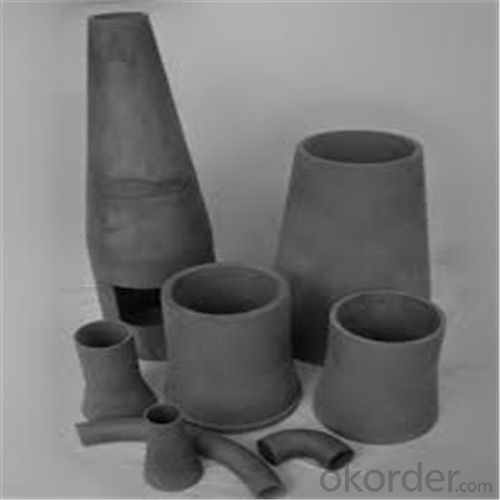
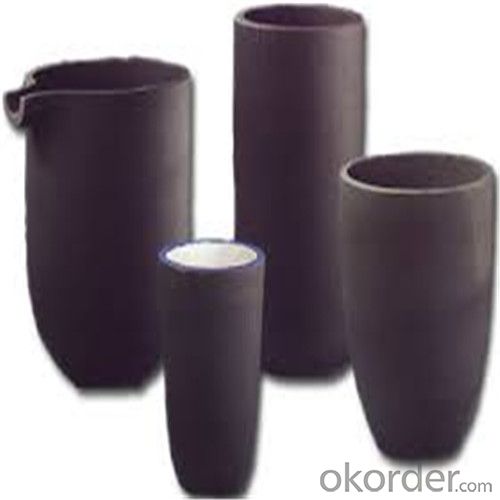
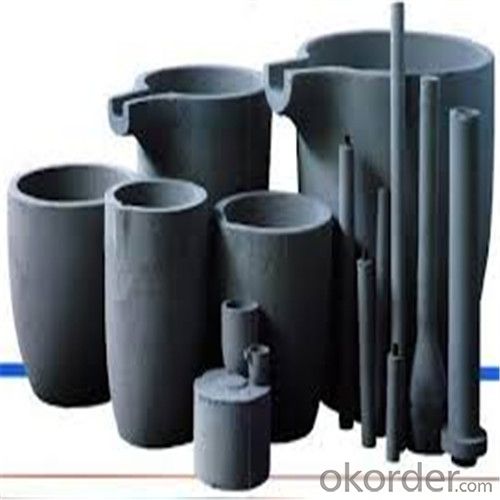
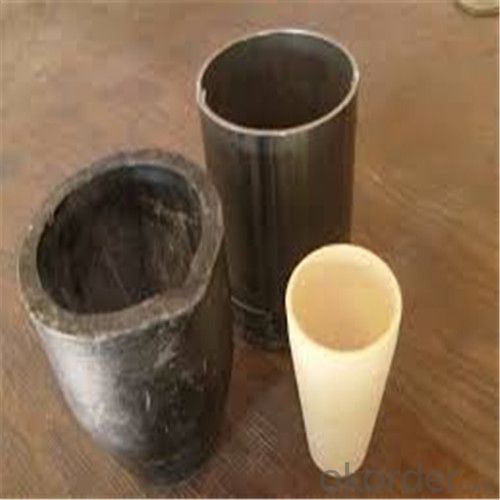
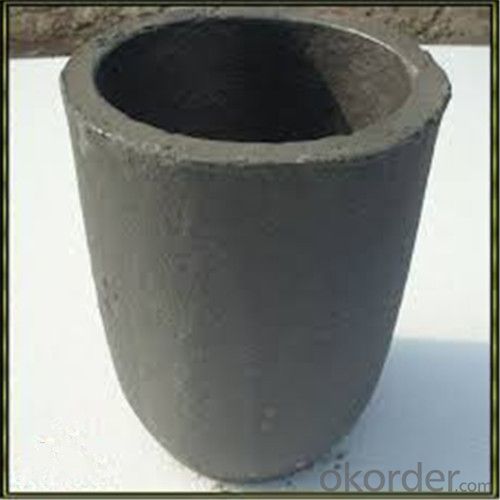
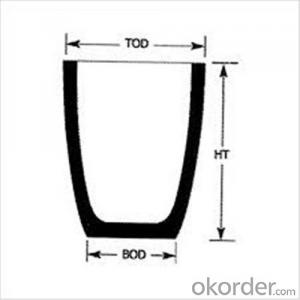
High Heat Resistance Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium and Copper
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
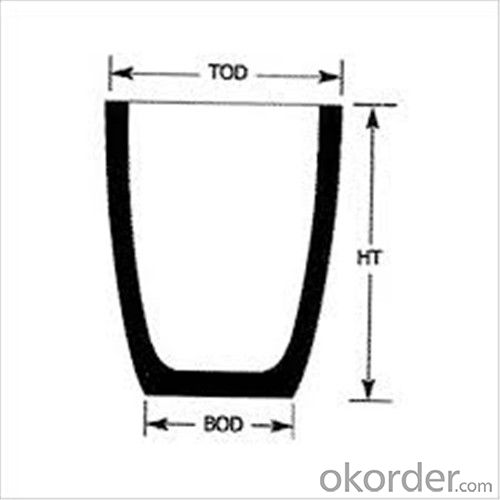

Features of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
1. resistance to deformation at high temperature,
2. thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance.
3. anti-oxidation, anti- erosion.
Usage of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
electricity and steel slag trench,
coal chemical and mining transport pipeline.

- Q: Why are there too many impurities in the gravity casting products of aluminum alloy, so they can not be welded well by argon arc welding?
- The filter is not added in the casting process, some slag ran in, leading to the casting surface or internal slag, leakage or air pressure testing, due to impurities, argon arc welding welding is up to where there is always staying, not fusion. The solution, first of all to choose high purity aluminum ingots, some rural plant products do not choose, are turning or cutting scrap materials in investment, not too many impurities; secondly in the casting process, increase to two times to minimize the filtering impurities.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for gold melting?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for gold melting. Graphite crucibles have high melting points and excellent heat resistance, making them suitable for melting and containing gold during the refining process.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible handle for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible handle for a specific application, one must consider factors such as the size and weight of the crucible, the material being melted or heated, and the temperature at which it will be used. The handle should be sturdy enough to support the weight of the crucible and provide a comfortable grip for the user. Additionally, it is important to choose a handle material that can withstand the high temperatures without melting or deforming. Consulting the manufacturer's guidelines or seeking expert advice can help in selecting the right crucible handle for the specific application.
- Q: Graphite crucible heat resistance, then graphite crucible can ignite? Charcoal is mainly composed of graphite, why charcoal can be ignited?
- Graphite is a very pure material, graphite is a transitional type crystal. Each layer of graphite carbon atoms in nonpolar covalent bond connected between molecular layer and graphite by intermolecular forces. The melting point of connection is 3652 to 3697 DEG C (sublimation), so the high temperature graphite crucible.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible stirring rod for a specific application?
- To identify the appropriate stirring rod for a particular crucible application, one must take into account several factors. Firstly, it is necessary to evaluate the nature of the material being stirred in the crucible. The different materials may necessitate distinct stirring rods to guarantee efficient blending and avoid contamination. For instance, if the substance being stirred is corrosive, a stirring rod composed of corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) should be chosen. Secondly, the size and shape of the crucible need to be considered. The stirring rod must be of sufficient length to reach the bottom of the crucible and possess a shape that permits effective stirring without excessive splashing or turbulence. Furthermore, the temperature and pressure conditions of the application must be taken into account. Elevated temperatures or pressures may require the use of stirring rods made from heat-resistant materials such as quartz or ceramic. Lastly, the specific requirements of the experiment or process should be accounted for. If precision and accuracy are vital, a stirring rod with a specific shape or design that allows for precise control of the mixing process may need to be selected. In conclusion, the selection of an appropriate stirring rod for a specific crucible application necessitates the consideration of the material being stirred, the size and shape of the crucible, the temperature and pressure conditions, and the specific requirements of the experiment or process. By thoroughly evaluating these factors, one can choose a stirring rod that ensures effective mixing and optimal outcomes.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic molding?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for ceramic molding. Graphite crucibles are primarily used for melting and holding metals and alloys at high temperatures. They are not suitable for ceramic molding as they do not possess the necessary properties to withstand the high temperatures required for ceramic firing and molding processes. Ceramic molding typically involves firing the ceramic material at temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 degrees Celsius, which can cause graphite crucibles to degrade, crack, or even melt. For ceramic molding, it is recommended to use crucibles made from materials such as alumina, zirconia, or other refractory materials that can withstand the extreme temperatures involved in the ceramic firing process.
- Q: Single crystal furnace quartz crucible cast 22 inch 175 kilograms of feed it
- Back chaos, in fact we are very worried about the recovery of this material strength and composition by crucible crucible change can not be used, but also fast, so the results will soon be out.
- Q: What are the common uses of graphite?
- As a wear-resistant and lubricating material, graphite is often used as a lubricant in the mechanical industry. Lubricants can not be used in high speed, high temperature, high pressure conditions, and graphite wear-resistant materials can be at -200 - 2000 temperature, and at a high sliding speed, without lubricating oil work. Many transporting corrosive media devices are widely used, which is made of graphite material piston ring, the sealing ring and the bearing, they are running, without adding lubricating oil, graphite and many metal processing (drawing, drawing) the good lubricant.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder sintering?
- Indeed, metal powder sintering can be accomplished using graphite crucibles. The utilization of graphite as crucible material is widespread owing to its elevated melting point, chemical inertness, and thermal conductivity. The process of metal powder sintering entails subjecting the powder to intense heat in order to fuse the particles together, and graphite crucibles possess the capability to withstand such high temperatures without undergoing any reaction with the metal powders. Moreover, the commendable thermal conductivity of graphite crucibles facilitates the even distribution of heat, thereby ensuring the uniform sintering of the metal powder. Consequently, graphite crucibles are an appropriate choice for carrying out metal powder sintering procedures.
- Q: How do you see the conch alive?
- Slightly touched conch soft tissue, it will be sensitive to contraction, the more sensitive, the more fresh, but not fresh or dead
Send your message to us
High Heat Resistance Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium and Copper
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords