Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid ATMP
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 6000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Amino tris(methylene phosphonic acid) / Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid/ ATMP / 6419-19-8 / C3H12NO9P3
CAS No. 6419-19-8
Molecular Formula: N(CH2PO3H2)3
Molecular weight: 299.05
Structural Formula: 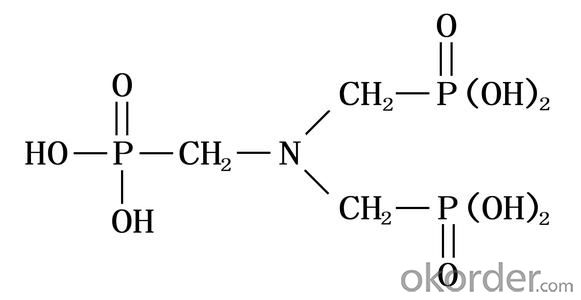
Properties:
ATMP has excellent chelation, low threshold inhibition and lattice distortion ability. It can prevent scale formation, calcium carbonate in particular, in water system. ATMP has good chemical stability and is hard to be hydrolyzed in water system. At high concentration, it has good corrosion inhibition.
ATMP is used in industrial circulating cool water system and oilfield water pipeline in fields of thermal power plant and oil refinery plant. ATMP can decrease scale formation and inhibit corrosion of metal equipment and pipeline. ATMP can be used as chelating agent in woven and dyeing industries and as metal surface treatment agent.
The solid state of ATMP is crystal powder, soluble in water, easily deliquescence, suitable for usage in winter and freezing districts. Because of its high purity, it can be used in woven & dyeing industries and as metal surface treatment agent.
Specification:
| Items | Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Solid | |
| Appearance | Clear, Colorless to pale yellow aqueous solution | White crystal powder |
| Active acid % | 50.0-51.0 | 95.0min |
| Chloride (as Cl-)% | 1.0 max | 1.0 max |
| pH value (1% solution) | 2.0 max | 2.0 max |
| Fe,mg/L | 10.0max | 20.0max |
| Density (20°C)g/cm3 | 1.31-1.35 | - |
| Colour APHA (Hazen) | 30.0max | - |
Application range&using method:
ATMP is usually used together with other organophosphoric acid, polycarboxylic acid and salt to built all organic alkaline water treatment agent. ATMP can be used in many different circulating cool water system. The recommended dosage is 5-20mg/L. As corrosion inhibitor, The recommended dosage is 20-80mg/L.
Package and Storage:
ATMP liquid: Normally In 30kg or 250kg net Plastic Drum;ATMP solid: 25kg inner liner polyethylene (PE) bag, outer plastic woven bag, or confirmed by clients request.Storage for ten months in room shady and dry place.
Safety Protection:
ATMP is Acidity, Avoid contact with eye and skin, once contacted, flush with water.
Shipping Date: Within 7-10 workdays after receiving your deposit.
Our Service:
Own Lab and joint venture factory.
Superb r&d team;Safety standardization production.
Rich experience in export and strong logistical support.
Good relationship with many large domestic pharmaceutical factory.
Perfect service, perfect supply chain.
- Q: Are biological enzymes harmful to humans?
- Biological enzymes through scientists more than a century of research, usually known as more than 3,000 kinds of enzymes, the current application of biological enzymes in the textile a wide range of technology, fiber modification, silk degumming, raw hemp (ramie, linen, Kenaf) degumming, dyeing and finishing of the desizing, refining, finishing and net cleaning processing, textile printing and dyeing wastewater treatment and garment processing and other aspects of the application. Enzyme technology has a unique advantage in improving dyeing and finishing processes, saving energy, reducing environmental pollution, improving product quality, adding value and developing new raw materials. At present in the textile processing using a wide range of enzyme preparations are mainly cellulase, protease, amylase, pectinase, lipase, peroxidase, laccase, glucose oxidase eight categories.
- Q: Can Cuo react as a catalyst with H2O2, does its quality and chemical properties change?
- 2H2O2 (CuO catalyzed) ====== 2H2O + O2 ↑
- Q: What is a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
- Hi Ganah! A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being used up in the reaction. They lower the activation energy for a reaction and also speed up the rate of the reaction (both in reverse and forward reactions). Let's look at a generic chemical reaction: A + B---C + D C + D---B + E Here, the catalyst is substance B because it is part of the chemical reaction but then it is not used up in the net reaction. See how it seems to be used up in the first step, but by the second step, the catalyst is made once again. The net reaction is A + B--->B + E and you can see how it is not consumed in the reaction. There are also 3 types of catalysts. Heterogeneous catalysts are catalysts that are in different phases than the reactants. An example would be like a reaction between two solids but a liquid is added to speed up the reaction. The liquid is in a different state of matter than the solids but it can still function as a heterogeneous catalyst. Homogeneous catalysts are catalysts that are in the same states of matter as the reactants. An example would then be ethyl acetate reacting with water to form acetic acid and ethanol with an acidic catalyst. They would all be liquids. Lastly, there are enzyme catalysts. These are proteins in your body that speed up biological reactions by reacting with substrates. I hope this helped and good luck with chem!
- Q: pls give one or two catalysts that are used in the industry for example:Rhodium catalyst in a catalytic converter of a car or the Iron catalyst for making ammoniaTHANKS :)
- i will tell you the hydrogen and carbonmonixide production in indsutry they will use alumina based nickel catalyst for adsorption of gases, at high temperature it will breaks as small molecules like hydrogen, co2, co,ch4, after they will separate them using carbon molecular seives as catalyst. another catalyst for hydrogenation of double bond is copper chromate for sulphur removal from disel and petrol they will use COMOX ( copper and molybdinum catalyst ) after then pass through zinc sulfide with hydrogen gas , the sulfur will removed as a hydrogen sulfide.
- Q: Seems intuitive that it wouldn't, but I dunno the qualitative difference between activation energy & Gibbs free energy. I'M TOO LAZY TO GOOGLE I GOTS STUFF TO DO
- A catalyst can change the activation energy not the Gibbs energy. The Gibbs energy is the energy difference between the initial state and final state. A catalyst cannot change that. Imagine you are driving from school to home. How you drive do not change the height difference between the school and your home. However, a catalyst can change your path which can change the routine you drive from school to home. So if there is a hill in between your school and you home, you have the choice to drive through it or drive around. Here is a picture: upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/co... A catalyst can change the height of the barrier, but cannot alter the initial or final state.
- Q: Can manganese dioxide be used as a catalyst for various chemical reactions?
- he catalyst does not participate in the reaction, such as on the platinum - rhodium alloy network, nitrogen and hydrogen reaction to produce ammonia .Piplatin - rhodium alloy network in the process of providing electrons (or similar effects, the specific is not clear, but does not react itself), the reaction Before and after the platinum - rhodium alloy network shape has not changed.
- Q: What are the catalysts?
- The catalyst is a substance that can change the rate of the reaction without changing the standard of the reaction Gibbs free, according to the definition of the International Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in 1981, Enthalpy change. This action is called catalysis. The reaction involving the catalyst is a catalytic reaction. The catalyst will induce a chemical reaction to change, causing the chemical reaction to become faster or slower or to undergo a chemical reaction at a lower temperature The catalyst is also known as a catalyst in industry, and the composition, chemical properties and quality of the catalyst itself do not change before and after the reaction;
- Q: In biology, the enzyme seems to be a tool for opening a reaction, such as the decomposition of cellulose, such as linked RNA and protein, no enzyme can not. But in chemistry, the catalyst is only a regulatory role, change the reaction rate only. The teacher said that the enzyme is the catalyst. Is there any other effect of the enzyme? (Ignorant high three dogs, you do not spray the big god)
- In fact, the chemical reaction is from the substrate (S) to the product (P). The chemical reaction is from the substrate (S) to the product (P). The chemical reaction is from the substrate (S) to the product (P) the process of. However, there is a free energy barrier between S and P, and in the absence of a catalyst, it is difficult to step through it and will pull something about it. Or understood to want you to jump 3 meters high, it is simply to life.
- Q: Are the catalysts for upgrading the weapons components that i may have a few of, or very rare ones?
- catalyst's cannot be used apart from transforming items. They will be greyed out at all other times. They always say in the description can be used as a catalyst as well. btw, are you using 36 sturdy bones or vibrance ooze to get the 3x multiplyer strait up? oh yeah, never ever use any item at all that says can be sold for a premium. Always sell those items, they are worth lots of money. And when you start buying components, only ever buy particle accelerator, perfect conductor or ultra compact reactor. Perfect conductor gives least bang for $$$ out of the 3, whereas ultra compact reactor gives most bang for $$$. And the sturdy bones and vibrance ooze for multiplyer purposes. Hope this helped :)
- Q: Write a chemical formula in a chemical laboratory without the use of a catalyst for oxygen
- 2KMnO4 ==== K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2 ↑
Send your message to us
Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid ATMP
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 6000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches





















