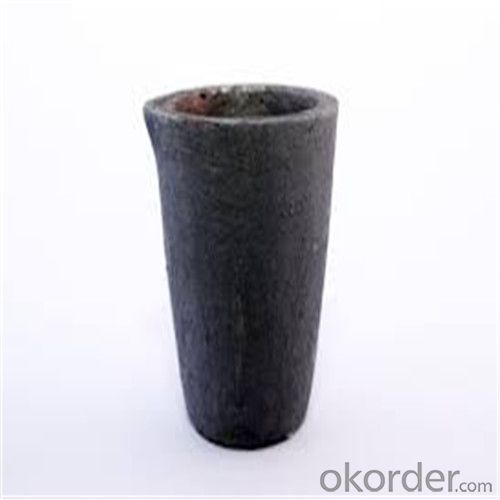
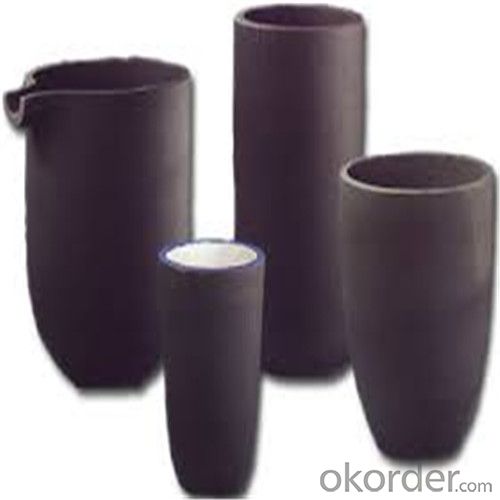
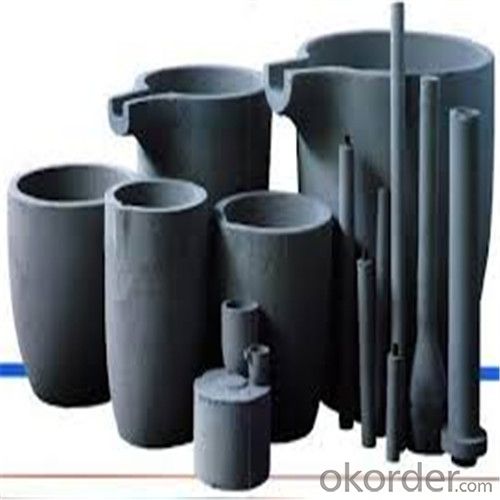
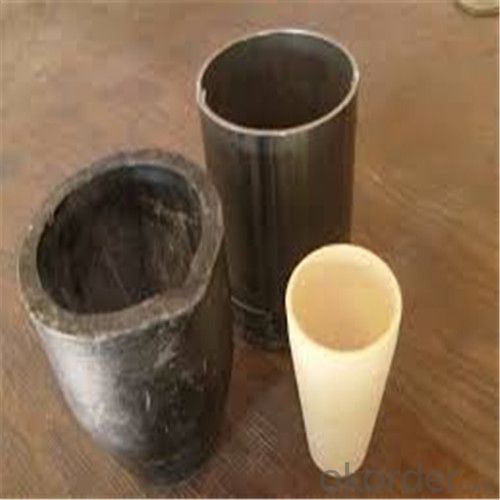
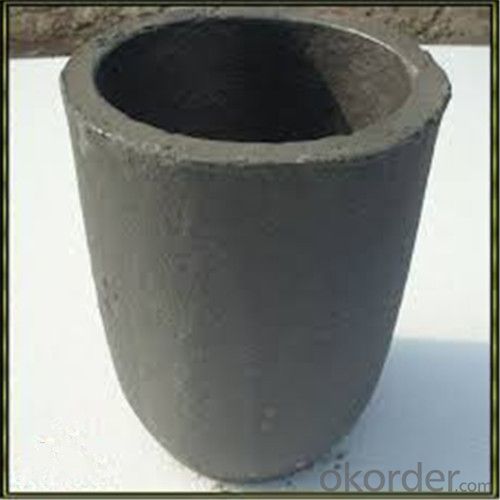
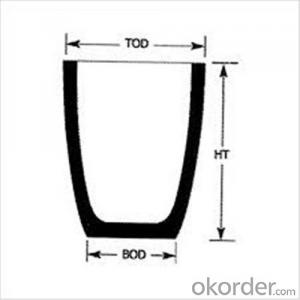
Graphite Crucible for Steel - Refractory SIC Crucible for Melting Copper
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
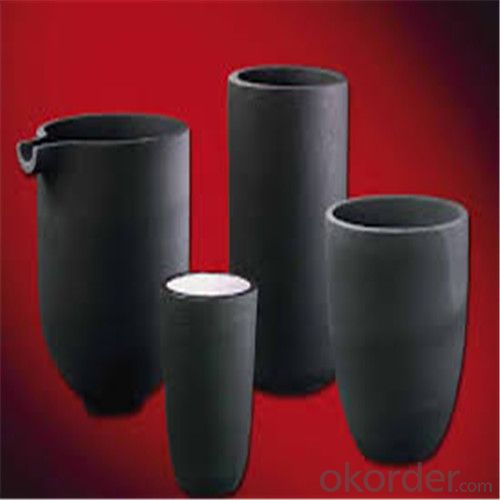
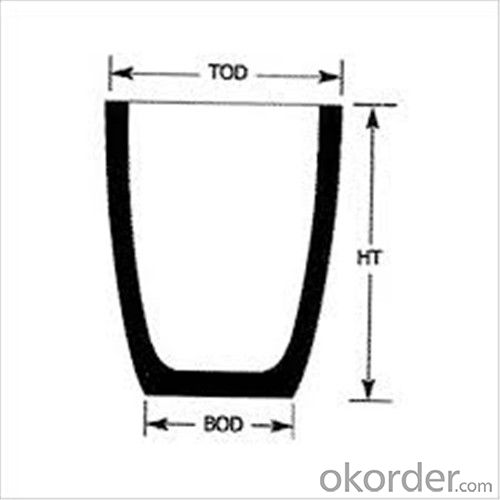

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
5.Can I visit you?
Sure. If you're a volume buyer and would like to visit our in-house products and production line, please contact us to make an appointment.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting thorium?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for melting thorium. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in high-temperature applications, including melting metals and alloys. Thorium has a relatively low melting point of 1,750 degrees Celsius, which is well within the range of temperatures that graphite crucibles can withstand. Graphite crucibles are known for their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures, making them suitable for melting and handling various metals and alloys, including thorium.
- Q: Does a graphite crucible require any preheating before use?
- Yes, a graphite crucible typically requires preheating before use. This is because graphite crucibles are often used in high-temperature applications, such as melting metals or performing other heat-intensive processes. Preheating the crucible helps to reduce thermal shock and prevent cracks or damage to the crucible. Additionally, preheating helps to remove any moisture or impurities that may be present in the crucible, ensuring a clean and reliable container for the intended application. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for preheating to ensure the proper use and longevity of the graphite crucible.
- Q: Graphite products are mainly used in what industry?
- Graphite has good chemical stability. After special processing of graphite, with corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, low permeability, is widely used in the manufacturing of the heat exchanger, the reaction tank, condenser, combustion tower, absorption tower, cooler, heater, filter and pump equipment. Widely used in petroleum, chemical, hydrometallurgy, acid and alkali production, synthetic fiber, papermaking and other industrial sectors, can save a lot of metal materials.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for ceramic production?
- No, graphite crucibles cannot be used for ceramic production. Ceramic production requires crucibles made from materials like alumina or zirconia, which can withstand high temperatures and provide a stable environment for the ceramic materials. Graphite crucibles are generally used for high-temperature applications involving metals and alloys.
- Q: Are there any safety concerns associated with using graphite crucibles?
- Yes, there are some safety concerns associated with using graphite crucibles. Firstly, graphite crucibles can become very hot when used in high-temperature applications, such as melting metals. This can pose a burn hazard if not handled properly. It is important to use appropriate protective equipment, such as heat-resistant gloves and clothing, when working with hot graphite crucibles. Secondly, graphite can release fine particles or dust when it is used or manipulated. Inhaling graphite dust can be harmful to the respiratory system, especially if exposure is prolonged or in high concentrations. It is advisable to work in a well-ventilated area or use respiratory protection, such as masks, to minimize the risk of inhalation. Additionally, graphite crucibles can react with certain chemicals or substances, particularly strong oxidizers, which can cause chemical reactions and potentially result in fires or explosions. It is crucial to be aware of the compatibility of graphite crucibles with the materials being handled and to handle them accordingly to prevent any hazardous reactions. Lastly, graphite crucibles can be fragile and prone to breakage if mishandled or subjected to sudden temperature changes. Broken crucibles can cause sharp edges or fragments that can cause injuries if not handled with caution. Overall, while graphite crucibles are widely used and generally considered safe, it is important to be aware of and address these safety concerns to ensure safe handling and minimize any potential risks.
- Q: Is it possible to cast or mold materials using a graphite crucible?
- Yes, it is possible to cast or mold materials using a graphite crucible. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in various industries, such as metal casting, jewelry making, and foundries, due to their high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity. Graphite crucibles can withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for melting and casting materials like metals and alloys. Graphite crucibles also have good chemical resistance, which prevents contamination of the molten material. Additionally, graphite crucibles have low thermal expansion and are non-wetting, meaning they do not adhere to the melted material, making it easier to remove the cast or molded material once it has solidified. Overall, graphite crucibles are widely used and highly effective for casting and molding various materials.
- Q: What is the importance of carbon graphite as biological material?
- What is the importance of carbon graphite as biological material?Because graphite has many excellent properties, it has been widely used in metallurgy, mechanical, electrical, chemical, textile, national defense and other industrial sectors.
- Q: How does the electrical resistivity of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The electrical resistivity of graphite affects the performance of a crucible by influencing its ability to conduct heat. Graphite has low electrical resistivity, which allows it to efficiently transfer heat to the substance being melted or heated in the crucible. This results in faster and more uniform heating, which is beneficial for various high-temperature applications such as melting metals or glass. Additionally, low electrical resistivity helps to prevent the buildup of excessive heat within the crucible, reducing the risk of thermal stress or damage.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting rare earth metals?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting rare earth metals. Graphite is known for its high melting point, good thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical reactions, making it an ideal material for high-temperature applications such as melting rare earth metals. Additionally, graphite crucibles are durable and can withstand the harsh conditions of molten metals, making them a suitable choice for melting and refining rare earth metals. However, it is important to note that some rare earth metals, such as cerium, can react with graphite at high temperatures, leading to the formation of carbonates. Therefore, it is advisable to consult the specific properties and reactivity of each rare earth metal before using graphite crucibles for melting.
- Q: Is it possible to achieve a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible?
- Achieving a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible is indeed possible. Graphite crucibles find common usage in high-temperature applications, particularly for melting metals and alloys. Various methods can be employed to achieve a controlled atmosphere. One approach involves the use of a gas purging system. This entails introducing a specific gas into the crucible to create the desired atmosphere. For instance, if an inert atmosphere is necessary, gases like argon or nitrogen can be used to displace any oxygen or other reactive gases present. The gas flow rate and pressure can be adjusted to maintain the desired atmosphere. Another method involves creating a sealed environment around the crucible. This can be accomplished by utilizing a furnace or an induction heating system equipped with a gas-tight enclosure. By controlling the gas composition and pressure within this enclosure, a specific atmosphere can be maintained surrounding the crucible. Moreover, the choice of crucible material is crucial to consider. Graphite possesses high thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid heat transfer. However, it can also react with certain gases or metals at elevated temperatures. Hence, selecting the appropriate grade of graphite and ensuring proper crucible conditioning are essential in maintaining a controlled atmosphere. Ultimately, by utilizing suitable equipment and employing effective techniques, it is feasible to establish a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible, thereby enabling precise control of the environment during high-temperature processes.
Send your message to us
Graphite Crucible for Steel - Refractory SIC Crucible for Melting Copper
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords