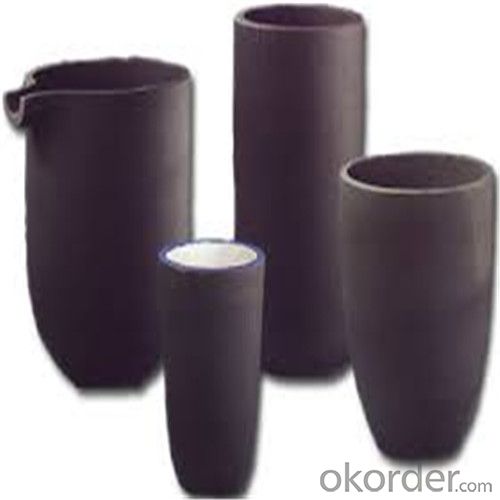
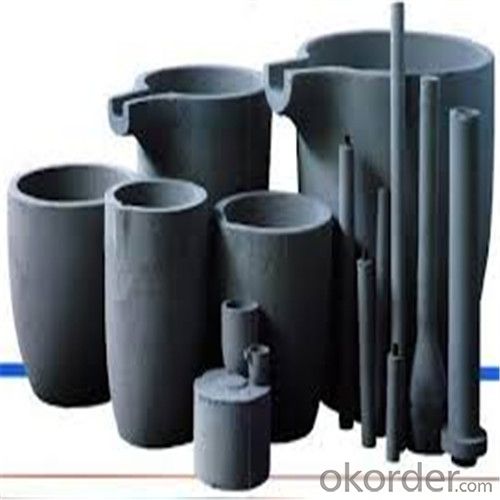
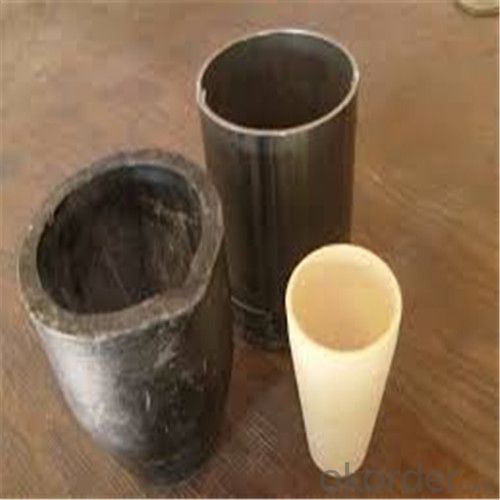
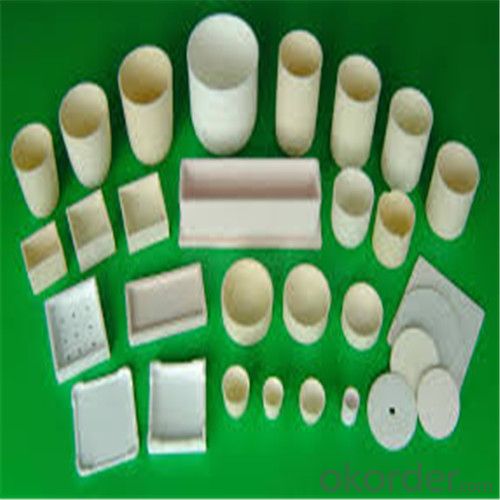
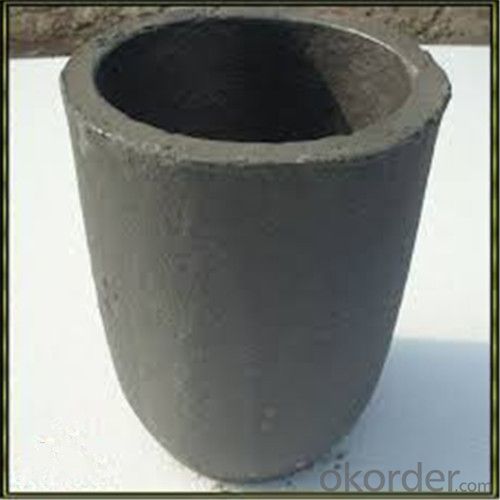
2kg Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
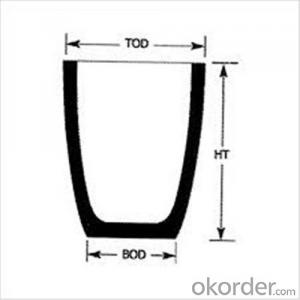
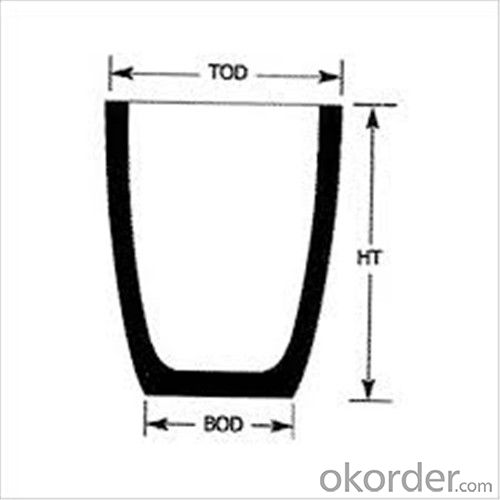
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace

Features of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
1. resistance to deformation at high temperature,
2. thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance.
3. anti-oxidation, anti- erosion.
Usage of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
electricity and steel slag trench,
coal chemical and mining transport pipeline.
Packaging & Shipping
Package: Wooden case and wooden pallet or pack as customer's requirement of graphite crucible.
Delivery time: depend on distance, usually 20 days to 50days after deposit of graphite crucible.
We can supply the products according to customer's drawings, samples and performance requirement.
Other Products


- Q: How can food detect heavy metals and microbes?
- Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry, atomizer the graphite furnace atomizer is, will be placed in the graphite tube wall, graphite platform, carbon sample holes or graphite crucible with electric heating to a high temperature so as to achieve atomization, the detection limit is Sug/kg. Flame atomic absorption spectrometry. This method uses flame atomizer and flame atomizer. It consists of three parts: sprayer, premixing chamber and burner. The detection limit is 0.Img/kg.
- Q: Help: how can the graphite crucible be heated to 1000 degrees?
- No matter what heat is used, heat it to 1000 degrees. Just keep heating it. Graphite crucible can be used to contact outer ring refractory plant
- Q: Is it possible to customize the shape or design of a graphite crucible?
- Certainly, the shape or design of a graphite crucible can be personalized. Graphite, being a highly adaptable material, can be molded and formed into various shapes. Industries like metallurgy, foundries, and laboratories often utilize graphite crucibles for the purpose of melting and casting metals. Manufacturers employ specialized techniques such as CNC machining or graphite molding to customize the shape or design of graphite crucibles. CNC machining involves the use of computer-controlled machines to precisely shape the graphite material according to the desired form. This method facilitates the creation of intricate and accurate designs. On the other hand, graphite molding is a process where graphite powder is compressed into a specific shape using a mold. This technique is commonly employed for simpler and more standardized crucible shapes. Customization of graphite crucibles may involve modifications in dimensions, addition of handles or spouts, or the creation of unique designs to cater to specific applications. This customization process ensures that the crucible is tailored to meet the user's specific requirements, thereby ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. It is important to note that customizing the shape or design of a graphite crucible may result in additional costs and lead times. This is because the customization process requires specialized equipment and expertise. Hence, it is crucial to engage in communication with the manufacturer or supplier to discuss customization options, feasibility, and associated costs.
- Q: How does the density of the molten metal affect the performance of a crucible?
- The density of the molten metal can affect the performance of a crucible in a few ways. Firstly, a higher density molten metal can exert more pressure on the walls of the crucible, potentially causing it to crack or break. On the other hand, a lower density molten metal may not exert enough pressure on the crucible, leading to poor heat transfer and uneven melting. Additionally, the density of the molten metal can also impact the thermal conductivity of the crucible, influencing its ability to evenly distribute heat and maintain a consistent temperature.
- Q: What is graphite?
- Graphite is a crystalline mineral of carbonaceous elements. Its crystalline framework is hexagonal layered structure. The distance between each network layer is 3.40, and the distance between the carbon atoms in the same network layer is 1.42A.
- Q: Are graphite crucibles suitable for melting magnetic materials?
- Graphite crucibles are not appropriate for melting magnetic materials. Graphite, being non-magnetic and having a low melting point, is not compatible for use with magnetic materials, which usually necessitate higher temperatures for melting. Furthermore, graphite can interact with certain magnetic materials, causing contamination and impurities in the molten metal. To melt magnetic materials, it is advised to opt for crucibles crafted from materials that can withstand high temperatures and exhibit low reactivity towards the specific magnetic material being melted.
- Q: Single crystal furnace quartz crucible cast 22 inch 175 kilograms of feed it
- Back chaos, in fact we are very worried about the recovery of this material strength and composition by crucible crucible change can not be used, but also fast, so the results will soon be out.
- Q: How is a graphite crucible used in the production of graphite electrodes?
- A graphite crucible is an essential tool used in the production of graphite electrodes. Graphite electrodes are widely used in industries such as steelmaking, electric arc furnaces, and various other high-temperature applications. In the production process, a graphite crucible is used to hold and melt raw materials used for creating graphite electrodes. The crucible is made of high-quality graphite material, which has excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand extremely high temperatures. To begin, the raw materials are placed inside the graphite crucible. These materials typically consist of a mixture of petroleum coke, coal tar pitch, and other additives. Once loaded, the crucible is placed in a furnace or an electric arc furnace, where it is subjected to intense heat. As the temperature rises, the raw materials inside the crucible begin to melt and react with each other. Various chemical reactions take place, leading to the formation of a homogenous molten mass. The molten mixture is then carefully poured into molds, where it solidifies and takes the shape of a graphite electrode. The use of a graphite crucible is critical in this process for several reasons. Firstly, graphite has a high melting point, making it ideal for containing and withstanding the extreme temperatures required for melting the raw materials. The crucible also ensures that the molten mixture remains separate from the furnace, preventing any impurities or contaminants from affecting the quality of the final electrode. Furthermore, the thermal conductivity of graphite allows for efficient heat transfer, ensuring that the entire mass of raw materials melts uniformly. This uniformity is crucial for obtaining consistent and high-quality graphite electrodes. Additionally, the chemical inertness of graphite prevents any reactions between the crucible and the molten mixture, ensuring that the purity of the final electrode is not compromised. In conclusion, a graphite crucible plays a vital role in the production of graphite electrodes by providing a reliable and efficient container for melting raw materials. Its high melting point, thermal conductivity, and chemical inertness make it an ideal choice for this application, ensuring the production of high-quality graphite electrodes that meet the stringent requirements of various industries.
- Q: What are the characteristics of jade? There are jade and jade on the market. How do you distinguish it from jade?
- Artificial jade, like artificial diamond, is a kind of natural gem product made by artificial simulation of natural gem. It has certain characteristics of natural gem. Emerald is based on the super bedrock rock are widely distributed, actinolite glaucophane schist and chlorite schist, high temperature and ultra high pressure on the geological environment in the formation of the process of imitation jade.
- Q: How to make the aluminum liquid in the round graphite crucible solidified without holes in the middle?
- Aluminum water is melted and silicon is added. It should be noted that the surface of the aluminum should be cleaned before making the silicon. The broken silica fume should not be added, and the process of mixing silicon should be properly stirred. After a good silicification, a certain amount of aluminum ingot is used as a cooling material, because the temperature of the silicon will be higher, and the cooling material will be higher.
Send your message to us
2kg Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords