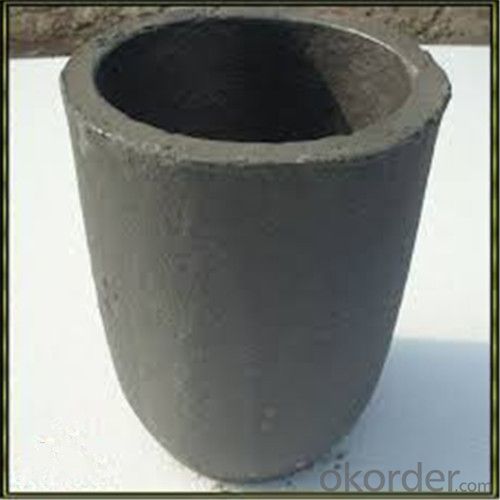
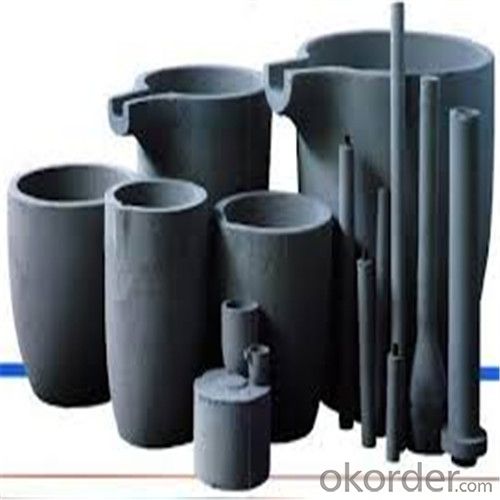
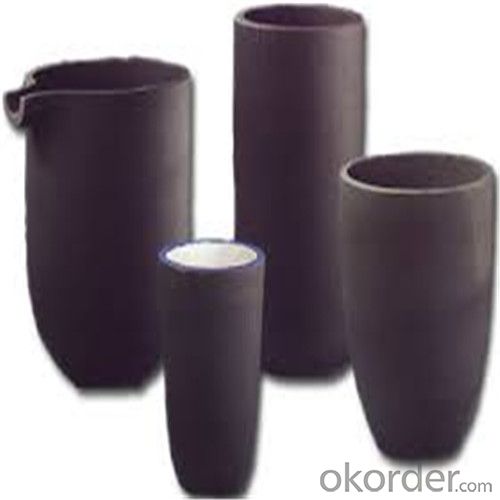
Graphite Vs Ceramic Crucible - SIC Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles For Gold, Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
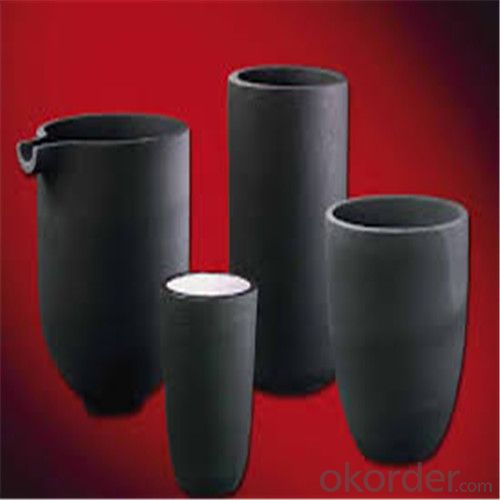

Physicochemical Properties of graphite crucible:
The crucible is an utensil or melting tank vessels that is made of refractory material (such as clay, graphite, quartz or difficult molten metal iron, etc.).
Graphite crucible, with is special advantages and Plasticity, is widely used in the smelting area, e.g. gold smelting, silver smelting, aluminum smelting, cooper smelting, etc.
high pure graphite | ||||
Item | Unit | baked twice | baked three time | baked four times |
impregnated once | impregnated twice | impregnated three times | ||
grain size | mm | ≤325μm | ≤325μm | ≤325μm |
Bulk density | g/cm3 | ≥1.68 | ≥1.78 | ≥1.85 |
Specific resistance | μΩ.m | ≤14 | ≤14 | ≤13 |
Bending strength | MPa | ≥25 | ≥40 | ≥45 |
Compressive strength | MPa | ≥50 | ≥60 | ≥65 |
Ash content | % | ≤0.15 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.05 |
Fine-grain Specialty Graphite FXG-1 | Fine-grain Specialty Graphite FXG-2 | ||||
Item | Unit | Guarantee value | Typical value | Guarantee value | Typical value |
Max grain size | mm | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
Bulk density | g/cm3 | ≥1.70 | 1.73 | ≥1.73 | 1.76 |
Specific resistance | μΩ.m | ≤8.5 | 7.5 | ≤8.0 | 7 |
Bending strength | MPa | ≥10.0 | 11 | ≥12.0 | 12.5 |
Compressive strength | MPa | ≥24.0 | 27 | ≥31.0 | 34 |
Thermal Condcutivity | W/(m.k) | ≥120 | 150 | ≥130 | 160 |
C.T.E.(100-600) °C | 10-6/°C | ≤2.5 | 2.2 | ≤2.5 | 2.1 |
Ash content | % | ≤0.3 | 0.09 | ≤0.3 | 0.09 |
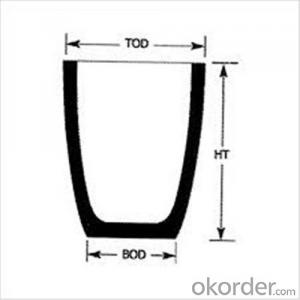
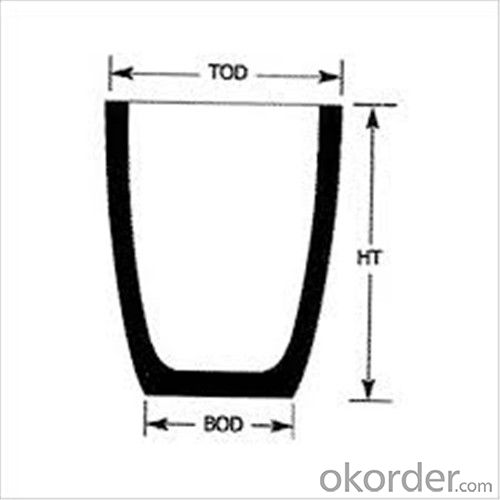
NO | Top diameter | Bottom diameter | Height | Tolerance | Capacity(Kg5%) |
2 | 90 | 50 | 55 | 2 | 0.3 |
3 | 105 | 80 | 93 | 2 | 0.5 |
4 | 102 | 80 | 100 | 2 | 0.6 |
5 | 112 | 82 | 130 | 2 | 0.8 |
6 | 120 | 82 | 141 | 2 | 0.9 |
8 | 138 | 90 | 153 | 2 | 1.2 |
12 | 148 | 100 | 181 | 2 | 1.8 |
16 | 156 | 110 | 190 | 2 | 2.3 |
20 | 180 | 120 | 230 | 2 | 3 |
25 | 186 | 128 | 248 | 2 | 3.7 |
- Q: What graphite crucible is used to smelt aluminium by electromagnetic induction heating?
- Electromagnetic induction heating is the heating of graphite, and can soon rise to 1000 degrees, but aluminum is a magnetic material, will block the electromagnetic field, so this scheme is not feasible
- Q: How long can a graphite crucible last for a long time?
- The special thermal shock resistance, thermal expansion of graphite is anisotropic, and the macro expansion coefficient is small, the temperature change under the condition that the volume change of graphite is not large, coupled with its good thermal conductivity, good thermal shock resistance and graphite.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible depth for a specific application?
- Several factors need to be considered when determining the appropriate crucible depth for a specific application. The type of material being melted or processed is a crucial factor. Different materials have varying densities, melting points, and expansion properties, which affect the necessary depth for effective processing. For example, materials with low melting points or high expansion rates may require a deeper crucible to accommodate volume changes during heating. The desired quantity of material to be processed is also important. Larger quantities generally necessitate deeper crucibles to ensure sufficient space for the molten material without overflowing or creating excessive turbulence during processing. Additionally, the heating method and equipment being used should be taken into account. Certain heating methods, such as induction or resistance heating, may require specific crucible depths to optimize heat transfer and uniformity. The dimensions and specifications of the heating equipment also play a role in determining the appropriate crucible depth. Moreover, the desired processing conditions and requirements should be considered. Factors like desired mixing, stirring, or agitation, temperature gradients, or the need for controlled cooling may influence the crucible depth. These requirements should be evaluated to ensure the chosen crucible depth can meet the specific application's needs. Lastly, safety considerations and practical limitations should be taken into account. The crucible depth should be chosen to prevent potential hazards, such as overflowing or splashing of molten material, and to ensure ease of handling and accessibility for loading and unloading. In conclusion, determining the appropriate crucible depth for a specific application involves assessing material properties, processing requirements, heating method, and equipment specifications, while considering safety and practical limitations. It is advisable to consult relevant literature, equipment manufacturers, or experienced professionals for an accurate determination of the crucible depth for optimal performance and safety.
- Q: What are the different accessories available for graphite crucibles?
- There are several different accessories available for graphite crucibles that can enhance their performance and make them more suitable for specific applications. Some of the common accessories include: 1. Crucible Tongs: These are long-handled tools specifically designed to safely handle hot crucibles. They allow for easy and secure gripping of the crucible, preventing accidental burns or spills. 2. Crucible Covers: These are lids or covers that can be placed on top of the crucible to protect the contents from contamination or oxidation. They help maintain a controlled environment inside the crucible, ensuring the purity of the materials being melted or heated. 3. Crucible Holders: These are support structures that hold the crucible in place during heating or pouring. They provide stability and prevent the crucible from tipping over or spilling its contents. 4. Crucible Racks: These are storage racks or holders designed to safely store crucibles when they are not in use. They help keep the crucibles organized and prevent any accidental damage or breakage. 5. Crucible Stirrers: These are specialized tools used to stir the contents inside the crucible during melting or mixing processes. They assist in achieving uniform temperature distribution and homogeneity of the molten material. 6. Crucible Cleaning Tools: These tools are used to clean the graphite crucible after use, removing any residue or impurities. They may include brushes, scrapers, or solvents specifically designed for graphite crucibles. 7. Crucible Lids: In addition to covers, there are also specialized lids that can be used to seal the crucible tightly during certain applications. These lids help create a controlled atmosphere or prevent the escape of volatile substances. 8. Crucible Lifters: These tools are used to safely lift and transport hot crucibles from one location to another. They are designed to withstand high temperatures and provide a secure grip on the crucible. 9. Crucible Insulation: Insulating materials such as ceramic fiber blankets or jackets can be used to surround the graphite crucible, providing additional thermal insulation. This helps to maintain a consistent temperature and prevent heat loss. 10. Crucible Liners: Liners made of ceramic or other refractory materials can be used to protect the graphite crucible from chemical reactions or erosion caused by aggressive materials or corrosive environments. These accessories offer various advantages and options to optimize the performance and utilization of graphite crucibles based on specific requirements and applications.
- Q: What special attention should be paid to the use of graphite crucible in vacuum induction melting of titanium alloy?
- Titanium alloy smelting, no one using graphite crucible
- Q: How do you prevent overheating of a graphite crucible?
- To prevent overheating of a graphite crucible, it is important to control the temperature and optimize the heating process. Some effective measures include using appropriate heating methods such as induction or resistance heating, avoiding sudden temperature changes, maintaining a suitable power input, and ensuring proper insulation of the crucible. Additionally, regular monitoring of the temperature and implementing cooling measures when necessary can also help prevent overheating.
- Q: How long is the service life of the cast iron crucible?
- The service life of cast iron crucibles for electric furnaces ranged from 1 months to 2 months.
- Q: How does the thermal stability of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The performance of a crucible is greatly influenced by the thermal stability of graphite. Graphite is renowned for its high melting point and exceptional thermal conductivity, making it an ideal material for crucibles used in high-temperature scenarios. Industries such as metallurgy, foundries, and laboratories commonly employ crucibles that are subjected to extreme temperatures. The thermal stability of graphite guarantees that the crucible can endure these high temperatures without distorting or melting. With a melting point of approximately 3,600 degrees Celsius, graphite's high melting point allows the crucible to maintain its shape and structural integrity under intense heat. This characteristic is crucial since it prevents the crucible from warping or collapsing, which can lead to uneven heating and material loss. Furthermore, graphite's outstanding thermal conductivity enables the crucible to evenly distribute heat across its surface. This is essential as it ensures uniform heating of the materials held within the crucible, preventing localized hotspots or uneven temperature gradients. In applications requiring precise temperature control, such as alloy production or chemical reactions, this characteristic is vital for achieving accurate and consistent results. Moreover, the thermal stability of graphite also impacts the crucible's ability to resist thermal shock. Thermal shock occurs when there is a sudden and drastic change in temperature, resulting in the cracking or even breaking of the crucible. Graphite's high thermal stability allows it to endure thermal shock without significant damage, guaranteeing the longevity and durability of the crucible. To summarize, the thermal stability of graphite is crucial for the performance of a crucible. It enables the crucible to withstand high temperatures without distorting or melting, ensures even heat distribution, and enhances its resistance to thermal shock. These properties make graphite crucibles highly dependable and suitable for demanding applications that require high-temperature stability and precise temperature control.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible material for a specific application?
- To ascertain the suitable crucible material for a particular application, one must take into account several factors. First and foremost, it is crucial to assess the temperature range of the application. Different crucible materials possess varying temperature limitations. For applications that involve high temperatures, materials like graphite or refractory metals such as tungsten or molybdenum might be appropriate. Conversely, for applications with lower temperatures, materials like porcelain or alumina may suffice. Secondly, one should evaluate the chemical compatibility between the crucible material and the substances employed in the application. Certain materials may react with specific chemicals or gases, resulting in contamination or deterioration of the crucible. Therefore, it is imperative to choose a material that is chemically inert or resistant to the substances utilized. Thirdly, consideration should be given to the thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance of the crucible material. Some applications necessitate rapid heating and cooling cycles, which can subject the crucible to thermal stress. In such cases, materials with high thermal shock resistance, such as quartz or boron nitride, may be more suitable. Furthermore, the mechanical strength and durability of the crucible material should be taken into account. Certain applications involve mechanical forces, stirring, or pouring of molten materials, which can impose physical stress on the crucible. Materials like silicon carbide or stainless steel exhibit good mechanical strength and can withstand such conditions. Lastly, the cost and availability of the crucible material should be considered. While certain materials, like platinum or iridium, offer exceptional performance, they can be expensive and challenging to procure. Thus, striking a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness is important. In conclusion, determining the appropriate crucible material for a specific application necessitates careful consideration of factors such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, thermal conductivity and shock resistance, mechanical strength, and cost. By thoroughly evaluating these factors, one can select a crucible material that will effectively meet the requirements of the application.
- Q: Who is the melting point of graphite and diamond?
- When material melts, molecular crystals need to destroy intermolecular forces; atomic crystals need to destroy covalent bonds; ionic crystals need to destroy ionic bonds; metal crystals need to destroy metal bonds. The stronger the bond, the higher the energy required for the breaking key, the higher the melting point.
Send your message to us
Graphite Vs Ceramic Crucible - SIC Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords