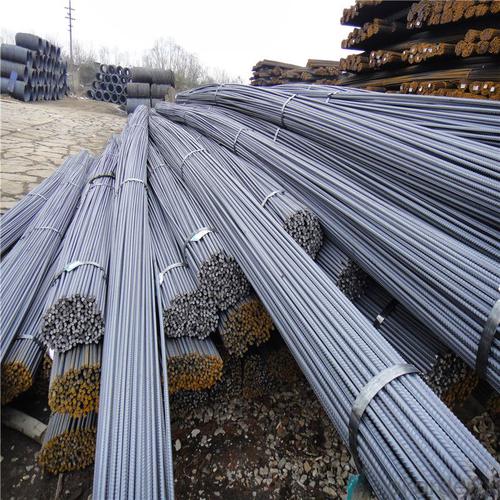
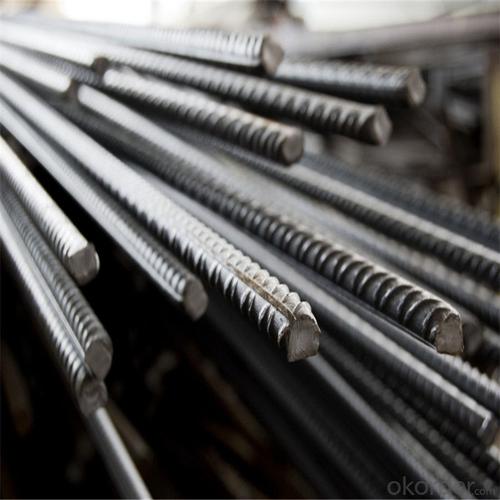
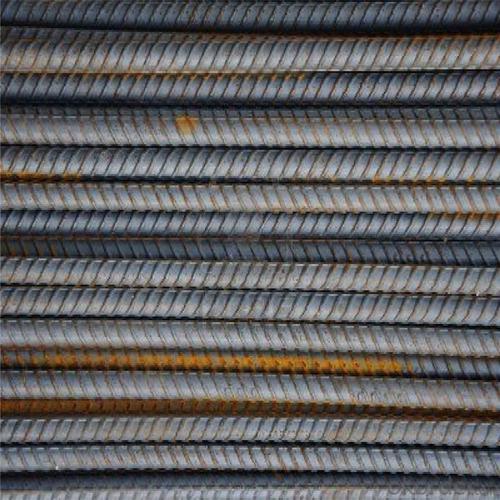
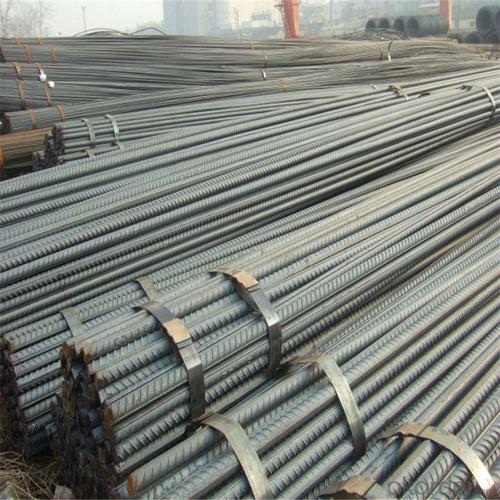
Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 140 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
Description of Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
10m- 40mm Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
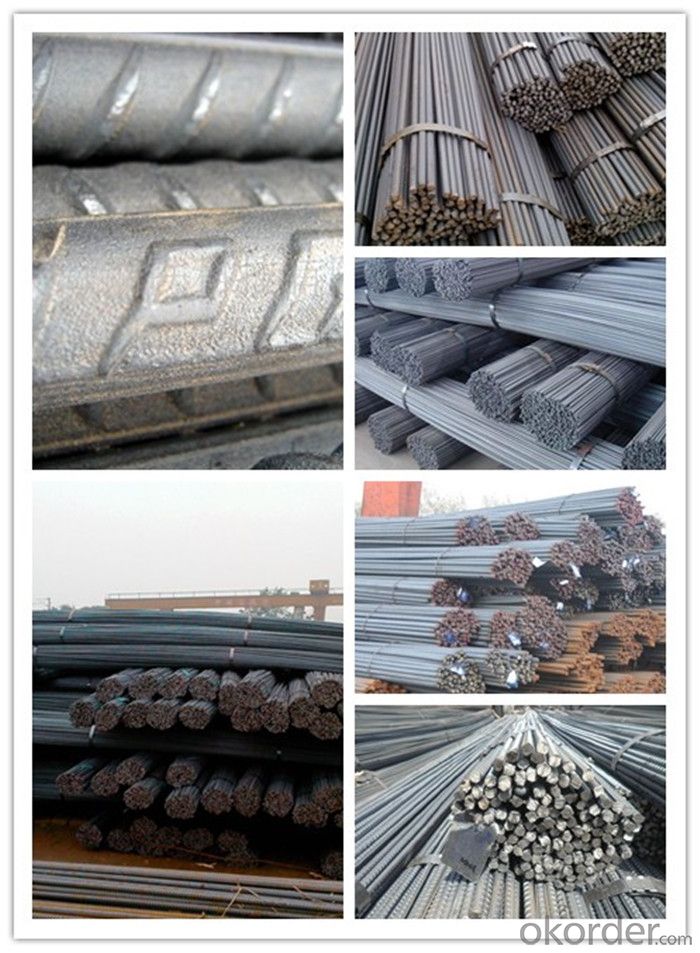
Products Show of Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
Company Information
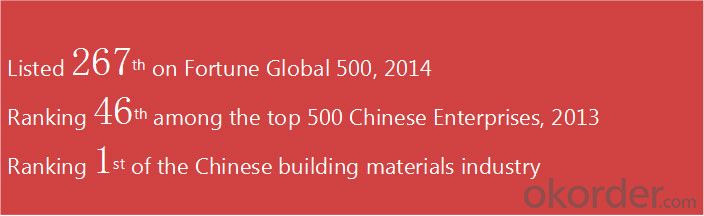
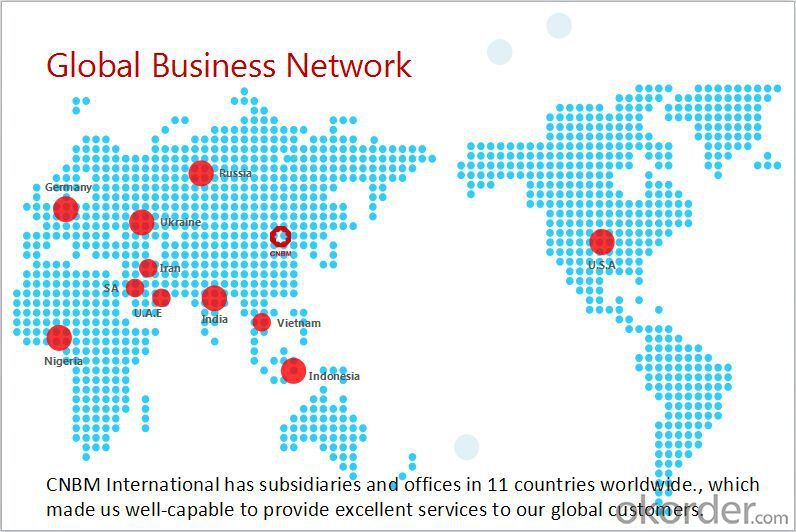
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the cost implications of using special steel?
- The cost implications of using special steel can vary depending on several factors. Special steel generally refers to alloyed or high-grade steel that offers enhanced properties such as improved strength, corrosion resistance, or heat resistance. One of the main cost implications is the higher initial cost of special steel compared to regular carbon steel. Special steel often requires more complex and expensive production processes, which can drive up the cost of raw materials. Additionally, the limited availability of certain alloying elements used in special steel can further increase its price. However, using special steel can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Its improved properties can result in reduced maintenance and replacement costs. For example, special steel that offers better corrosion resistance may require less frequent painting or coating, saving on maintenance expenses. Similarly, using high-strength special steel can allow for the use of lighter and thinner components, reducing material costs and transportation expenses. Furthermore, special steel's enhanced performance characteristics can lead to improved product quality and durability, which may result in higher customer satisfaction, increased sales, and potentially higher profits. In summary, while the initial cost of special steel is usually higher, its long-term benefits in terms of improved performance, reduced maintenance, and potential sales growth can offset these expenses, making it a cost-effective choice in many applications.
- Q: What are the main applications of special steel in the automotive electrical systems?
- Special steel is widely used in automotive electrical systems for various applications. One of the main uses is in the production of electrical connectors and terminals, where special steel offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Additionally, special steel is utilized in the manufacturing of electrical contacts, relays, and switches, ensuring reliable and efficient performance in the automotive electrical systems.
- Q: How is special steel recycled?
- Special steel is typically recycled through a process called electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking. During this process, scrap steel, including special steel, is melted down in an electric arc furnace. The furnace reaches extremely high temperatures, causing the steel to melt. Once melted, the impurities are removed, and the steel is then refined and shaped into new products. This recycling method helps to conserve natural resources, reduce energy consumption, and minimize environmental impacts associated with traditional steel production.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the manufacturing of cutting-edge technology products?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the manufacturing of cutting-edge technology products. Special steel, such as high-strength alloys or stainless steel, offers various desirable properties like durability, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio. These characteristics make it suitable for the production of components used in advanced technology products like smartphones, laptops, aerospace equipment, and medical devices.
- Q: How is corrosion-resistant stainless tool steel used in the production of food processing equipment?
- Corrosion-resistant stainless tool steel is used in the production of food processing equipment due to its ability to resist rust and corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, and food acids. This steel is specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions present in food processing environments, ensuring the equipment remains durable and hygienic. It is commonly used to manufacture blades, cutting tools, and various components of machines that come into direct contact with food. Its corrosion-resistant properties make it a reliable and safe choice for maintaining the quality and integrity of food during processing.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the aerospace fastener industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the aerospace fastener industry by providing high strength, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. Aerospace fasteners are essential components that hold various parts of an aircraft together, ensuring structural integrity and safety during flight. The use of special steel in manufacturing these fasteners allows them to withstand the demanding requirements of the aerospace industry. One of the key contributions of special steel to the aerospace fastener industry is its ability to maintain strength at high temperatures. Aircraft engines operate at extremely high temperatures, and fasteners made from special steel can withstand these conditions without losing their integrity. This is essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of the aircraft, as any failure of the fasteners could lead to catastrophic consequences. In addition to temperature resistance, special steel also offers exceptional strength and corrosion resistance. Aerospace fasteners made from special steel can withstand the tremendous forces and stresses experienced during flight, ensuring that the components remain securely fastened together. Moreover, they are highly resistant to corrosion, which is crucial considering the exposure of aircraft to harsh environmental conditions, including moisture and chemicals. The unique properties of special steel also enable the production of lightweight fasteners without compromising their strength. Weight reduction is a primary concern in the aerospace industry as it directly impacts fuel efficiency and overall performance. By utilizing special steel, manufacturers can design fasteners that are both strong and lightweight, contributing to the overall weight reduction efforts of modern aircraft. Furthermore, special steel allows for the production of fasteners with precise dimensions and tight tolerances. This is essential for achieving a secure fit between components, minimizing vibrations and potential damage caused by movement during flight. The accuracy and reliability of special steel fasteners are crucial for maintaining the structural integrity and safety of the aircraft. In conclusion, special steel significantly contributes to the aerospace fastener industry by providing the necessary strength, durability, temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance needed for aircraft applications. Its unique properties enable the production of lightweight yet robust fasteners, ensuring the structural integrity and safety of modern aircraft. Without special steel, the aerospace industry would face significant challenges in meeting the demanding requirements of aviation.
- Q: What are the specific requirements for special steel used in the nuclear industry?
- Special steel used in the nuclear industry must meet specific requirements to ensure safety, durability, and reliability. These requirements include: 1. Radiation Resistance: Special steel used in the nuclear industry must possess high radiation resistance to withstand the intense radiation levels present in nuclear reactors. This means that the steel should have low neutron absorption and minimal degradation under irradiation. 2. High Strength and Toughness: Nuclear reactors operate under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and pressure. Special steel used in the nuclear industry must have excellent strength and toughness to withstand these conditions and prevent structural failure. 3. Corrosion Resistance: The steel used in nuclear applications must be highly resistant to corrosion, as exposure to corrosive environments can compromise the integrity of the reactor components. This involves the steel having low susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking, intergranular corrosion, and pitting corrosion. 4. Low Impurity Content: Special steel used in the nuclear industry must have a low impurity content to minimize the potential for radioactive contamination. Any impurities present in the steel can become activated and release radioactive particles, posing a significant safety hazard. 5. Thermal Stability: The steel must have excellent thermal stability to maintain its mechanical properties even under high-temperature conditions. This ensures that the steel remains reliable and performs as expected during prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. 6. Non-Magnetic Properties: Some components in nuclear reactors require non-magnetic materials to prevent interference with sensitive instruments and equipment. Special steel used in these applications must possess non-magnetic properties to meet this requirement. 7. Regulatory Compliance: Special steel used in the nuclear industry must meet specific regulatory standards and certifications to ensure its suitability for use in nuclear facilities. These standards may vary depending on the country or region, but they typically encompass rigorous quality control, testing, and inspection procedures. Meeting these specific requirements for special steel used in the nuclear industry is crucial for maintaining the safety and integrity of nuclear reactors. Compliance with these standards ensures that the steel can withstand the harsh conditions and the potential hazards associated with nuclear power generation.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to product innovation?
- Special steel contributes to product innovation in several ways. Firstly, special steel offers enhanced mechanical properties such as high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. This allows designers and engineers to create innovative products that can withstand higher stresses, operate in extreme conditions, and have improved longevity. For example, special steel is commonly used in the aerospace industry to manufacture lightweight yet strong components that increase fuel efficiency and improve overall aircraft performance. Additionally, special steel can be tailored to have specific characteristics such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, or magnetic properties. This enables the development of innovative products that can operate in challenging environments, such as marine structures, power plants, or electronic devices. For instance, special stainless steel alloys are extensively used in the medical field to produce implants and surgical instruments that are biocompatible, durable, and resistant to harsh sterilization processes. Furthermore, special steel can be manufactured with precise dimensions and tolerances, allowing for intricate and complex designs. This promotes product innovation by enabling the creation of intricate components, such as gears, bearings, or turbine blades, that require high precision and reliability. These advanced designs can improve the efficiency, performance, and overall functionality of various products, ranging from automotive engines to wind turbines. Moreover, the versatility of special steel enables it to be combined with other materials, such as polymers or composites, to create hybrid products with unique properties. This opens up possibilities for innovation in various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer electronics. For example, special steel-reinforced concrete structures can be more robust and durable, while special steel-reinforced polymers can improve the strength and impact resistance of lightweight components. In conclusion, special steel contributes to product innovation by providing enhanced mechanical properties, tailored characteristics, precise dimensions, and the ability to be combined with other materials. These capabilities empower designers and engineers to create innovative products that have improved performance, durability, and functionality, leading to advancements in various industries.
- Q: How is special steel used in the production of bearings for high-speed applications?
- Special steel is used in the production of bearings for high-speed applications due to its unique properties such as high strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and fatigue. These bearings are subjected to intense loads and rotational speeds, and special steel helps ensure optimal performance and longevity. The use of special steel in bearing production allows for improved precision, reduced friction, and increased durability, ultimately enabling bearings to withstand the demanding requirements of high-speed applications.
- Q: What are the main properties of special steel?
- The main properties of special steel include high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, superior heat resistance, good toughness, and exceptional wear resistance. Additionally, special steel often exhibits high ductility, machinability, and weldability, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Send your message to us
Bs4449 500B Reinforcing Steel Rebar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 140 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































