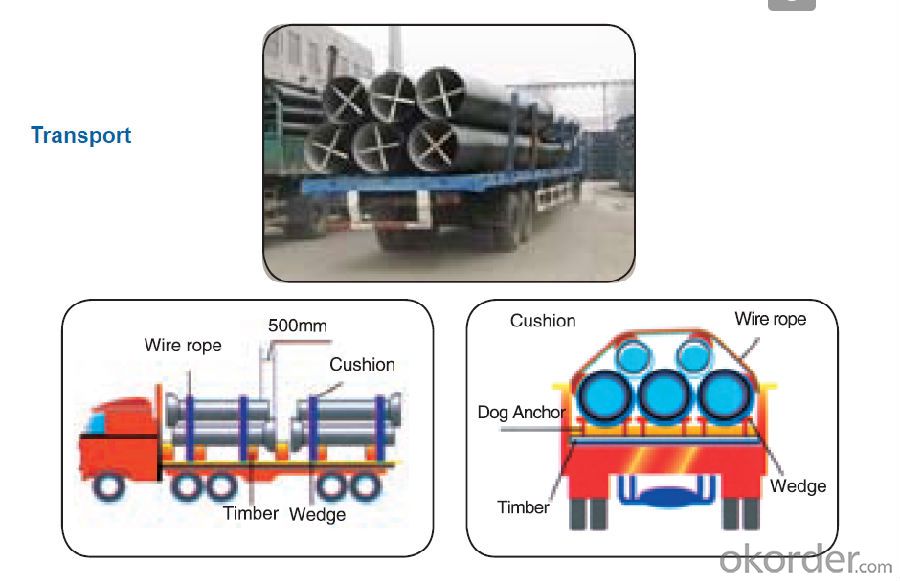
Transport:
- Q: Can ductile iron pipes be used for underground hydrocarbon pipelines?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes can be used for underground hydrocarbon pipelines. Ductile iron pipes are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for transporting hydrocarbons underground. However, it is important to consider factors like the specific hydrocarbon being transported, pressure requirements, and regulatory standards before selecting the appropriate material for the pipeline.
- Q: What are the common pressure ratings for ductile iron pipes?
- Common pressure ratings for ductile iron pipes vary depending on the specific application and industry standards. However, the most commonly used pressure ratings for ductile iron pipes are Class 150, Class 200, Class 250, and Class 350. Class 150 ductile iron pipes are typically used for low-pressure applications, with a working pressure of up to 150 psi (pounds per square inch). These pipes are commonly used for water distribution systems, irrigation, and gravity flow sewer systems. Class 200 ductile iron pipes have a higher working pressure of up to 200 psi. These pipes are often used for applications that require a slightly higher pressure, such as industrial water supply, fire protection systems, and wastewater treatment plants. Class 250 ductile iron pipes have a working pressure of up to 250 psi. These pipes are suitable for more demanding applications, such as high-pressure water supply systems, power plants, and municipal water distribution networks. Class 350 ductile iron pipes have the highest working pressure rating, with a maximum pressure of up to 350 psi. These pipes are typically used for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial water supply, oil and gas pipelines, and large-scale water transportation projects. It's important to note that these pressure ratings are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific manufacturer and product specifications. Consulting industry standards and guidelines, as well as working with qualified engineers and professionals, is essential to ensure the correct pressure rating is selected for a particular ductile iron pipe application.
- Q: How much water seepage is allowed in the water pressure test for water hose DN300?
- The main control parameters of ductile iron pipes are nominal diameter, working pressure, connection mode, etc.. Light, high, thin wall, pressure resistance, shock resistance, corrosion resistance, earthquake resistance and other properties. The flexible interface is used for the pipeline interface, and there is a certain elongation and deflection angle. He has the advantages of raw iron pipes and steel pipes, avoiding the defects of iron and steel.
- Q: What are the disadvantages of using ductile iron pipes?
- One disadvantage of using ductile iron pipes is their susceptibility to corrosion. Over time, exposure to moisture and various chemicals can cause the pipes to deteriorate and develop leaks. Another disadvantage is their relatively high cost compared to other pipe materials, such as PVC or HDPE. Additionally, ductile iron pipes are heavy and require specialized equipment for installation, which can increase labor and transportation costs.
- Q: How much is the working pressure of ductile iron pipe used in water supply pipe and how is MPa determined?
- In general, building materials products are production standards, the production process and specifications are required, pipe work pressure is based on the use of coffins and other factors set standards, pipes with different purposes, the pressure level is different.
- Q: What is ductile iron?
- Ductile iron is a type of cast iron that has improved strength and ductility due to its unique microstructure. It is created by adding small amounts of magnesium to molten iron, which causes the graphite in the iron to form in a nodular shape rather than in flakes. This nodular graphite structure gives ductile iron its characteristic properties, making it more resistant to cracking and allowing it to be easily machined and welded. Ductile iron is widely used in various industries for its excellent strength, impact resistance, and durability.
- Q: Can centrifugal cast iron pipe be galvanized or coated with asphalt which is good for corrosion prevention?
- By spraying zinc and epoxy coal tar coating of ductile iron pipe wall (or epoxy resin paint, polyurethane, etc.) wall using Portland cement (or epoxy powder, epoxy, polyurethane, ceramics etc.) wall coating can effectively active substances in soil and the formation of an insoluble zinc salt protection tube, the internal coating can inhibit corrosion of pipe body fluid medium.
- Q: Can ductile iron pipe be used for underground applications?
- Indeed, underground applications can employ ductile iron pipe. Renowned for its robustness and endurance, ductile iron pipe proves to be well-suited for a multitude of underground uses, including water and sewage systems, gas pipelines, and irrigation systems. Its exceptional resistance to corrosion and external burdens renders it a dependable selection for underground installations, where sustained functionality and structural soundness are pivotal considerations. Moreover, ductile iron pipe's pliability enables it to endure ground shifting and settling sans fracturing or shattering, making it an apt choice for regions susceptible to seismic occurrences.
- Q: Advantages and disadvantages of ductile iron pipes?
- Nodular cast iron has high strength and strong plasticity. The tensile strength of ductile iron is twice that of gray iron, and the yield strength even exceeds that of cast steel. So, the ball compressive strength of ductile iron pipe is much higher than that of cast iron pipes, buried in the ground, the car is not easy to be crushed.
- Q: Are ductile iron pipes suitable for use in oil refineries?
- Yes, ductile iron pipes are suitable for use in oil refineries. They have excellent corrosion resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for transporting various fluids and gases in harsh environments such as oil refineries. Additionally, their flexibility and durability allow for easy installation and maintenance, ensuring reliable operations in refinery facilities.
Send your message to us
Duct Iron Pipe DI Pipe ISO 2531 DN 80-2000mm Double Socked 90° Bend
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords