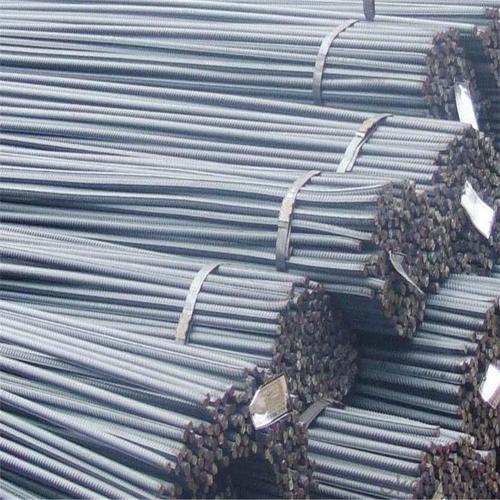
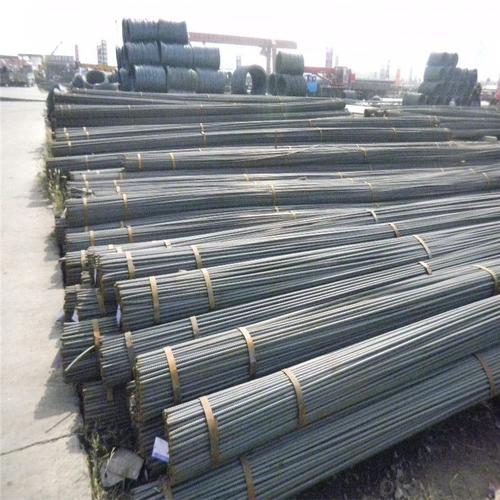
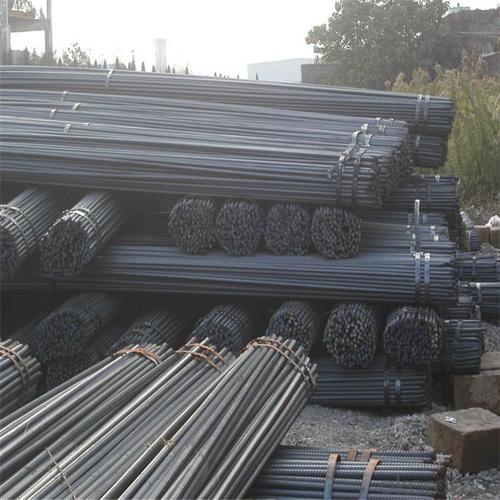
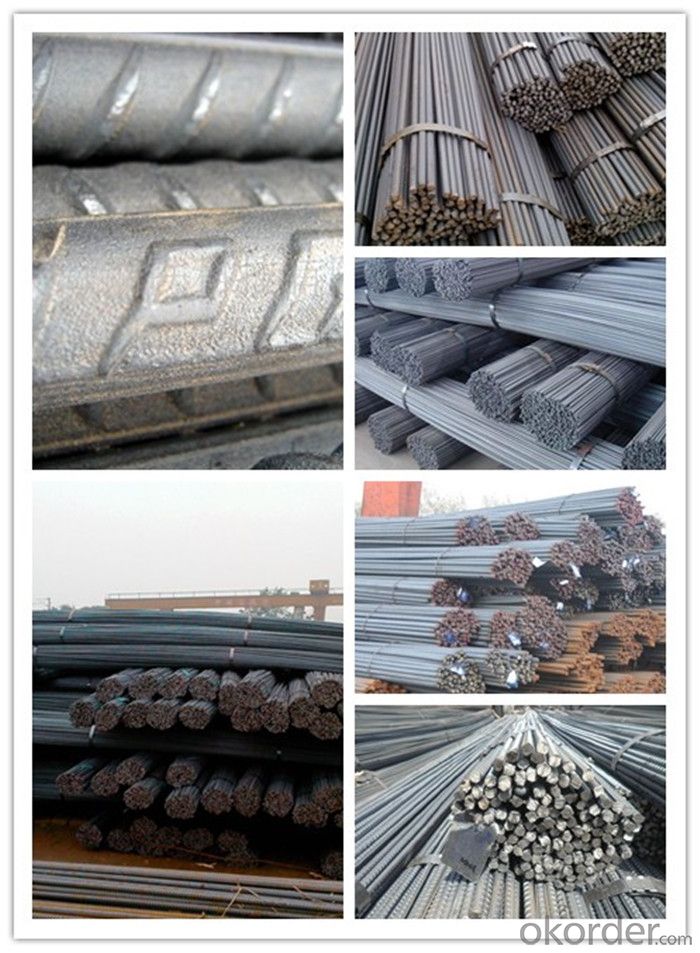
ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 180 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
Description of ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
10m- 40mm ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
Company Information
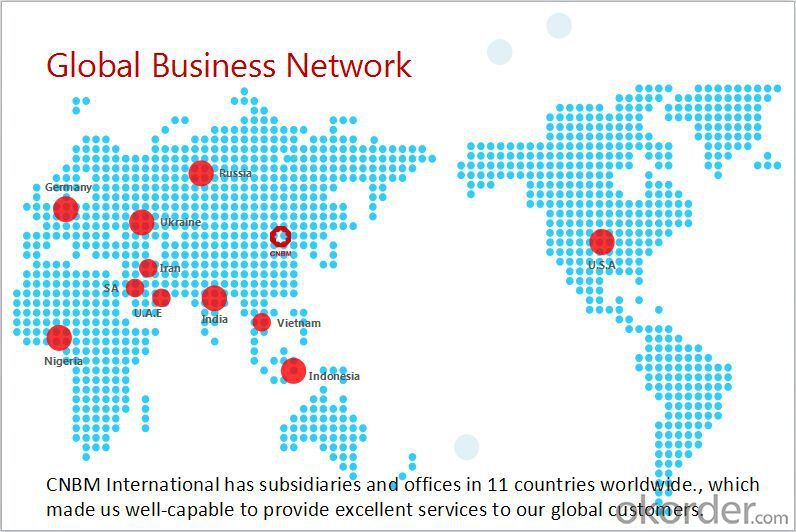
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the marine machinery industry?
- The marine machinery industry greatly relies on special steel, which offers numerous advantages and contributes significantly to the efficiency and reliability of marine machinery. Above all else, special steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and durability. In the harsh marine environment, where machinery is constantly exposed to extreme weather conditions and high levels of corrosion, special steel ensures that marine machinery can withstand these challenges and maintain its integrity over a prolonged period. This enhanced durability not only extends the lifespan of marine machinery but also reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, thereby resulting in cost savings for shipbuilders and operators. Furthermore, special steel possesses excellent welding and fabrication properties, making it easier to construct complex components of marine machinery. The ability to weld and fabricate special steel allows for the production of intricate and customized parts, which can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different marine vessels. This design flexibility ensures that marine machinery is optimized for performance, efficiency, and safety. Moreover, special steel exhibits outstanding resistance to corrosion and erosion, which are common problems in marine environments due to saltwater and other corrosive agents. By utilizing special steel, marine machinery can effectively resist corrosion, preventing premature failure and reducing the need for maintenance. This corrosion resistance also enhances the overall safety of marine operations by significantly reducing the risk of machinery malfunction due to corrosion-related issues. In terms of efficiency, special steel contributes to the marine machinery industry by offering superior heat resistance and thermal conductivity. This enables marine machinery to operate at high temperatures without compromising performance, ensuring efficient energy conversion and optimal functioning of critical systems. The improved thermal properties of special steel also contribute to the overall fuel efficiency of marine vessels, resulting in reduced operational costs and environmental impact. In conclusion, special steel plays a vital role in the marine machinery industry by providing the necessary strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties for the efficient and reliable operation of marine machinery. By harnessing the benefits of special steel, shipbuilders and operators can enhance the longevity, safety, and performance of marine vessels, ultimately contributing to the growth and sustainability of the marine industry.
- Q: How is corrosion-resistant tool steel used in the production of molds and dies?
- Corrosion-resistant tool steel is commonly used in the production of molds and dies due to its ability to withstand exposure to corrosive environments. This steel helps to prevent rust and degradation, ensuring that the molds and dies maintain their structural integrity and dimensional accuracy over time. By using corrosion-resistant tool steel, manufacturers can produce high-quality molds and dies that are durable and resistant to wear and tear, ultimately improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the production process.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the aerospace fuel efficiency?
- Special steel contributes to aerospace fuel efficiency in several ways. Firstly, special steel alloys are used in the construction of aircraft engines, which helps reduce their weight while maintaining strength and durability. This reduction in weight results in lower fuel consumption as the engines require less energy to propel the aircraft. Additionally, special steel is also utilized in the manufacturing of lightweight airframe components, such as wings and landing gear, which further contributes to fuel efficiency by reducing the overall weight of the aircraft. Furthermore, special steel's corrosion resistance properties ensure the longevity of aerospace components, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, which in turn helps optimize fuel efficiency.
- Q: Can special steel be used in aerospace turbine components?
- Yes, special steel can be used in aerospace turbine components. Special steel alloys, such as nickel-based superalloys, are commonly used in the manufacturing of turbine blades and other critical components in aerospace engines. These alloys possess high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand extreme temperatures and stress conditions, making them suitable for the demanding environment of aerospace turbines.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the renewable energy conversion efficiency?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in improving the efficiency of renewable energy conversion by providing strength, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. It is used in various components of renewable energy systems such as wind turbines, solar panels, and hydropower plants. The high strength-to-weight ratio of special steel enables the construction of taller wind turbine towers, allowing them to capture more wind energy at higher altitudes. Additionally, special steel is used in the production of high-efficiency solar panels, as it helps enhance their performance by increasing structural integrity and resistance to corrosion. In hydropower plants, special steel is employed to construct turbines and generators that can withstand the immense pressures and forces involved in generating electricity from water. Overall, the use of special steel in renewable energy systems contributes to their overall efficiency and longevity, aiding in the transition towards a sustainable energy future.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface polishing for special steel?
- Some of the different methods of surface polishing for special steel include mechanical polishing, chemical polishing, electropolishing, and abrasive blasting. Mechanical polishing involves using abrasive materials like sandpaper or polishing wheels to remove imperfections and create a smoother surface. Chemical polishing uses chemical solutions to dissolve a thin layer of the steel's surface, resulting in a polished finish. Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes surface material through the application of an electric current, resulting in a smooth and shiny surface. Abrasive blasting, also known as sandblasting, involves propelling abrasive particles at high speeds to remove rust, scale, or other surface contaminants, leaving a polished surface.
- Q: How is special steel used in the production of cutting tools?
- Special steel is used in the production of cutting tools due to its exceptional properties such as high hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. These qualities enable the cutting tools to effectively cut through various materials, including metal and wood, with precision and efficiency. The special steel used in the manufacturing process undergoes specific heat treatment and alloying techniques to optimize its performance and durability, making it an ideal choice for producing high-quality cutting tools.
- Q: What are the specific requirements for special steel used in the defense sector?
- Due to the critical nature of its applications, the defense sector imposes highly demanding requirements on special steel. These requirements encompass: 1. Exceptional strength and durability: Special steel utilized in the defense sector must possess outstanding strength and durability to withstand extreme conditions and endure wear and tear. It should have the capacity to endure high levels of stress, impact, and pressure. 2. Superior corrosion resistance: Defense equipment frequently operates in harsh environments and is exposed to elements that can cause corrosion. Consequently, special steel employed in the defense sector must display excellent corrosion resistance properties to ensure the equipment's longevity and reliability. 3. Heat resistance: Defense applications often involve exposure to high temperatures, such as in jet engines or armored vehicle components. Special steel used in these sectors must retain its strength and structural integrity even at elevated temperatures. 4. Machinability and weldability: Special steel employed in the defense sector should possess favorable machinability and weldability characteristics to facilitate manufacturing and assembly processes. This allows for ease of fabrication, repair, and maintenance of defense equipment. 5. Hardness and toughness: Defense applications necessitate a combination of hardness and toughness in special steel. It must resist penetration and deformation while simultaneously being able to absorb energy and resist fracture. 6. Non-magnetic properties: In specific defense applications, such as submarines and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment, non-magnetic properties are essential. Special steel employed in these sectors must possess low magnetic permeability to prevent interference with sensitive electronic systems. 7. Certification and compliance: Special steel used in the defense sector must meet specific certification and compliance standards, such as those established by defense organizations or international quality management systems like ISO 9001. These standards guarantee the quality, traceability, and reliability of the steel. Meeting these specific requirements for special steel utilized in the defense sector is crucial to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and longevity of defense equipment and systems. Rigorous testing and quality control processes are implemented to ensure that the steel meets the required specifications and standards.
- Q: What are the properties of ultra-high-strength steel?
- Ultra-high-strength steel possesses exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, excellent toughness, and superior resistance to deformation, making it incredibly durable and robust. It exhibits remarkable load-bearing capabilities, enabling it to withstand heavy loads and extreme conditions without experiencing significant deformation or failure. Additionally, ultra-high-strength steel offers exceptional fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and the ability to maintain its structural integrity under high temperatures, making it an ideal material for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in aerospace defense applications?
- Due to the critical nature of aerospace defense applications, the demands for special steel are highly rigorous. The steel must meet several key requirements: 1. Exceptional strength is necessary to withstand extreme conditions and loads, ensuring the structural integrity of aircraft and defense equipment. 2. The steel must have excellent corrosion resistance to combat the harsh environments it encounters, such as moisture, saltwater, and chemicals. This prevents degradation and maintains performance over time. 3. Withstanding high temperatures without compromising mechanical properties is crucial for components operating in high-temperature environments, like jet engines and rocket nozzles. 4. Fatigue resistance is essential as aerospace defense applications involve repeated stress cycles. The steel should be able to resist fatigue failure, ensuring long service lives without failure. 5. Weight reduction is a critical factor to enhance fuel efficiency, payload capacity, and overall performance. The special steel must have a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for lighter structures without compromising strength. 6. To ensure reliability and longevity in demanding operational conditions, the steel used must have a high level of purity and cleanliness, minimizing the presence of impurities and defects. 7. Compatibility with other materials, such as aluminum alloys and composite materials commonly used in aerospace defense applications, is essential for reliable and efficient integration of different components and structures. Meeting these requirements often involves utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques such as vacuum melting, precise alloying, and heat treatment processes. Additionally, strict quality control measures, including non-destructive testing and material certification, are crucial to guarantee the performance and reliability of special steel in aerospace defense applications.
Send your message to us
ASTM A615/BS4449 Reforcing Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 180 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































