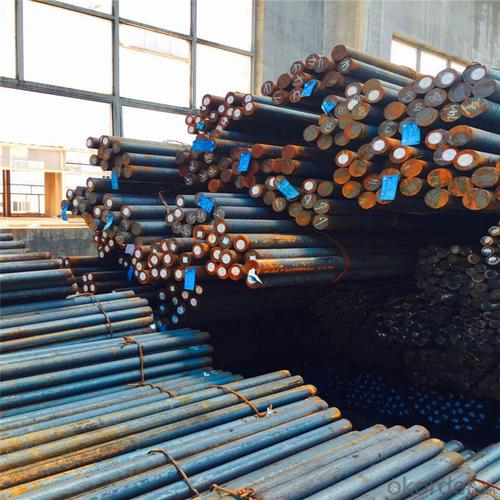
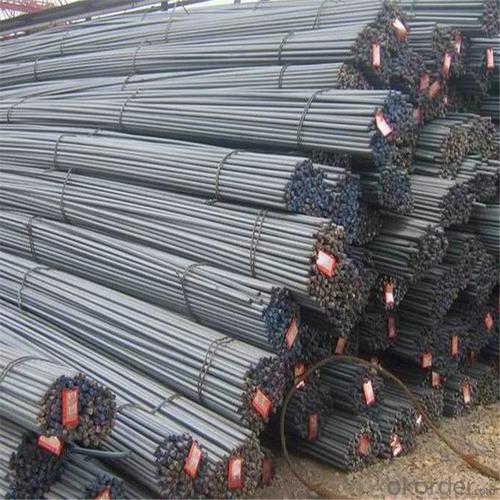
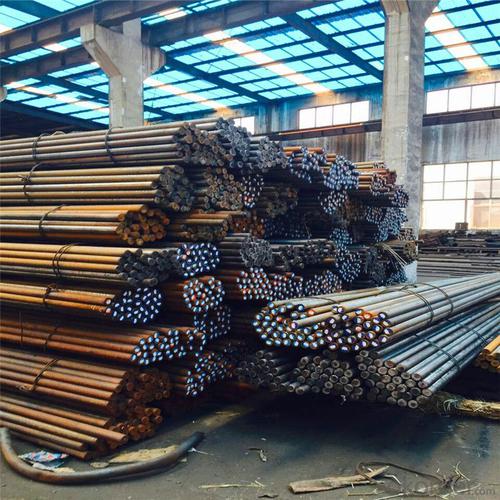
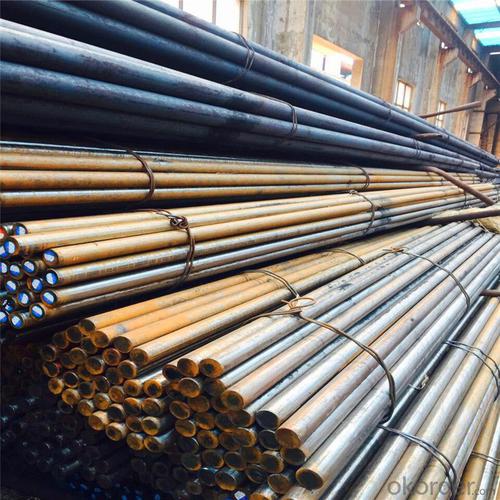
ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
Description of ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
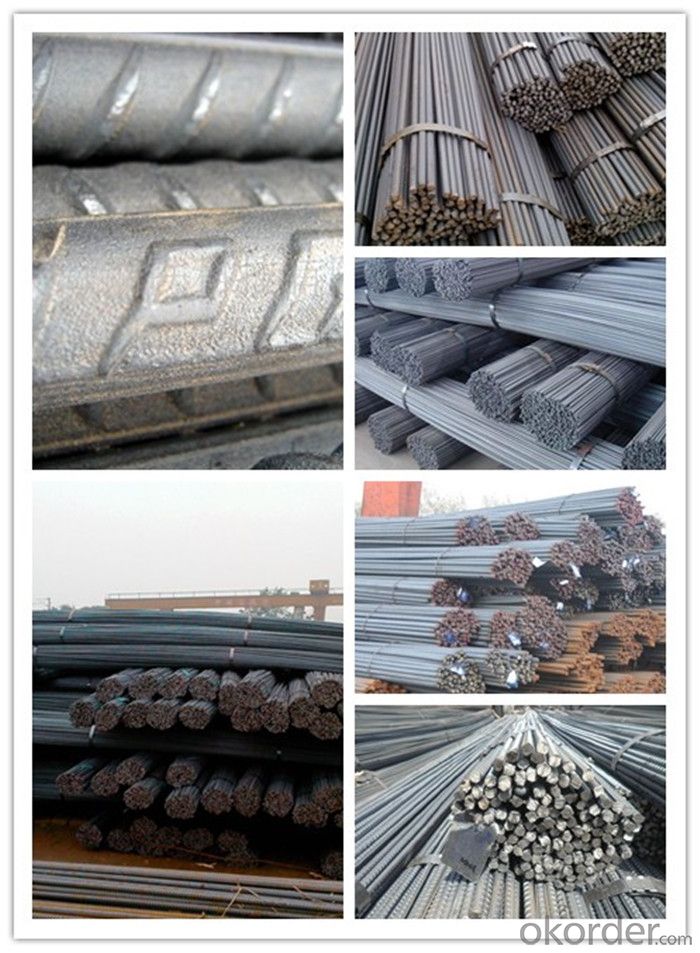
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
10m- 40mm ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
Company Information
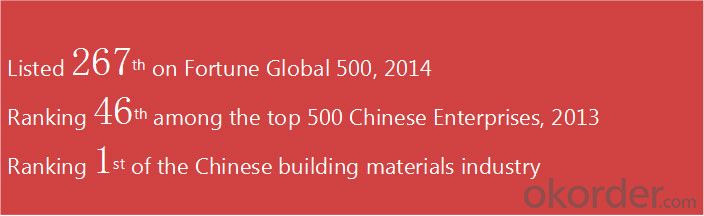
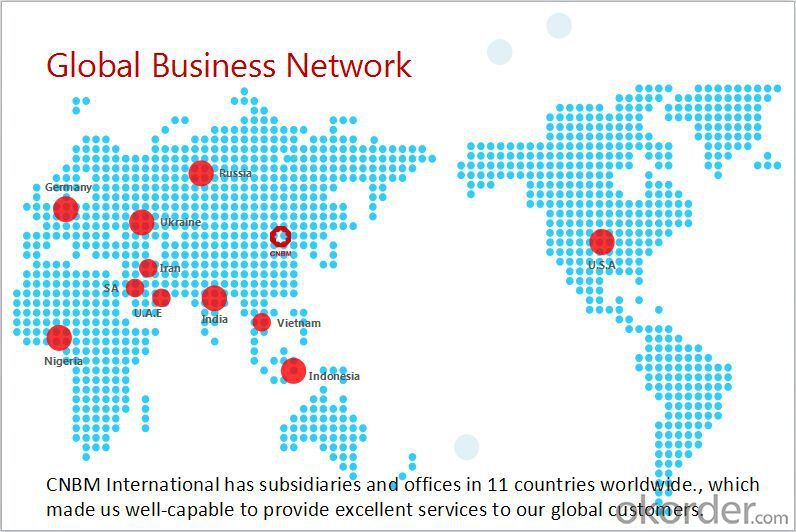
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the different electroplating techniques used for special steel?
- There are several electroplating techniques used for special steel, including electroless nickel plating, zinc plating, and chromium plating. Each technique offers unique benefits and properties that are tailored to the specific requirements of the special steel being plated.
- Q: How is special steel used in the production of automotive parts?
- Special steel is used in the production of automotive parts due to its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. It is commonly used for manufacturing critical components such as engine parts, chassis, drive shafts, and suspension systems. Special steel helps enhance the overall performance, safety, and longevity of automobiles, making them more reliable and efficient on the road.
- Q: What are the different methods of machining special steel?
- There are several different methods of machining special steel, each with its own advantages and applications. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Turning: Turning is a machining process that involves rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material from the surface. This method is typically used to create cylindrical shapes and can produce high-quality finishes. 2. Milling: Milling is a versatile machining method that uses rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. It can be used to create complex shapes and contours, and is often employed in the production of special steel components. 3. Drilling: Drilling is a machining process that involves creating holes in a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool. It can be used to create both through holes and blind holes in special steel, and is commonly used in various industries. 4. Grinding: Grinding is a precision machining method that uses an abrasive wheel to remove material from a workpiece's surface. It is often used to achieve tight tolerances and smooth finishes on special steel components. 5. Broaching: Broaching is a machining process that uses a sharp cutting tool with multiple teeth to remove material in a series of linear cuts. It is commonly used to create keyways, splines, and other intricate shapes in special steel. 6. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): EDM is a non-traditional machining method that uses electrical discharges to remove material from a workpiece. It is particularly useful for machining special steel with complex shapes or for creating small features. 7. Laser Cutting: Laser cutting utilizes a high-powered laser to cut through special steel with extreme precision. It is commonly used for intricate designs and can produce smooth edges without the need for subsequent processing. Each of these methods has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of machining method depends on factors such as the desired outcome, the complexity of the part, and the properties of the special steel being machined.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the textile industry?
- Special steel contributes to the textile industry by providing high-strength and durable components for textile machinery, such as looms, knitting machines, and textile processing equipment. The use of special steel in these machines ensures improved performance, precision, and longevity, thereby enhancing productivity and efficiency in textile manufacturing processes. Additionally, special steel's resistance to corrosion and wear helps maintain the quality and reliability of textile machinery, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs for manufacturers.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the manufacturing of surgical instruments?
- Special steel is a crucial material in the manufacturing of surgical instruments due to its exceptional properties such as high corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. These qualities enable surgical instruments to withstand the harsh sterilization processes and provide long-lasting performance in medical settings. Additionally, special steel's ability to be shaped into intricate designs and its compatibility with sterilization methods ensures precision and hygiene in surgical procedures.
- Q: How is the toughness of special steel measured?
- The toughness of special steel can be assessed by specific tests and methodologies that evaluate its capacity to absorb energy and withstand fractures. One widely used approach is the Charpy V-Notch (CVN) test, in which a notched specimen is struck by a pendulum hammer, and the energy absorbed during fracture is measured. The results are then expressed as the energy absorbed per unit area, typically in joules per square centimeter (J/cm²) or foot-pounds per square inch (ft-lb/in²). Another commonly employed test is the Izod test, which is similar to the CVN test but involves a different specimen geometry. Furthermore, engineers and manufacturers may also employ other mechanical tests such as tensile strength, impact strength, and fracture toughness measurements to evaluate the toughness of special steel. These tests are invaluable in determining the suitability of special steel for various applications, particularly those requiring exceptional resistance to impact or sudden loading.
- Q: How does special steel perform in hot forging processes?
- Special steel is specifically engineered to endure high temperatures and excel in hot forging procedures. When subjected to extreme heat, special steel retains its strength and hardness, rendering it perfect for utilization in hot forging applications. One of the principal benefits of special steel in hot forging lies in its superb heat resistance. It can endure elevated temperatures without compromising its structural integrity, guaranteeing the preservation of its desired properties throughout the forging process. This enables the production of forged components with consistent quality and dimensional accuracy. Moreover, special steel demonstrates commendable thermal conductivity, aiding in the even distribution of heat during forging. This facilitates efficient heating and diminishes the likelihood of localized overheating or cold spots. The uniform distribution of heat also contributes to a homogeneous grain structure, enhancing the overall strength and mechanical properties of the forged parts. Furthermore, special steel possesses exceptional wear resistance and toughness, even in elevated temperatures. This ensures that the steel can withstand the substantial forces and pressures involved in the hot forging process without succumbing to deformation or failure. The combination of high strength, wear resistance, and toughness allows for the production of forged components capable of enduring heavy loads and harsh operating conditions. Additionally, special steel lends itself to easy machining and shaping, enabling the forging of intricate designs and complex forms. This versatility makes it suitable for a broad range of hot forging applications, including automotive parts, industrial machinery components, and aerospace components. In conclusion, special steel excels in hot forging processes. Its heat resistance, thermal conductivity, wear resistance, toughness, and machinability establish it as an ideal material for the production of high-quality, long-lasting, and intricate forged components.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface cleaning for special steel?
- There are several different methods of surface cleaning for special steel, each with its own advantages and applications. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Mechanical Cleaning: This method involves the use of mechanical tools like wire brushes, sandpaper, or abrasive pads to physically remove dirt, rust, or other contaminants from the surface of the steel. Mechanical cleaning is effective for light to moderate surface contamination and is often used as a pre-treatment before other cleaning methods. 2. Chemical Cleaning: Chemical cleaning involves the use of specific chemicals or cleaning agents to dissolve or loosen contaminants on the surface of the special steel. These chemicals can be applied through brushing, spraying, or immersion methods. Acid-based cleaners are commonly used for removing scale, rust, or oxide deposits, while alkaline cleaners are effective for removing oils, greases, or organic residues. 3. Electrochemical Cleaning: This method utilizes electrochemical reactions to remove surface contaminants from special steel. Electrochemical cleaning involves the use of an electric current and an electrolyte solution to dissolve or dislodge dirt, rust, or other deposits. This method is particularly useful for cleaning intricate or hard-to-reach areas on the steel surface. 4. Ultrasonic Cleaning: Ultrasonic cleaning involves the use of high-frequency sound waves in a liquid medium to agitate and remove contaminants from the surface of special steel. This method is highly effective for removing fine particles, oils, greases, or other organic residues from complex or delicate surfaces. 5. High-pressure Water Jetting: High-pressure water jetting uses a focused stream of pressurized water to remove contaminants from the special steel surface. This method is particularly useful for removing heavy deposits, coatings, or paints from large areas. It can be adjusted to different pressure levels to accommodate various degrees of surface contamination. It is important to note that the choice of surface cleaning method for special steel will depend on factors such as the type and extent of contamination, the condition of the steel surface, the desired level of cleanliness, and the specific requirements of the application. It is recommended to consult with experts or professionals in the field to determine the most suitable method for a given situation.
- Q: What are the main advantages of using special steel in the construction of bridges?
- The main advantages of using special steel in the construction of bridges are its exceptional strength and durability. Special steel alloys offer high tensile strength, allowing for lighter bridge designs and reducing the overall weight of the structure. This not only makes construction and transportation easier but also minimizes the environmental impact. Additionally, special steel exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring the longevity of the bridge even in harsh weather conditions. Its superior toughness and resistance to fatigue make it ideal for withstanding heavy loads and frequent use, ensuring the safety and reliability of the bridge for many years.
- Q: How are copper alloys used in electrical applications?
- Copper alloys are widely used in electrical applications due to their excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity properties. These alloys, such as brass and bronze, are used in the production of electrical connectors, terminals, and conductors. They are also utilized in circuit breakers, switches, and motors due to their high strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, copper alloys are used in the manufacturing of electrical cables and wiring systems, ensuring efficient transmission of electricity with minimal power loss.
Send your message to us
ASTM Standard Reinforced Steel D Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



































