Spring Steel Plate AISI 6150 Steel Sheet
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Spring Steel Plate AISI 6150 Steel Sheet
Product information:
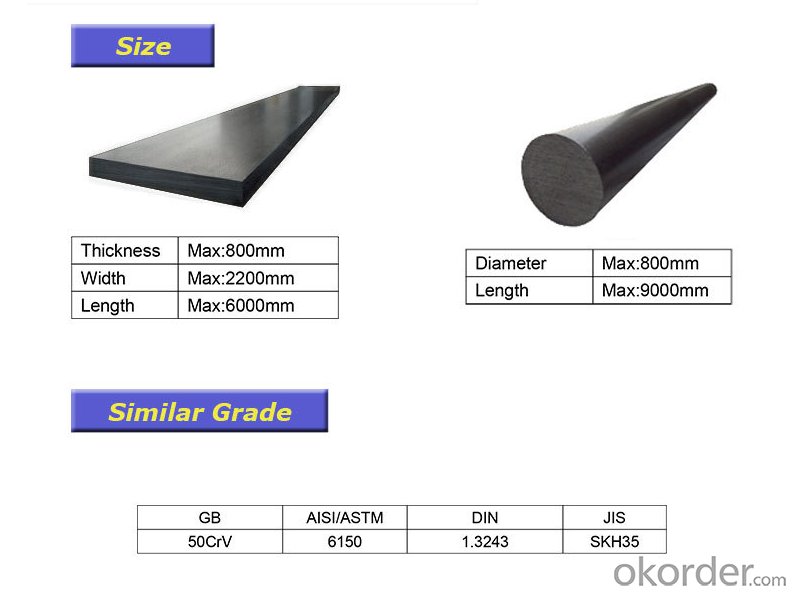
| Measurement | Thickness | Width |
| 6mm~35mm | 40mm~150mm | |
| Edge(Cross Section) | Round edge profile to DIN59145 | Square edge profile to DIN59146 |
| Bundle Weight | Around 2.0 MT | |
| Technique | Hot Rolled | |
| Surface | Grooved | Plain-smoothed |
| Quenchant | Oil/Water | |
| Temper Stressing | 480째C-560째C | |
| Quenching Temprature: | 800째C-1000째C | |
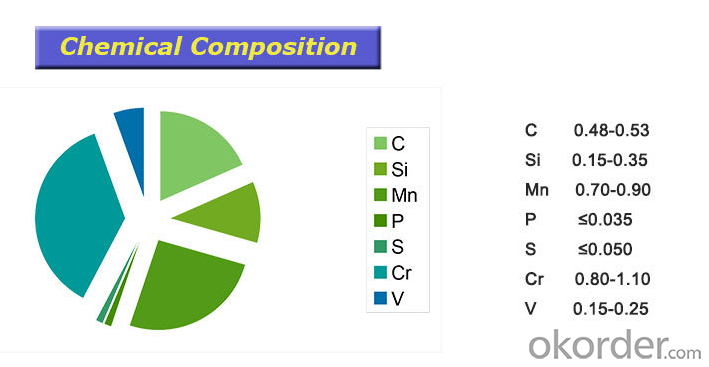
| OEM | Material Composition Offered by Customers | |
| Application | sup9/sup9a/sup10/55Cr3/50CrV4 | Automotive suspension springs |
| sup7/9260/30CrMnB/27CrMnB/1045 | Rotary tools and Blades | |
| Payment Term | 100% L/C at Sight. | 30% T/T Down Payment, Balance Against B/L Copy. |
| Packing | In bundles. Each bundle packed with 2 steel strips and 3 steel wires. | |

Other products show:

Our workshop show:

Our service:
-High manufacturing accuracy
-High strength
-Small inertia resistance
-Strong heat dissipation ability
-Good visual effect
-Reasonable price
Chose happens because of quality, then price, We can give you both.Additionally, we can also offer professional products inquiry, products knowledge train(for agents), smooth goods delivery, exellent customer solution proposals.Our service formula: good quality+good price+good service=customer's trust
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem.
If you need the sample, please feel free to let me know. Any question, we will contact you ASAP!
- Q: What are the applications of special steel in the aerospace sector?
- Special steel has various applications in the aerospace sector due to its exceptional properties. It is used for manufacturing critical components such as turbine blades, landing gear, and structural parts. The high strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance of special steel make it ideal for withstanding extreme conditions experienced during flight. Additionally, its lightweight nature contributes to fuel efficiency and overall performance improvement in aircraft.
- Q: How is high-temperature stainless steel used in the production of gas turbines?
- High-temperature stainless steel is used in the production of gas turbines due to its exceptional heat resistance and corrosion resistance properties. It is utilized to make critical components such as turbine blades, rotors, and casings that are exposed to extreme temperatures and harsh environments. This stainless steel helps gas turbines operate efficiently and reliably by withstanding high temperatures without losing strength or degrading, ultimately enhancing the performance and lifespan of gas turbines.
- Q: What are the different forging grades of special steel?
- There are several different forging grades of special steel, including but not limited to stainless steel, alloy steel, carbon steel, tool steel, and high-speed steel.
- Q: What are the effects of different heat treatment processes on special steel?
- Different heat treatment processes have varying effects on special steel. Annealing, for example, helps to soften the steel and increase its ductility, making it easier to shape and work with. Hardening processes, such as quenching and tempering, increase the steel's hardness and strength, making it suitable for applications that require toughness and resistance to wear. Tempering, on the other hand, reduces the hardness of the steel while increasing its toughness. Additionally, heat treatment processes can also influence the steel's internal structure, such as the size and distribution of grains, which in turn affects its mechanical properties. Overall, the choice of heat treatment process can significantly impact the final characteristics of special steel, allowing for customization to meet specific performance requirements.
- Q: What is the significance of tensile strength in special steel?
- Tensile strength is of great significance in special steel because it determines the steel's ability to withstand stretching or pulling forces without breaking or deforming. This property is crucial in various industries, especially in manufacturing and construction, where high tensile strength is required for structural integrity and safety. Special steel with superior tensile strength can withstand heavy loads, resist impacts, and provide durability, making it highly sought after in applications such as building infrastructure, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace engineering.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the automotive engine industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the automotive engine industry by providing superior strength, durability, and performance to various engine components. The unique properties of special steel make it an ideal choice for manufacturing critical parts, such as crankshafts, connecting rods, camshafts, valves, and cylinder liners. One of the key contributions of special steel to the automotive engine industry is its exceptional strength and resistance to high temperatures. Special steel alloys are designed to withstand the intense heat and pressure generated within an engine, ensuring that these components maintain their structural integrity and functionality under extreme conditions. This durability translates into increased engine efficiency, reliability, and longevity. Moreover, special steel's superior mechanical properties, including high tensile and impact strength, allow for the production of lighter yet stronger engine components. By reducing the weight of these parts, special steel helps to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, making it an environmentally friendly choice for automotive manufacturers. Special steel also contributes to the automotive engine industry by enabling the production of more complex and precise engine components. The excellent machinability and formability of special steel alloys allow for intricate designs, tighter tolerances, and improved performance. This, in turn, contributes to the overall efficiency and power output of the engine. Furthermore, special steel's corrosion resistance properties are crucial in preventing engine components from deteriorating over time. The ability to resist rust and other forms of corrosion ensures that the engine operates at optimal levels for an extended period, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall performance. In summary, special steel's unique properties, including strength, durability, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance, make it an essential material in the automotive engine industry. Its contribution lies in providing superior performance, efficiency, and longevity to critical engine components, ultimately enhancing the overall driving experience for consumers.
- Q: What is the maximum temperature that special steel can withstand?
- The maximum temperature that special steel can withstand depends on the specific type of steel being used. Special steels are designed to have enhanced properties, such as high heat resistance, which allows them to withstand higher temperatures than standard steels. For example, some special steels, such as heat-resistant stainless steels, can withstand temperatures up to around 1200 degrees Celsius (2200 degrees Fahrenheit). These steels are often used in applications where high temperatures are encountered, such as in furnaces, boilers, and exhaust systems. Other types of special steels, such as tool steels or high-speed steels, may have different maximum temperature limits. These steels are commonly used in cutting tools, molds, and machining applications, where they need to maintain their hardness and strength at elevated temperatures. It is important to note that the maximum temperature that special steel can withstand also depends on factors such as the duration of exposure to the high temperature, the specific alloy composition, and any additional heat treatment processes that have been applied. Therefore, it is crucial to consult the manufacturer's specifications or seek professional advice for accurate information on the maximum temperature limit for a particular type of special steel.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the medical industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the medical industry. It is commonly employed in the production of surgical instruments, medical implants, and equipment due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Special steel alloys, such as stainless steel and titanium alloys, are extensively utilized in various medical applications to ensure patient safety and enhance the effectiveness of medical procedures.
- Q: What are the casting methods for special steel?
- There are several casting methods used for special steel, including investment casting, sand casting, and centrifugal casting. Investment casting involves creating a wax pattern of the desired shape, which is then coated in ceramic and melted away, leaving a cavity that is filled with molten steel. Sand casting involves making a mold from a mixture of sand and a binder, and pouring molten steel into the mold cavity. Centrifugal casting utilizes centrifugal force to distribute molten steel into a mold, resulting in a more uniform casting with fewer defects.
- Q: What are the key characteristics to consider when selecting special steel?
- When selecting special steel, key characteristics to consider include the steel's composition, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and cost efficiency.
Send your message to us
Spring Steel Plate AISI 6150 Steel Sheet
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























