alloy angle steel 5#
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3.Material: JIS G3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
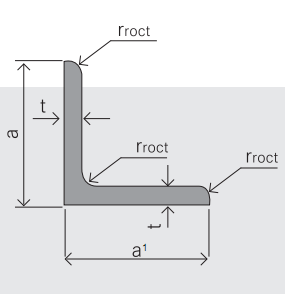
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material Specifications:
Grade | Yield Strength,N/mm² | Extension Strength N/mm² | |||
Thickness of Steel,mm | |||||
≦16 | >16-≦40 | >40-≦100 | >100 | ||
SS330 | ≧205 | ≧195 | ≧175 | ≧165 | 330-430 |
SS400 | ≧245 | ≧235 | ≧215 | ≧205 | 400-510 |
SS490 | ≧285 | ≧275 | ≧255 | ≧245 | 490-610 |
SS540 | ≧400 | ≧390 | - | - | ≧540 |
Usage & Applications JIS SS400 Angle Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
Production flow of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation



- Q: How do steel angles contribute to the sustainability of transportation systems?
- Several ways contribute to the sustainability of transportation systems through the utilization of steel angles. To begin with, steel angles find wide use in constructing infrastructure, such as bridges, highways, and railway tracks. These structures boast a longer lifespan and necessitate fewer repairs and replacements compared to alternative materials. As a result, maintenance costs and resource consumption are reduced. Furthermore, steel angles possess exceptional durability and resistance to severe weather conditions. This quality ensures the longevity and safety of transportation systems. Consequently, the need for frequent repairs or replacements is minimized, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact and carbon emissions associated with transportation infrastructure. In addition, steel angles possess a high strength-to-weight ratio, enabling the design of lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicles. Utilizing steel angles in the manufacturing process of automobiles, trains, and ships leads to reduced vehicle weight, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Moreover, steel angles can be easily recycled at the end of their lifecycle. Globally, steel is one of the most recycled materials, boasting a recycling rate of over 85%. By recycling steel angles, not only is the demand for virgin steel production reduced, but energy is also saved, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with extraction and manufacturing processes are decreased. Overall, the incorporation of steel angles in transportation systems promotes sustainability by fostering durability, decreasing maintenance needs, improving fuel efficiency, and enabling efficient recycling. These factors collectively contribute to minimizing the environmental impact and enhancing the long-term viability of transportation infrastructure.
- Q: What are the common welding techniques for steel angles?
- Some common welding techniques for steel angles include: 1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as stick welding, SMAW is a popular technique for welding steel angles. It involves using a consumable electrode coated in flux, which creates a protective shield around the weld pool. SMAW is versatile and can be used for various thicknesses of steel angles. 2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): This technique, also known as MIG welding, uses a continuous wire electrode and a shielding gas, typically a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide. GMAW offers high welding speeds and good control over the weld pool, making it suitable for welding steel angles. 3. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW): Similar to GMAW, FCAW uses a continuous wire electrode, but instead of a shielding gas, it utilizes a flux-filled wire. This flux creates a protective gas shield when heated, preventing contamination of the weld. FCAW is ideal for outdoor welding or in windy conditions. 4. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): Also known as TIG welding, GTAW uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas, usually argon. GTAW is a precise and clean welding process that produces high-quality welds on steel angles. It is commonly used for thin steel angles or when aesthetics and control are crucial. 5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): SAW is a semi-automatic or automatic welding process that involves feeding a continuous wire electrode and a granular flux into the weld zone. The flux covers the weld, preventing atmospheric contamination. SAW is often used for thicker steel angles and provides high deposition rates. It is important to choose the appropriate welding technique based on the specific requirements of the steel angle joint, such as thickness, joint design, and desired weld quality. Additionally, proper preparation, including cleaning and preheating if necessary, is essential to ensure successful welds on steel angles.
- Q: Can steel angles be used as decorative elements?
- Certainly, steel angles have the potential to serve as delightful decorative elements. Steel angles, also referred to as L-shaped metal profiles, possess the ability to introduce an industrial or contemporary aesthetic to any given area. They possess a multitude of applications that can elevate the overall design and appearance of a room or outdoor space. One commonly employed application of steel angles as decorative elements is in the realm of architectural and interior design. These angles can be utilized as trim or edging on walls, ceilings, or furniture, thereby bestowing a distinct and fashionable appearance. Moreover, they can be employed to craft captivating patterns or designs on surfaces, such as herringbone or chevron patterns, which add visual allure and a contemporary ambiance. Furthermore, steel angles can be employed as decorative supports or brackets for shelves, countertops, or other fixtures. In addition to providing structural support, these angles contribute a modern and industrial touch to the overall design concept. By painting or powder-coating steel angles in various colors, they can be further enhanced to match the desired aesthetic, thereby augmenting their decorative appeal. Additionally, steel angles can also be employed as decorative elements in outdoor spaces. They can be incorporated into fences, gates, or railings, offering a durable and stylish solution. In the realm of landscaping, steel angles can be employed as decorative accents, such as creating borders or delineating flower beds, thereby introducing a contemporary design approach to the outdoor environment. In summary, steel angles present a versatile and visually appealing option for incorporating decorative elements into a wide range of design projects. Their sleek and industrial appearance, coupled with their strength and durability, render them a popular choice for both interior and exterior decorative purposes.
- Q: Can steel angles be welded or joined together?
- Yes, steel angles can be welded or joined together. Welding is a commonly used method to connect steel angles, as it provides a strong and durable bond. The process involves melting the edges of the angles and then fusing them together using a welding electrode. Welding not only creates a secure connection between the steel angles but also ensures structural integrity. It is important to follow proper welding procedures and techniques to ensure the quality and strength of the joint. Additionally, steel angles can also be joined together using other methods such as bolting or riveting, depending on the specific application and requirements.
- Q: What are the limitations of using steel angles in certain applications?
- There are several limitations to consider when using steel angles in certain applications. Firstly, steel angles may not be suitable for applications that require high strength or load-bearing capacities. While steel angles are generally strong and durable, they may not be able to withstand extremely heavy loads or forces. In such cases, other types of structural steel sections, such as I-beams or hollow sections, may be more appropriate. Secondly, steel angles may not be ideal for applications that require tight tolerances or precise dimensions. Due to the manufacturing process, steel angles can have slight variations in size and shape, which may not be acceptable in certain applications. In these cases, custom-made or precision-machined steel components may be necessary. Furthermore, steel angles may have limitations in terms of corrosion resistance. If the application involves exposure to harsh environments, such as marine or chemical environments, the steel angles may corrode over time. In these situations, alternative materials with better corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or aluminum, may be more suitable. Lastly, steel angles may not provide the desired aesthetic appearance in certain applications. While steel angles are commonly used in structural and industrial applications, they may not be visually appealing or compatible with architectural or decorative applications. In such cases, alternative materials or finishes may be preferred to achieve the desired aesthetics. Overall, while steel angles have numerous advantages in terms of strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, they also have limitations in certain applications. It is essential to carefully assess the specific requirements of the application and consider these limitations before choosing to use steel angles.
- Q: How do steel angles perform in terms of electromagnetic shielding?
- Steel angles have a reputation for being highly effective in terms of electromagnetic shielding. This is mainly because of their exceptional electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability. These particular qualities enable steel angles to efficiently redirect or absorb electromagnetic waves, resulting in a reduced impact on adjacent electronic devices or sensitive equipment. The shape and geometry of steel angles also play a role in their shielding capabilities, as they can be strategically positioned to create barriers or enclosures that obstruct or redirect electromagnetic fields. Additionally, the thickness or gauge of the steel angle can further amplify its shielding performance. In general, steel angles find widespread use in a variety of applications where minimizing or controlling electromagnetic interference is crucial, such as in the construction, telecommunications, electronics, and automotive industries.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface preparation for steel angles?
- To ensure proper adhesion of coatings, improve corrosion resistance, and enhance overall durability, there are various methods available for preparing the surface of steel angles. Some commonly used methods include the following: 1. Mechanical Cleaning: Physical tools like wire brushes, sandpaper, or abrasive discs are used to physically eliminate dirt, rust, mill scale, and other contaminants from the steel angle's surface. While this method is simple and cost-effective, it may not be effective for heavy corrosion or stubborn deposits. 2. Chemical Cleaning: Acid-based solutions or pickling pastes are applied to dissolve rust, scale, and other contaminants on the surface. After a specific period of time, the solution is rinsed off. Chemical cleaning is highly effective for removing stubborn deposits but requires careful handling and proper disposal of the chemicals. 3. Power Tool Cleaning: Power tools such as grinders, sanders, or needle guns with abrasive attachments are utilized to remove rust, scale, and contaminants. This method is faster and more efficient than manual mechanical cleaning, making it suitable for large-scale surface preparation. 4. Blast Cleaning: Also known as abrasive blasting, this method involves projecting abrasive materials (e.g., sand, steel grit, or glass beads) onto the steel surface at high velocity using compressed air or centrifugal force. Blast cleaning effectively removes rust, scale, and contaminants, resulting in a clean and profiled surface. While widely used in industrial applications, it requires proper safety measures to protect workers from exposure to abrasive materials. 5. Flame Cleaning: By directing a high-temperature flame onto the steel surface, flame cleaning removes contaminants. The intense heat burns off organic materials and evaporates moisture, leaving a clean surface. This method is particularly effective for removing oil, grease, and paint residues. 6. Conversion Coating: A chemical solution is applied to the steel surface, reacting with the metal to form a thin protective layer. This layer enhances the adhesion of subsequent coatings and provides additional corrosion resistance. Phosphating, chromating, and passivation are common types of conversion coatings. It's important to consider factors such as the extent of corrosion, desired coating system, and environmental conditions when selecting the most suitable surface preparation method for steel angles. Consulting experts or referring to industry standards can assist in determining the appropriate method for a specific application.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for support structures in sports arenas or stadiums?
- Sports arenas or stadiums can make use of steel angles for their support structures. The construction industry often opts for steel angles due to their strength, durability, and versatility. These angles are particularly suitable for support structures as they can handle heavy loads and offer stability. In the realm of sports arenas or stadiums, steel angles serve various purposes. They can be utilized to support the roof, create seating platforms, construct staircases, and form the framework for walls and partitions. Architects and engineers can design custom support structures that meet the specific requirements of each sports arena or stadium, thanks to the flexibility of steel angles. Moreover, steel angles can be easily fabricated and joined, which makes them ideal for constructing complex support systems. Their ability to resist bending, twisting, and compression ensures the overall stability and safety of the structure. Additionally, steel is an environmentally friendly material as it is 100% recyclable. By using steel angles for support structures, the construction industry can contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting a more sustainable future. In conclusion, steel angles are a dependable and efficient choice for support structures in sports arenas or stadiums. Their strength, durability, versatility, and sustainability make them an excellent option for ensuring the safety and stability of these large-scale structures.
- Q: What is the cost of steel angles compared to other materials?
- The price of steel angles compared to other materials can differ based on various factors such as the grade and type of steel, market conditions, and availability. Nevertheless, in general, steel angles are typically a cost-effective choice when compared to other materials commonly utilized for structural or construction purposes. Steel angles find extensive use in numerous industries, including construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure, owing to their durability, strength, and versatility. When compared to materials like aluminum or stainless steel, steel angles are often more economical. This is due to the wide availability of steel as a material and its ability to be manufactured in large quantities, resulting in cost efficiencies in the production process. Moreover, steel angles have a lengthy lifespan and necessitate minimal upkeep, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness over time. They also possess exceptional load-bearing capabilities, making them suitable for a broad range of applications, including building frames, support structures, and machinery. However, it is crucial to note that the cost of steel angles can still fluctuate depending on the specific requirements and specifications of a project. Factors such as size, length, thickness, and any additional treatments or finishes can impact the price. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with suppliers or manufacturers to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing information based on the individual needs of the project.
- Q: How do you inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle?
- To inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle, the following steps can be followed: 1. Tools required for the task are a measuring tape or ruler, a protractor, and a square. 2. Begin by examining the length of the steel angle. Place one end of the measuring tape or ruler on one side of the angle and extend it to the opposite side. Make sure the measuring tape is straight and aligned with the edge of the angle. Read the measurement in inches or millimeters to determine the length. 3. Proceed to measure the width or thickness of the angle. Position the measuring tape or ruler perpendicular to the length of the angle and measure the distance between the two parallel sides. This will provide the width measurement. 4. To measure the height or depth of the angle, position the measuring tape or ruler perpendicular to the width measurement. Again, ensure that the measuring tape is aligned with the edge of the angle and measure the distance between the two sides. This will yield the height measurement. 5. To verify the accuracy of the angle being 90 degrees, employ a square. Place the square against one side of the angle and ensure alignment with the adjacent side. Check if the corner of the angle fits perfectly within the square. If it does, the angle is indeed 90 degrees. If not, adjustments may be necessary. 6. Lastly, if the angle of the steel angle needs measurement, a protractor can be employed. Align one side of the protractor with one side of the steel angle and observe where the other side intersects with the protractor scale. Read the angle measurement to determine the exact angle. By adhering to these steps and utilizing the appropriate tools, one can effectively inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle.
Send your message to us
alloy angle steel 5#
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























