Water Treatment Liquid Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 6000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Amino tris(methylene phosphonic acid) / Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid/ ATMP / 6419-19-8 / C3H12NO9P3
CAS No. 6419-19-8
Molecular Formula: N(CH2PO3H2)3
Molecular weight: 299.05
Structural Formula: 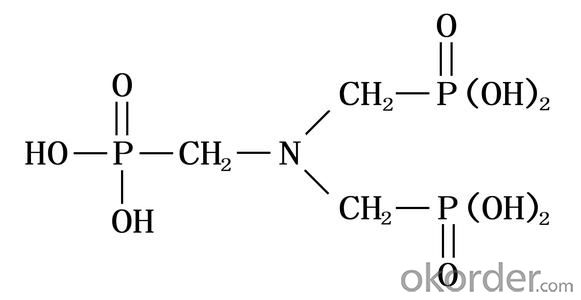
Properties:
ATMP has excellent chelation, low threshold inhibition and lattice distortion ability. It can prevent scale formation, calcium carbonate in particular, in water system. ATMP has good chemical stability and is hard to be hydrolyzed in water system. At high concentration, it has good corrosion inhibition.
ATMP is used in industrial circulating cool water system and oilfield water pipeline in fields of thermal power plant and oil refinery plant. ATMP can decrease scale formation and inhibit corrosion of metal equipment and pipeline. ATMP can be used as chelating agent in woven and dyeing industries and as metal surface treatment agent.
The solid state of ATMP is crystal powder, soluble in water, easily deliquescence, suitable for usage in winter and freezing districts. Because of its high purity, it can be used in woven & dyeing industries and as metal surface treatment agent.
Specification:
| Items | Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Solid | |
| Appearance | Clear, Colorless to pale yellow aqueous solution | White crystal powder |
| Active acid % | 50.0-51.0 | 95.0min |
| Chloride (as Cl-)% | 1.0 max | 1.0 max |
| pH value (1% solution) | 2.0 max | 2.0 max |
| Fe,mg/L | 10.0max | 20.0max |
| Density (20°C)g/cm3 | 1.31-1.35 | - |
| Colour APHA (Hazen) | 30.0max | - |
Application range&using method:
ATMP is usually used together with other organophosphoric acid, polycarboxylic acid and salt to built all organic alkaline water treatment agent. ATMP can be used in many different circulating cool water system. The recommended dosage is 5-20mg/L. As corrosion inhibitor, The recommended dosage is 20-80mg/L.
Package and Storage:
ATMP liquid: Normally In 30kg or 250kg net Plastic Drum;ATMP solid: 25kg inner liner polyethylene (PE) bag, outer plastic woven bag, or confirmed by clients request.Storage for ten months in room shady and dry place.
Safety Protection:
ATMP is Acidity, Avoid contact with eye and skin, once contacted, flush with water.
Shipping Date: Within 7-10 workdays after receiving your deposit.
Our Service:
Own Lab and joint venture factory.
Superb r&d team;Safety standardization production.
Rich experience in export and strong logistical support.
Good relationship with many large domestic pharmaceutical factory.
Perfect service, perfect supply chain.
- Q: in acid-catalyzed reaction,there are some books show the acid catalyst as H+ and there are some show it as H3O+ .Are they the same?
- Sort of. If the reaction is under aqueous conditions (any water is included in the reaction), then yes, H+ = H3O+. This is because free protons present (H+) will be coordinated generally to molecules of water [thus H2O + H+ =H3O+ ]. But there are reaction conditions where water is not present, but an acid catalyst is still possible. In these cases, the acid catalyst may frequently be indicated as simply H+. Either way, the function in most of your reaction mechanisms is basically the same, whether indicated as H+ or H3O+ -- and that's to protonate molecules (Lewis or Bronsted bases) with H+. Concentrated sulfuric acid would be an example of a mostly-anhydrous (no water) strong proton/acid source (H+). Hydrochloric acid (HCl) frequently is available as an aqueous solution, even concentrated HCl is an aqueous solution of HCl. HCl itself is a gas under ambient conditions... but it has solubility in water and thus is conveniently sold frequently as an aqueous solution (which could be represented as H3O+)
- Q: What is catalyst in Science?
- A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction by decreasing the activation energy (energy required to start the reaction). It does so by creating a new reaction mechanism (the way the reaction happens on a molecular level) that happens more easily and with less energy. For example, a catalyst could attract both reactants, thus bringing them directly together and facilitating the reaction.
- Q: Name one case in which catalyst poisoning is useful?
- Usually, catalyst poisoning is undesirable as it leads to a loss of usefulness of expensive noble metals or their complexes. However, poisoning of catalysts can be used to improve selectivities of reactions. In the classical Rosenmund reduction of acyl chlorides to aldehydes, the palladium catalyst (over barium sulfate or calcium carbonate) is poisoned by the addition of sulfur or quinoline. This system reduces triple bonds faster than double bonds allowing for an especially selective reduction. Lindlar's catalyst is another example — palladium poisoned with lead salts. As described by its inventor,[1][2] the catalyst is prepared by reduction of palladium chloride in a slurry of calcium carbonate followed by adding lead acetate. By this approach, one obtains a catalyst with a large surface area. Further deactivation of the catalyst with quinoline enhances its selectivity, preventing formation of alkanes. An example of alkyne reduction is the reduction of phenylacetylene to styrene.[1] en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lindlar%27s...
- Q: describe a biological catalyst?
- A biological catalyst is the almighty enzyme. An enzyme takes the food that animals eat, yes including you, and breaks the raw stuff into more tangible byte sizes pieces for all the cells of a living organism. So essentially a catalysts is a mover of a biological system. Whole systems such as the apex predator the great bald eagle. I think the whole system catalyst are the decomposer organisms. The little crawlers like shredders and mushrooms. I hope that this helps
- Q: Cl + O3 ---> ClO + O2O + ClO ---> Cl + O2= O + O3 ----> 2O2What is the catalyst? The intermediate?How do you know which is which? If the rate law is rate=k [O3] [Cl]determine:a) the overall order.b) unit for k.c) the rate determining step, justify your answer.
- Cl is the catalyst. ClO the intermediate. The catalyst is the component which does not change in overall reaction. He forms some intermediate component(s) with the reactants. In the later reaction steps the intermediate(s) react forming the catalyst in its original state. (a) The overall order is the sum of the orders with respect to the components: n = 1 +1 = 2 (b) the unit of the rate of reaction is r [=] mol/ (Ls) (more general mol per unit time and volume) compare dimensions mol / (Ls) [=] k · mo/L · mol/L =k [=] L/(s mol) (more general unit volume per unit time and mole) (c) First reaction For elementary reaction steps the order of the reaction rate with respect to a reactant is equal to stoichiometric coefficient. Hence the rate of first reaction is: r? = k?·[Cl]·[O?] Overall rate is given by the rate determining step, while other reaction steps are in equilibrium: r = r? = k?·[Cl]·[O?] If second reaction is the rate determine step r? = k?·[O]·[ClO] while reaction 1 is at equilibrium K? = ( [ClO]·[O?] ) / ( [Cl]·[O?] ) =[ClO] = K?·( [Cl]·[O?] ) / [O?] the overall rate would be: r = r? = k?·[O]·[ClO] = K?·k?·[O]·[Cl]·[O?] / [O?] = k·[O]·[Cl]·[O?] / [O?] That doesn't match the observed rate law
- Q: I dont know what it is but when i open up my computer it comes up and it says that its not working? so i really dont know what to do.
- ATI Catalyst Control Centre is a control program for ATI graphics cards. If you have an ATI graphics card, go to the ATI website and download and reinstall the program.
- Q: Seems intuitive that it wouldn't, but I dunno the qualitative difference between activation energy & Gibbs free energy. I'M TOO LAZY TO GOOGLE I GOTS STUFF TO DO
- A catalyst can change the activation energy not the Gibbs energy. The Gibbs energy is the energy difference between the initial state and final state. A catalyst cannot change that. Imagine you are driving from school to home. How you drive do not change the height difference between the school and your home. However, a catalyst can change your path which can change the routine you drive from school to home. So if there is a hill in between your school and you home, you have the choice to drive through it or drive around. Here is a picture: upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/co... A catalyst can change the height of the barrier, but cannot alter the initial or final state.
- Q: Is it not the rate to accelerate the addition of the catalyst to the catalyst, and that is why the balance does not move
- If the reaction before the catalyst, you can speed up the reaction rate, that is to achieve the balance required to reduce the time, but to balance the system when the same concentration
- Q: Why does the CuO catalyze the reaction rate faster and faster when catalyzing the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide or tell me how to make the catalyst catalyst faster
- Heating or increasing the contact surface of the reactants.
- Q: Does all chemical reactions have a catalyst?
- Not some reaction without catalyst
Send your message to us
Water Treatment Liquid Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 6000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches



















