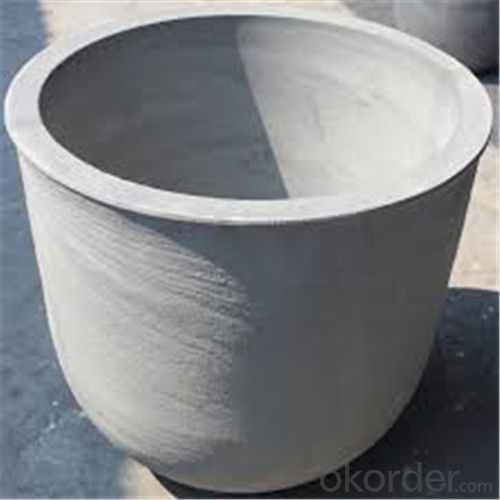
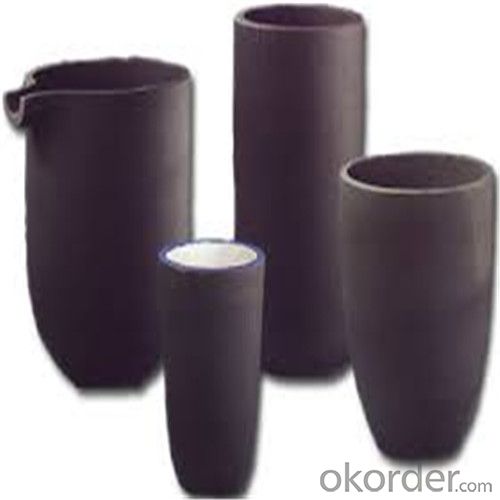
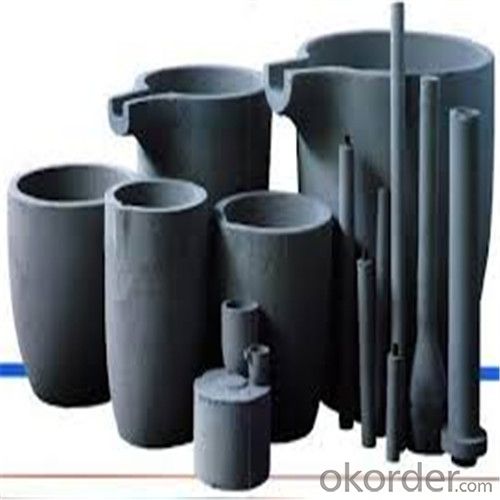
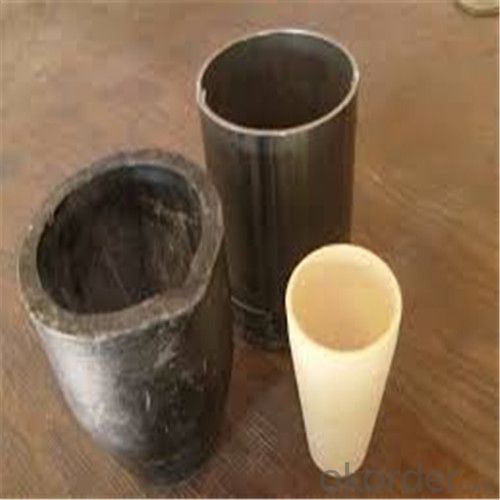
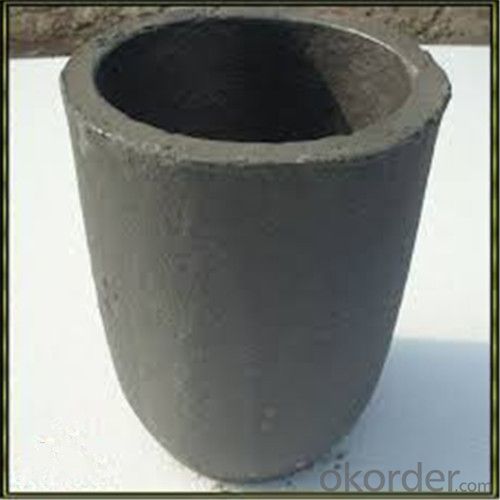
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
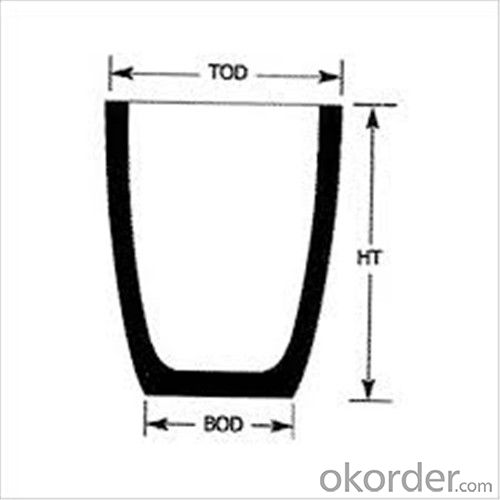
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
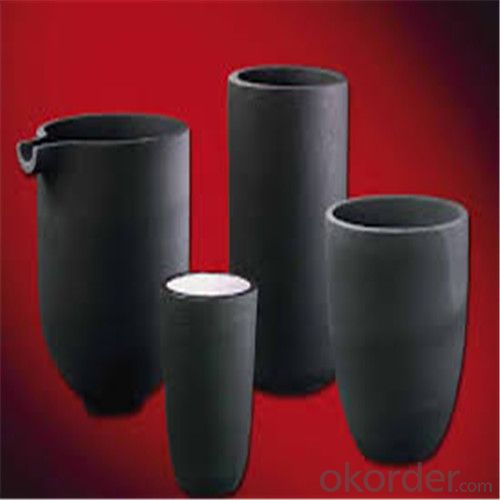

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
Welcome to visit our factory.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible lid seal for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible lid seal for a specific application, there are a few factors to consider. Firstly, you need to understand the compatibility of the seal material with the crucible and its contents. Different materials have varying resistance to temperature, chemicals, and pressure, so choose a seal that can withstand the specific conditions of your application. Secondly, assess the sealing mechanism required. Depending on the application, you may need a seal that provides airtight or vacuum-tight closure, or one that allows for controlled gas flow. Consider the type of lid and crucible design as well, as certain seals may be better suited for specific configurations. Lastly, take into account the lifespan and maintenance requirements of the seal. Some applications may require frequent lid removal and seal replacement, while others may need a more durable and long-lasting solution. Overall, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the compatibility, sealing mechanism, and maintenance considerations to determine the appropriate crucible lid seal for a specific application.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for powder compaction?
- Graphite crucibles possess the capability of being utilized for powder compaction. Typically composed of high-quality graphite material, graphite crucibles exhibit exceptional thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. As a result, they prove to be suitable for a diverse range of high-temperature applications, such as powder compaction. Throughout the process of powder compaction, the graphite crucible exhibits resilience against elevated pressures and temperatures, thereby ensuring effective compacting of the powder. The crucible's high thermal conductivity facilitates the uniform distribution of heat, enabling the powder to be compacted uniformly. Furthermore, graphite crucibles possess the advantage of being easily machinable into various shapes and sizes, rendering them versatile and adaptable to meet the requirements of different powder compaction scenarios. Their non-reactive nature with most substances also lends them the capability to handle a broad spectrum of powders without the risk of contamination. Nevertheless, it is crucial to take into consideration the specific demands of the powder being compacted and the compaction process itself. Certain powders may necessitate the use of specialized crucibles crafted from alternative materials in order to achieve optimal results. Therefore, it is advisable to seek guidance from experts or conduct comprehensive research to ascertain the suitability of graphite crucibles for a particular powder compaction application.
- Q: What kind of equipment is needed to refine the battery lead?
- Play with yourself, get a tin can, and burn it on the gas. Professional, can make the battery's lead reduction, need specialized equipment. High frequency furnace.
- Q: How does the gas permeability of graphite affect crucible performance?
- The gas permeability of graphite plays a crucial role in crucible performance. Graphite's high gas permeability allows for the escape of gases and volatile compounds during high-temperature processes. This helps prevent pressure build-up, potential explosions, and contamination of the material being processed. Additionally, the permeability of graphite assists in maintaining a stable temperature within the crucible, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the overall process.
- Q: Can the alumina crucible be heated by electromagnetic induction?
- May not!A substance that can induce heat in a high frequency electromagnetic field. Only substances with high levels of iron and iron can not be hot.
- Q: What material does the crucible belong to?
- There are several kinds of ceramics, glass and platinum, depending on the temperature of the use and the heating material
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing contamination from graphite particles?
- There are several methods to prevent contamination from graphite particles. One approach is to use air filtration systems that effectively capture and remove graphite particles from the air. Another method is to implement proper ventilation systems that minimize the accumulation of graphite particles in the environment. Additionally, using specialized containment measures such as sealed containers or enclosures can prevent graphite particles from spreading and contaminating other surfaces. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and work areas can also help to control graphite particle contamination.
- Q: Are there any special precautions to be taken while using graphite crucibles?
- Yes, there are several special precautions that should be taken while using graphite crucibles. First, it is important to handle graphite crucibles with care as they are fragile and can break easily. Avoid dropping or mishandling them to prevent cracks or damage. Secondly, graphite crucibles should be stored in a clean and dry environment to prevent any contamination. Graphite is susceptible to absorbing impurities from the surroundings, which can affect its performance and durability. During use, it is crucial to avoid exposing graphite crucibles to rapid temperature changes. Sudden heating or cooling can cause thermal shock, leading to cracks or even breakage. To prevent this, it is recommended to gradually heat or cool the crucible within the recommended temperature range. Additionally, graphite crucibles should be properly seasoned or preheated before using them for the first time. This involves slowly heating the crucible to a specific temperature to remove any moisture or volatile substances that might be present. Failure to properly season the crucible can lead to cracking or premature failure during subsequent use. Furthermore, it is important to avoid overloading the crucible with excessive material. Graphite crucibles have specific capacity limits, and exceeding these limits can cause the crucible to fail or reduce its lifespan. Lastly, when handling molten materials or pouring them into the crucible, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn. This includes heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and other protective clothing to prevent burns or injuries. By following these precautions, users can maximize the lifespan and performance of graphite crucibles while ensuring safe and effective use.
- Q: Which is a good quality graphite crucible?
- The ordinary graphite crucible can not guarantee the safety in the high temperature environment, moreover, the conduction speed is slow in the test, which is not good for the experiment.
- Q: What magnetic material is sintered with large corundum crucible?
- But the chemical stability is good, not in vacuum. Corundum, by contrast, is much cheaper.
Send your message to us
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords





























