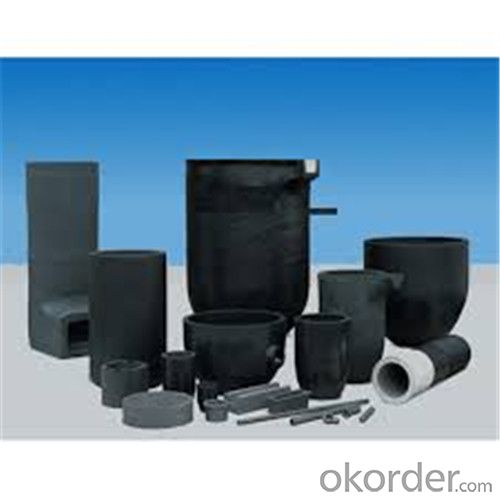
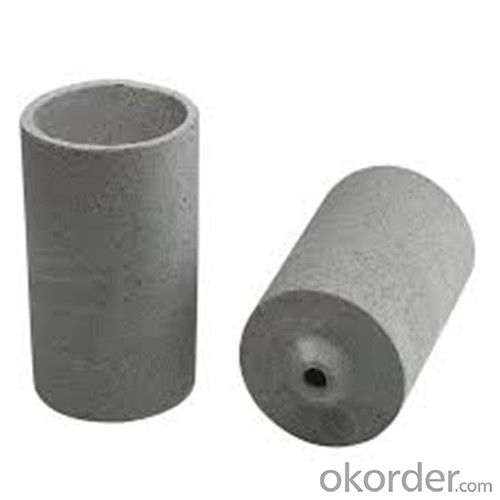
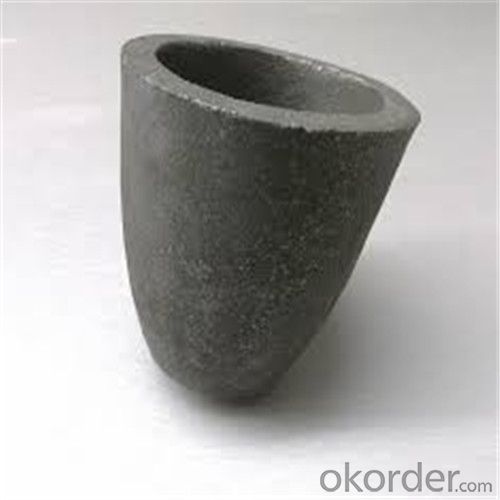
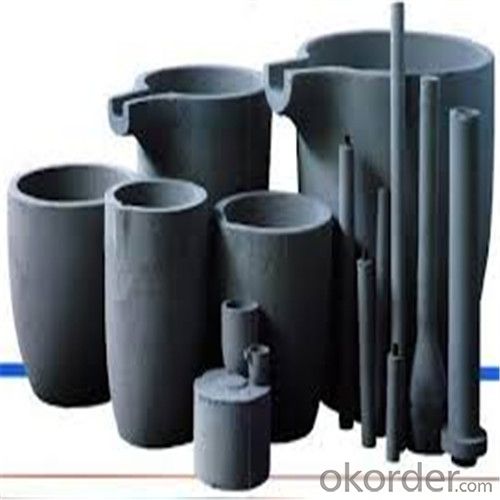
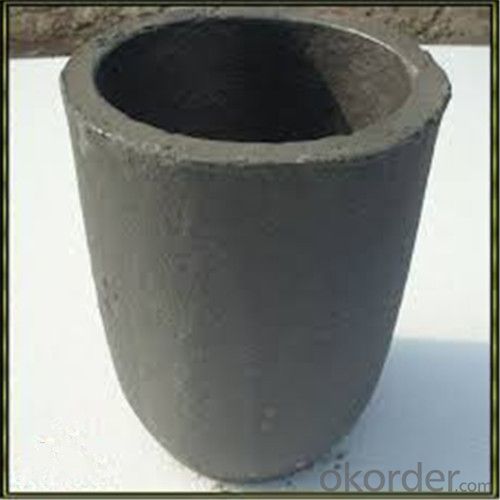
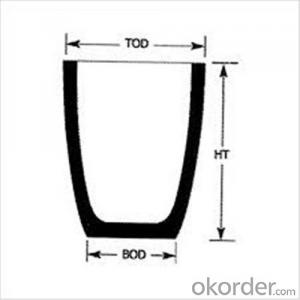
Graphite Crucible Small - Refractory SIC Crucible for Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
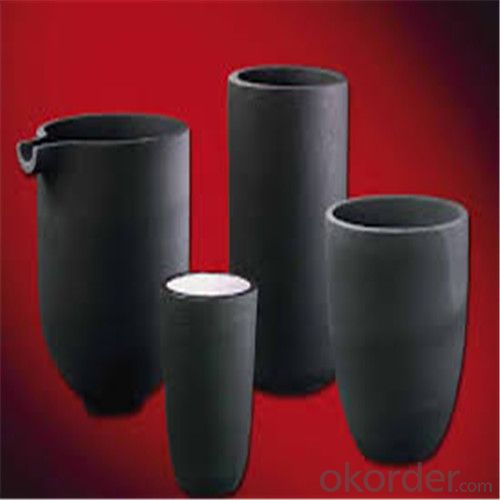
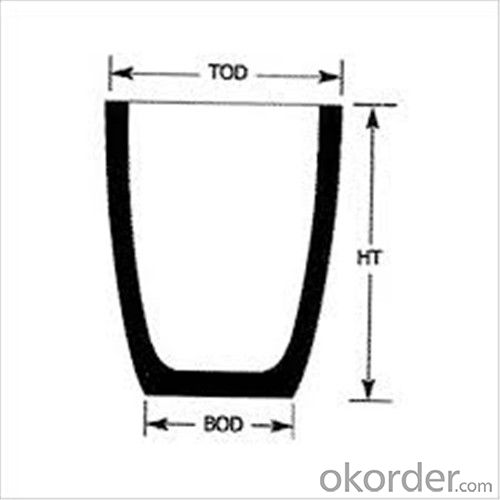

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
Packaging & Shipping
Package: Wooden case and wooden pallet or pack as customer's requirement of graphite crucible.
Delivery time: depend on distance, usually 20 days to 50days after deposit of graphite crucible.
We can supply the products according to customer's drawings, samples and performance requirement.
Other Products


FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
Welcome to visit our factory.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for powder metallurgy?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for powder metallurgy. Graphite is an excellent material for high-temperature applications and is commonly used in powder metallurgy processes. Graphite crucibles have a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for melting and holding metal powders during sintering or melting processes. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good chemical resistance, allowing them to withstand the corrosive effects of certain metal powders. Overall, graphite crucibles are a reliable and efficient choice for powder metallurgy applications.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting bronze?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting bronze. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in foundries and other metalworking industries because graphite has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity. These properties make graphite crucibles suitable for melting various metals, including bronze. Bronze typically melts at temperatures around 950°C (1742°F), which is well within the capabilities of graphite crucibles that can withstand temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F). Furthermore, graphite crucibles have good resistance to chemical reactions with molten metals, ensuring that the crucible does not contaminate the bronze during the melting process. Therefore, graphite crucibles are a reliable and popular choice for melting bronze and other metals.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for alloying or mixing metals?
- Indeed, the utilization of a graphite crucible is viable for the purpose of alloying or mixing metals. Graphite crucibles are renowned for their elevated melting point and exceptional heat resistance, rendering them appropriate for a plethora of high-temperature applications, including the alloying and mixing of metals. The graphite material itself is unreactive and does not taint the metals being melted or mixed. Moreover, graphite crucibles possess commendable thermal conductivity, guaranteeing uniform heating and efficient amalgamation of the metals. Consequently, they are widely employed in various industries such as metal casting, jewelry crafting, and metallurgy, serving the purpose of alloying and mixing dissimilar metals to achieve desired properties or compositions.
- Q: How does the porosity of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The porosity of graphite affects the performance of a crucible by influencing its thermal conductivity, chemical reactivity, and mechanical strength. Higher porosity allows for better heat transfer and distribution, making the crucible more efficient in conducting heat. However, excessive porosity can also increase the risk of chemical reactions between the crucible and its contents, leading to contamination or erosion. Additionally, porosity affects the mechanical strength and durability of the crucible, with lower porosity generally providing better resistance to cracking or breakage. Therefore, finding the right balance of porosity is crucial in determining the overall performance of a graphite crucible.
- Q: How do you use crucibles to process copper?
- The medium frequency furnace crucible is made of quartz sand lining material, and the crucible has a long service life, usually in three months. The power frequency furnace is also sintered with quartz sand.
- Q: How to extract pure silver from sundry Silver
- The reduction of silver: equal without rust and the silver chloride tightly alternately placed in the container and Diego. By adding 1% volume concentration of 16% hydrochloric acid, 8 - 12 hours after all. Silver is replaced, brown. Then rinse 3 to 4 times to no acid.
- Q: Can the alumina crucible be heated by electromagnetic induction?
- We used graphite crucibles to heat copper up to the melting temperature and then pour it into the needed parts
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting pharmaceutical compounds?
- Melting pharmaceutical compounds can be done using graphite crucibles. Graphite crucibles are well-known for their high melting point, making them suitable for high-temperature applications like melting metals, alloys, and certain chemicals. It is crucial to match the temperature range of the graphite crucible with the melting point of the specific compound being melted, as pharmaceutical compounds may have different melting points. Moreover, graphite crucibles have low reactivity and are chemically inert, minimizing the risk of contamination or chemical reactions during the melting process. Nevertheless, it is vital to consider the specific requirements and properties of the pharmaceutical compound to ensure compatibility with the graphite crucible.
- Q: How do you prevent graphite crucibles from cracking or breaking?
- In order to prevent the cracking or breaking of graphite crucibles, it is important to consider several key factors: 1. Careful handling is essential. Avoid any impact or rough handling that could cause stress and potential damage to the crucibles. Always use appropriate lifting tools and refrain from dropping or hitting the crucibles against hard surfaces. 2. Gradual heating and cooling is necessary. To prevent thermal shock, graphite crucibles should be heated and cooled slowly. Sudden temperature changes can result in stress and cracks. It is advisable to utilize a programmable furnace or kiln that allows for controlled and gradual temperature changes. 3. Prior to usage, new graphite crucibles or previously used ones should undergo preheating. This process is important to slowly eliminate any moisture or impurities that may cause thermal expansion and lead to cracking. The temperature in the furnace should be increased gradually. 4. It is crucial to avoid overloading graphite crucibles. These crucibles have a maximum capacity that should not be exceeded. Overloading can subject the crucible to excessive stress during heating, potentially causing cracks or breakage. Always adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the maximum capacity. 5. Rapid cooling should be avoided. After using a graphite crucible, it is important to allow it to cool down gradually. Do not expose the hot crucible to cold air or water, as this can result in thermal shock and cracking. Instead, let it cool naturally in the furnace or kiln before removing it. 6. Regular maintenance is key. Regularly inspect graphite crucibles for any signs of wear, such as cracks, chips, or erosion. If any damage is detected, replace the crucibles immediately to prevent further damage during use. Additionally, proper cleaning and storage of crucibles when not in use can help prolong their lifespan. By adhering to these guidelines, the risk of cracking or breaking graphite crucibles can be significantly reduced. This ensures their durability and optimal performance in various applications.
- Q: What are the catalysts for making SiC from rice husk?
- The rice husk is crushed, in the temperature range of 650 to 700 DEG C, the carbonization process in furnace will be closed after the first rice husk carbonization catalyst, according to a certain weight ratio and adding, evenly mixed, the mixture is filled in the graphite crucible, the carbon fiber arranged on the upper part of the mixture, cover crucible cover. The graphite crucible is placed in a vertical vacuum furnace with graphite as the heater, and argon gas is used to protect the silicon carbide whisker on the carbon fiber. The invention realizes the automatic separation of whisker and powder, and the whisker is attached to the upper part of the carbon fiber in the powder material, and does not need to be separated from the residual carbon or other powder for two times. The obtained whisker has a high direct crystal rate and a simple process.
Send your message to us
Graphite Crucible Small - Refractory SIC Crucible for Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords