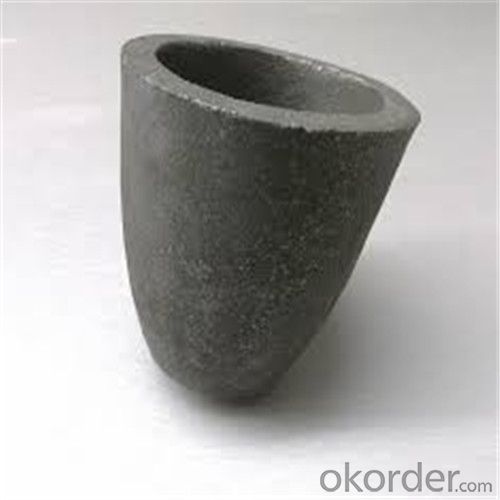
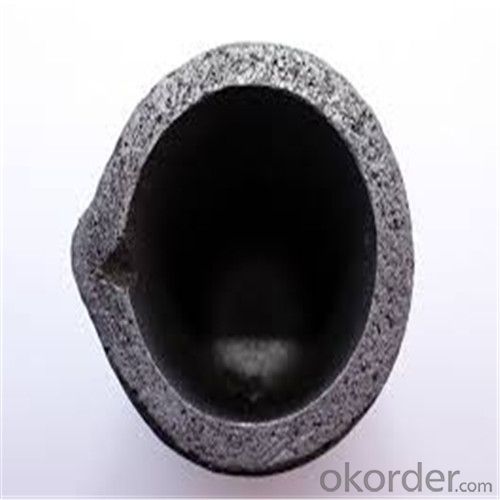
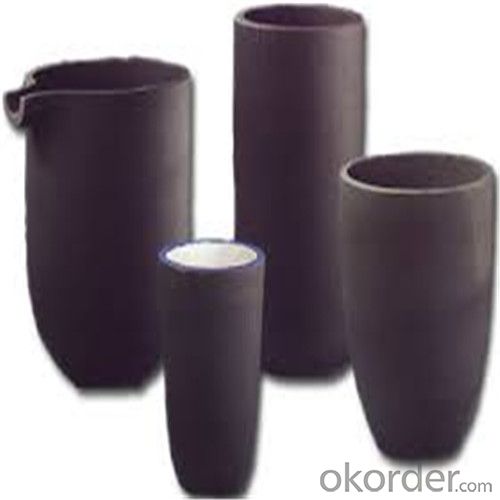
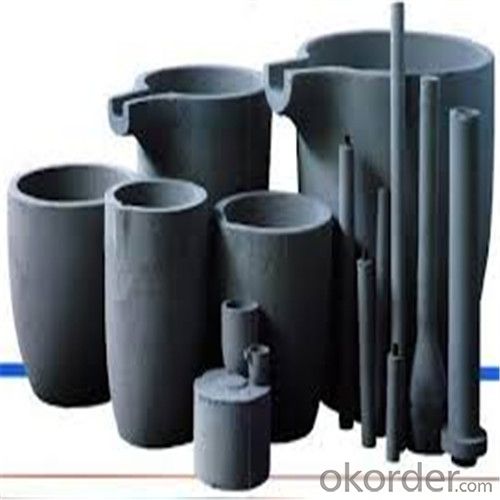
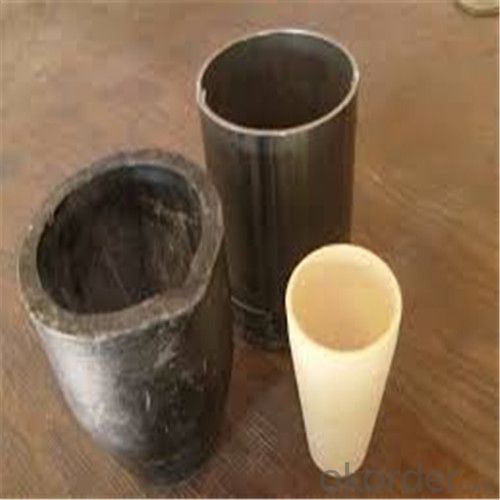
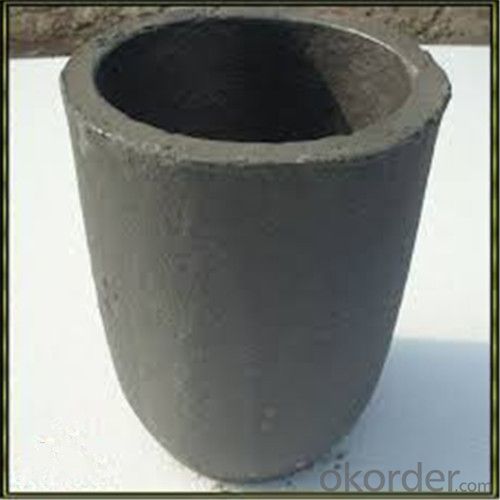
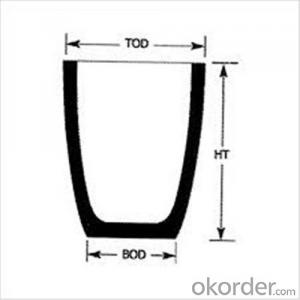
Ceramic Vs Graphite Crucible - Refractory Crucibles SiC Crucible for Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
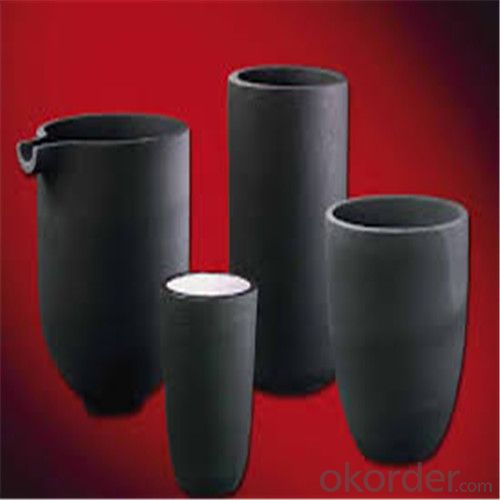
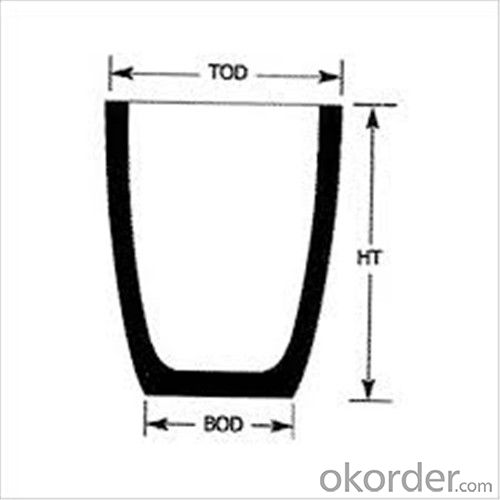

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q: Is the heat conductivity of the crucible good for graphite or iron?
- Purely from thermal conductivity, it must be graphite good. Graphite crucible in addition to resistance to fall, short life, all the performance is good.
- Q: The difference between the graphite rod and graphite electrode, graphite and blank refers to what
- The difference is: the graphite bar may be machined graphite electrode materials may be insulated with material of graphite.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting neptunium?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for melting neptunium. Neptunium is a radioactive and highly reactive element that requires specialized materials, such as refractory metals like tantalum or molybdenum, for melting and containment. Graphite crucibles are not suitable due to their lower melting point and reactivity with neptunium.
- Q: Cast iron into a casting. What is the state of the matter, change, sublimation?
- The graphite crucible has good thermal conductivity and high temperature resistance, and the thermal expansion coefficient is small in the process of high temperature use, and has a certain anti strain property for hot and cold quenching. The corrosion resistance of acid and alkaline solution is strong, and it has good chemical stability.
- Q: Where is the difference between the silicon carbide crucible and the graphite crucible?
- Graphite crucible special tips:1. Be careful not to let the mechanical outside hit, do not belong or strike from the top.2. Should not be exposed to water or stored in a dry place.3. Built in melt dry, without contact with water.4. In use, flames that are not directly in the crucible (jet to the bottom of the crucible) will have a marked black mark at the bottom of the crucible if it is sprayed.5. After the aluminum is stopped, the remaining copper material is tried without leaving residue in the crucible.6. Use the proper amount of oxide (slag, etc) to avoid erosion of the crucible. Excessive use may cause erosion and damage to the crucible.7. When placed in a crucible, there is no need to use mechanical power to have a significant impact.
- Q: How do you prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues?
- To prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues, one can use a technique called preheating. By gradually heating the crucible to the desired temperature before adding any material, the expansion is minimized, reducing the risk of cracking or warping. Additionally, proper cooling methods, such as controlled cooling or using an annealing process, can help alleviate thermal stress and extend the lifespan of the crucible.
- Q: Graphite producer / graphite manufacturer / graphite enterprise brand, where is there?
- There are a lot of production of graphite materials manufacturers, such as Henan Pingdingshan Kaiyuan, Wuxing, exhausted Shi ah, abroad with the East China Sea, Japan, Roland, SGL etc.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing contamination from graphite particles?
- There are several methods that can be used to prevent contamination from graphite particles. 1. Use of containment systems: One method is to use a containment system, such as an enclosed environment or a glove box, to prevent graphite particles from escaping into the surrounding area. These containment systems can be equipped with air filtration and ventilation systems to remove any graphite particles that may be present in the air. 2. Proper handling and storage: Another method of preventing contamination is to ensure that graphite particles are properly handled and stored. This may involve using sealed containers or bags to store graphite, and using appropriate handling techniques to minimize the release of particles into the environment. 3. Regular cleaning and maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and surfaces that come into contact with graphite can help prevent contamination. This may involve using specialized cleaning methods, such as wet cleaning or vacuuming, to remove any graphite particles that may be present. 4. Personal protective equipment: Using personal protective equipment, such as gloves, masks, and coveralls, can help prevent contamination from graphite particles. These protective measures can help minimize direct contact with graphite, reducing the risk of contamination. 5. Proper training and education: Providing training and education to personnel who handle graphite can help raise awareness about the risks of contamination and the proper precautions to take. This can include training on proper handling techniques, the use of personal protective equipment, and the importance of regular cleaning and maintenance. By employing these methods, contamination from graphite particles can be effectively prevented, ensuring a safe and clean working environment.
- Q: Can quartz ceramic crucibles instead of graphite crucibles?
- For the time being, I don't know what to replace. Since graphite was chosen, nothing else could be used.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic glazing?
- Using a graphite crucible for ceramic glazing is not possible. Graphite, a form of carbon with a high melting point, is commonly used for melting metals. However, ceramic glazing requires a crucible that can resist high temperatures and provide a non-reactive environment for the glaze to adhere properly to the ceramic. To meet these requirements, porcelain or stoneware crucibles are needed. These materials are capable of withstanding the high firing temperatures and do not react with the glaze. If a graphite crucible is used, it may react with the glaze and contaminate it, resulting in poor quality or unsuccessful glazing. Thus, it is crucial to use crucible materials specifically designed for ceramic glazing processes.
Send your message to us
Ceramic Vs Graphite Crucible - Refractory Crucibles SiC Crucible for Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords