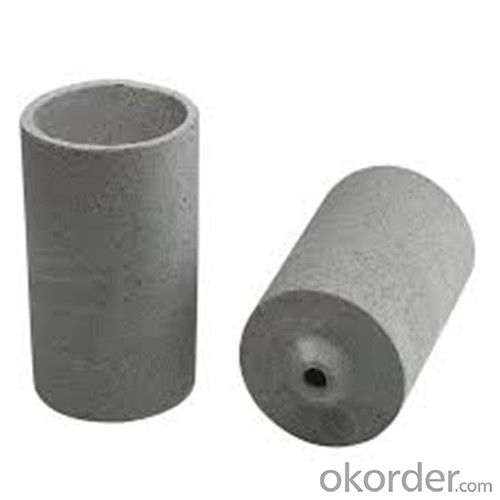
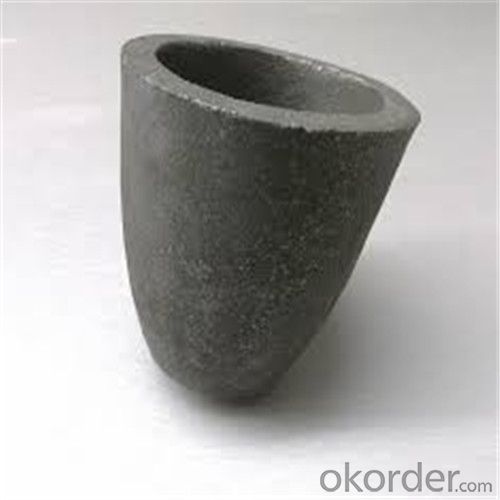
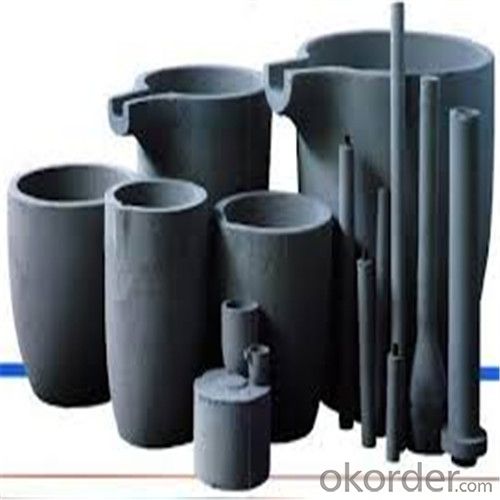
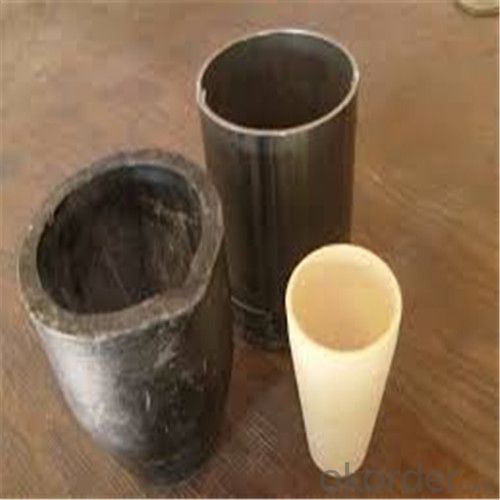
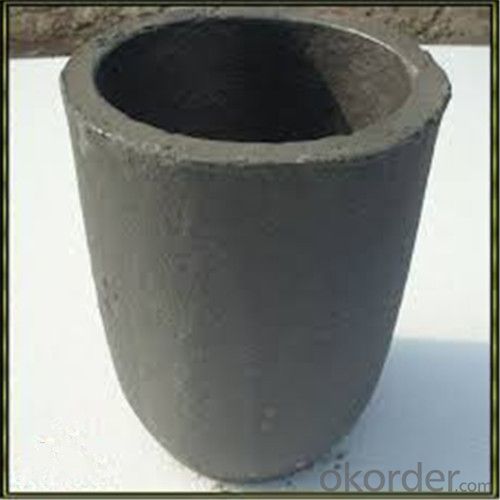
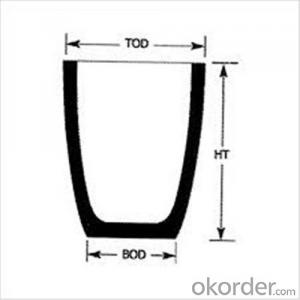
Carbon Graphite Crucible for Refractory SIC Crucible Melting Copper/Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
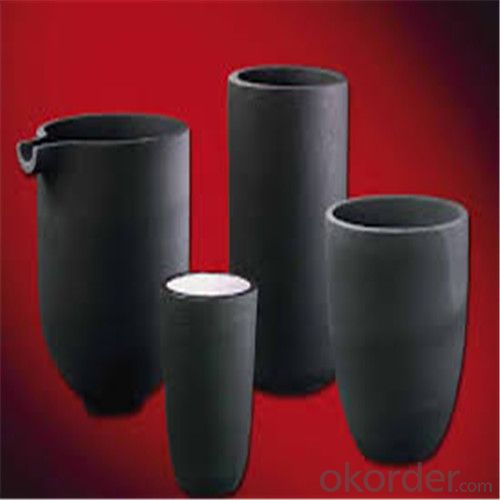
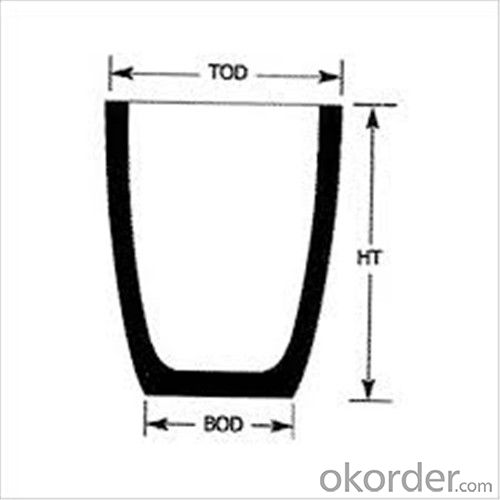

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
5.Can I visit you?
Sure. If you're a volume buyer and would like to visit our in-house products and production line, please contact us to make an appointment.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for nickel melting?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for nickel melting. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in high-temperature applications, including the melting of metals like nickel. Graphite has a high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and good resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for melting and containing nickel. Additionally, graphite crucibles offer good heat transfer, allowing for efficient and uniform melting of the metal. However, it is important to ensure that the graphite crucible is specifically designed for high-temperature applications and is compatible with the melting temperature of nickel to avoid any potential issues or damage.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for metal powder sintering?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for metal powder sintering. Graphite is a commonly used material for high-temperature applications, and it has excellent thermal conductivity and stability, making it suitable for sintering processes. Additionally, graphite crucibles can withstand the extreme heat required for sintering without reacting with most metals, allowing for efficient and reliable sintering of metal powders.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting reactive metals?
- No, graphite crucibles should not be used for melting reactive metals as they can react with certain elements at high temperatures, causing contamination and compromising the quality of the final product.
- Q: How do you ensure proper sealing of a graphite crucible?
- To ensure proper sealing of a graphite crucible, there are a few key steps that can be followed: 1. Clean the crucible: Before sealing the graphite crucible, it is crucial to ensure that it is clean and free from any debris, dust, or residues. This can be done by gently brushing the interior and exterior surfaces of the crucible with a soft brush or cloth. 2. Inspect for any cracks or damage: Carefully examine the crucible for any cracks, chips, or other types of damage. Even minor imperfections can affect the sealing process and compromise the integrity of the crucible. If any damage is found, it is advisable to replace the crucible with a new one. 3. Apply a suitable sealing material: Various sealing materials can be used to ensure proper sealing of the graphite crucible. One commonly used material is a high-temperature adhesive or cement specifically designed for crucible sealing. Apply the sealing material evenly along the edges of the crucible lid or cover. 4. Secure the lid or cover tightly: Once the sealing material is applied, carefully place the lid or cover onto the crucible. Make sure it is properly aligned and fits snugly. Apply gentle pressure to secure the lid in place. 5. Cure or dry the sealing material: Depending on the type of sealing material used, it may require a curing or drying process. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for the specific material being used. This step is crucial to ensure that the sealing material forms a strong and durable bond. 6. Heat the crucible gradually: To further enhance the sealing process, it is recommended to heat the crucible gradually. This can be done by placing the crucible in an oven or furnace and gradually increasing the temperature. Heating the crucible helps to activate the sealing material and create a tighter seal. 7. Cool the crucible slowly: After the sealing material has been activated, allow the crucible to cool down slowly. Rapid cooling can cause thermal stress and potentially lead to cracks or other damages. Once the crucible has reached room temperature, it is ready for use. By following these steps, one can ensure the proper sealing of a graphite crucible, which is essential for various high-temperature applications such as melting metals, conducting experiments, or performing chemical reactions.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal casting?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for metal casting. Graphite crucibles are known for their high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical erosion, making them a suitable choice for melting and casting various metals such as gold, silver, copper, and aluminum. They are commonly used in foundries and laboratories for their durability and ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Q: Why is graphite crucible smelting reducing properties of the burden is particularly vulnerable to corrosion?
- Temperature, high temperature resistance of graphite crucible in general, is not easy to happen, but it is possible to make mistakes. May the general errors include: (a) graphite crucible is exposed in the atmosphere at high temperature (b) cooling too fast or quench.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting titanium?
- No, graphite crucibles cannot be used for melting titanium. Titanium has a high melting point of about 1668°C (3034°F), which exceeds the temperature tolerance of graphite crucibles. Graphite crucibles are typically used for melting metals with lower melting points, such as gold, silver, or copper. Titanium requires a crucible made of materials with higher temperature resistance, such as ceramic or refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum. Using a graphite crucible for melting titanium would result in the crucible itself melting or reacting with the titanium, leading to contamination and an ineffective melting process.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for plasma arc melting?
- Graphite crucibles prove useful in plasma arc melting as they possess high thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. This makes them suitable for a range of high-temperature applications. Given that plasma arc melting involves the use of an electric arc to create and sustain a plasma state, it necessitates a crucible capable of enduring the intense heat generated throughout the process. Graphite crucibles excel in this regard, as they can withstand these extreme temperatures and serve as a stable and durable container for the resulting molten material. Moreover, graphite crucibles exhibit commendable chemical resistance, enabling them to handle corrosive substances that may arise during plasma arc melting. In summary, graphite crucibles remain a prevalent and effective choice for plasma arc melting applications.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible scaling?
- There are several methods that can be employed to prevent graphite crucible scaling, which refers to the formation of surface oxidation or corrosion on the crucible. These methods include: 1. Pre-treatment: A common method is to pre-treat the graphite crucible before its initial use. This involves heating the crucible at a high temperature in an inert atmosphere, such as argon or nitrogen, which helps to form a protective layer on the surface of the crucible. This layer acts as a barrier against oxidation and prevents scaling during subsequent operations. 2. Coating: Applying a protective coating on the surface of the crucible can also help in preventing scaling. Coatings made of materials like boron nitride, zirconium diboride, or alumina can be used to create a barrier between the crucible and the reactive environment. These coatings have high resistance to oxidation and corrosion, thereby prolonging the crucible's lifespan. 3. Fluxing agents: Adding fluxing agents to the crucible charge can help reduce scaling. Fluxes like borax or potassium carbonate react with any impurities or oxides present in the crucible, forming a slag. This slag layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation of the crucible. 4. Controlled atmosphere: Conducting operations in a controlled atmosphere can significantly reduce scaling. For example, using an inert gas like argon or nitrogen during the heating or melting process can create an oxygen-free environment, minimizing the chances of oxidation or scaling. This method is particularly effective for high-temperature applications. 5. Proper storage and handling: Proper storage and handling of the graphite crucible can also prevent scaling. It is crucial to keep the crucible in a dry and clean environment, away from any moisture or corrosive substances. Handling the crucible with clean gloves or tools can prevent contamination and minimize the risk of scaling. In conclusion, preventing graphite crucible scaling involves various methods, including pre-treatment, coating, the use of fluxing agents, controlled atmosphere, and proper storage and handling. Employing these measures can help extend the crucible's lifespan and ensure optimal performance in various high-temperature applications.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting brass?
- Indeed, melting brass can be accomplished by utilizing graphite crucibles. Graphite is frequently employed in the fabrication of crucibles meant for applications involving high temperatures, such as the melting of metals like brass. The reason behind this is that graphite boasts a high melting point and possesses exceptional thermal conductivity, rendering it suitable for enduring the elevated temperatures necessary for brass liquefaction. Moreover, graphite crucibles are renowned for their durability and ability to withstand thermal shock, a crucial aspect when handling molten metals. Given that brass possesses a lower melting point when compared to metals like steel or iron, graphite crucibles offer an effective and dependable approach to melt brass.
Send your message to us
Carbon Graphite Crucible for Refractory SIC Crucible Melting Copper/Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords