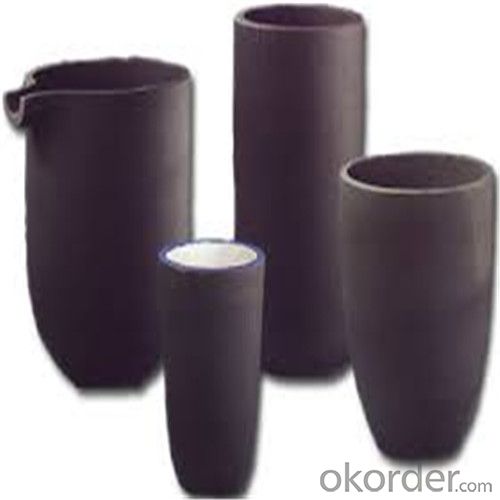
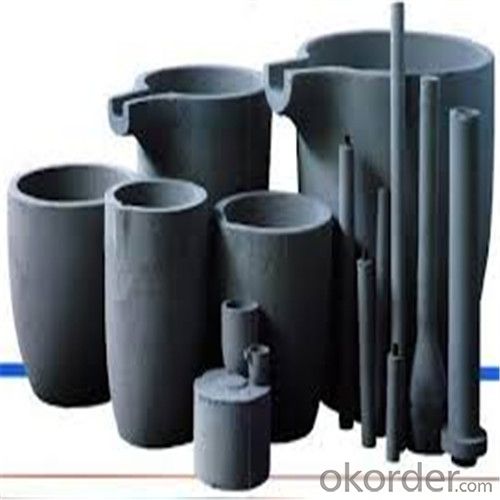
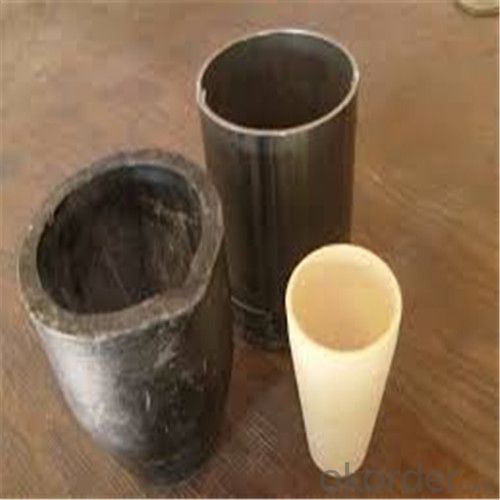
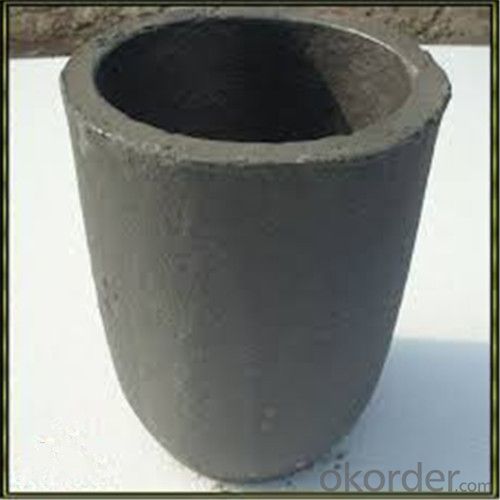
Large Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
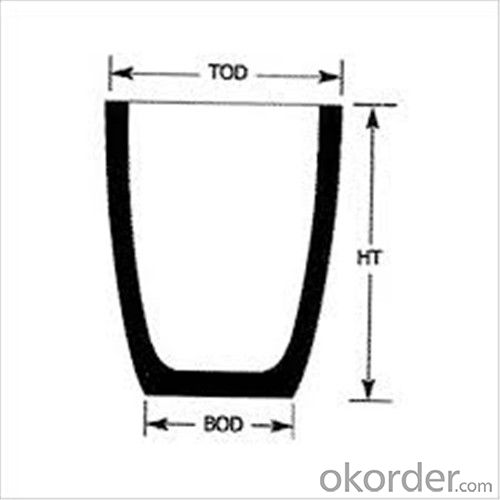

Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q: Are there any specific storage requirements for graphite crucibles?
- Yes, graphite crucibles have specific storage requirements. They should be stored in a dry and cool environment to prevent oxidation and damage. It is essential to keep them away from moisture, direct sunlight, and extreme temperature fluctuations. Additionally, they should be stored in a clean area to avoid contamination from dust or other substances.
- Q: How is a graphite crucible used in the production of carbon composites?
- A graphite crucible is a crucial tool used in the production of carbon composites. Carbon composites are materials that consist of carbon fibers embedded in a matrix material, typically a resin or a metal. In the production process, the graphite crucible acts as a container or a mold for the molten matrix material. The crucible is specifically made from graphite due to its high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand the extreme temperatures required for melting the matrix material, which can range from several hundred to several thousand degrees Celsius, depending on the type of composite being produced. First, the carbon fibers are prepared by aligning them in a specific orientation to achieve the desired mechanical properties of the final composite. These carbon fibers are then placed inside the graphite crucible, forming a pre-defined shape or structure. Next, the matrix material, such as a resin or metal, is heated to its melting point and poured into the graphite crucible. The crucible, being an excellent conductor of heat, helps to distribute the heat evenly throughout the molten matrix material, ensuring uniformity and preventing any hotspots or uneven curing. As the molten matrix material cools down, it solidifies around the carbon fibers, encapsulating them completely. This process is known as impregnation or infiltration, where the matrix material fills the gaps between the carbon fibers, binding them together and forming a solid composite structure. The graphite crucible is essential in maintaining the shape and structure of the composite during this process. After the impregnation process, the composite is allowed to cool and cure, resulting in a rigid and durable material with excellent mechanical properties. The crucible is then removed, leaving behind the carbon composite in the desired shape. In summary, a graphite crucible is used in the production of carbon composites as a container for the molten matrix material. It provides a stable and controlled environment for the impregnation process, ensuring uniformity and consistency in the final composite product.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible stirring mechanism for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible stirring mechanism for a specific application, one must consider factors such as the type of material being stirred, the desired level of agitation, the temperature and pressure conditions, as well as the size and shape of the crucible. Additionally, factors like the available power source and budget constraints should be taken into account. Conducting a thorough analysis of these parameters will help in selecting the most suitable stirring mechanism, whether it be magnetic stirrers, mechanical stirrers, or other specialized systems.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting and casting of non-ferrous metals?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting and casting of non-ferrous metals. Graphite crucibles are widely used in various industries, including foundries and metalworking, for their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. Non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper, zinc, and gold, have lower melting points compared to iron and steel, making them suitable for melting in graphite crucibles. The high thermal conductivity of graphite helps to evenly distribute heat throughout the crucible, ensuring efficient melting and casting of non-ferrous metals. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good chemical resistance and low reactivity with non-ferrous metals, which further enhances their suitability for this application. However, it is important to note that graphite crucibles may not be suitable for certain reactive or corrosive metals, as they can react with graphite and affect the quality of the casting.
- Q: How does a graphite crucible handle chemical resistance?
- A graphite crucible is highly resistant to chemical corrosion due to the inherent properties of graphite. Graphite is composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure, which provides it with exceptional chemical stability. It is non-reactive with most chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents. The chemical resistance of a graphite crucible is primarily attributed to its high melting point and low reactivity. Graphite has a melting point of over 3,500 degrees Celsius, which allows it to withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical degradation. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications involving high-temperature processes, such as melting metals and alloys. Furthermore, graphite has a non-porous structure, which prevents chemicals from permeating its surface. This non-porosity minimizes the risk of chemical absorption, ensuring that the crucible remains chemically inert and resistant to corrosion. As a result, it can be used with various reactive substances without the fear of contamination or chemical reactions. However, it is important to note that while graphite crucibles are highly resistant to most chemicals, they may still be susceptible to certain aggressive substances under specific conditions. For instance, graphite can react with strong oxidizing agents such as fluorine gas or molten alkali metals. Additionally, prolonged exposure to certain corrosive environments or extreme temperatures can gradually degrade the crucible's resistance. In summary, a graphite crucible exhibits excellent chemical resistance due to its high melting point, non-reactive nature, and non-porous structure. It can effectively withstand the corrosive effects of most chemicals encountered in various industrial processes, making it a reliable choice for applications requiring chemical stability. However, it is crucial to consider the specific chemical environment and conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the crucible.
- Q: The graphite boat loading and loading real real graphite boat is what?
- The graphite boat used for solar energy industry and real loading: PECVD carrying vehicles, loaded from silicon, preparation of middle and high efficiency filter, ensure that blows air purifying requirements.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for crystal growth?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for crystal growth. Graphite has several properties that make it suitable for this purpose. First, graphite has a high melting point, which allows it to withstand the high temperatures required for crystal growth. Second, graphite has good thermal conductivity, which ensures uniform heat distribution during the growth process. Third, graphite is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with most substances, which is important for maintaining the purity of the crystal being grown. Additionally, graphite crucibles are often used in crystal growth techniques such as the Czochralski method, where a seed crystal is dipped into a molten solution and slowly withdrawn to grow a larger crystal. In summary, graphite crucibles are commonly used and well-suited for crystal growth due to their high melting point, good thermal conductivity, and chemical inertness.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic coating applications?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for ceramic coating applications. Graphite is a highly conductive material and can react with certain chemicals used in ceramic coating processes, resulting in contamination of the coating material. Additionally, graphite has a relatively low melting point compared to ceramic coating temperatures, which may cause the crucible to degrade or fail during the coating process. It is recommended to use crucibles made of materials specifically designed for ceramic coating applications, such as alumina or silica. These materials have higher melting points and are chemically inert, ensuring the integrity of the ceramic coating process.
- Q: To sum up the different uses (and causes) of various crucibles in ChemistryQuartz glass crucibles, for examplealumina crucibleGlass crucibles, iron crucibles, and the like are different and should be noted
- 2, can not touch the HF and, at high temperature, easy and caustic effects of carbonate and alkali metal.3. quartz crucibles are suitable for melting samples with K2S2O7, KHSO4 as flux, and treating samples with Na2S207 (first drying at 212 degrees) as flux4. quartz brittle, easy to break, use should pay attention to5. except for HF, ordinary dilute inorganic acid can be used as cleaning solutionAlumina crucible: 1. corundum crucible is made of porous fused alumina, which is compact and resistant to melting
- Q: Can the alumina crucible be heated by electromagnetic induction?
- We used graphite crucibles to heat copper up to the melting temperature and then pour it into the needed parts
Send your message to us
Large Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























