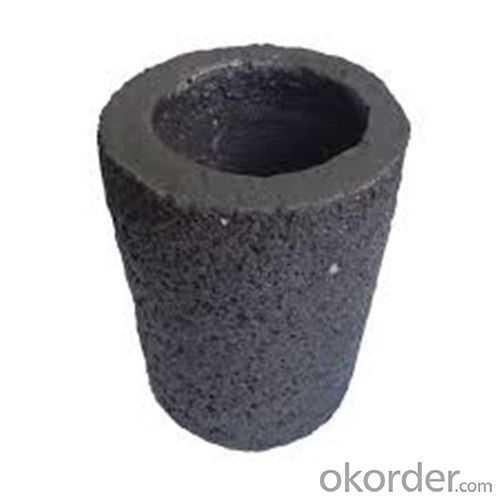
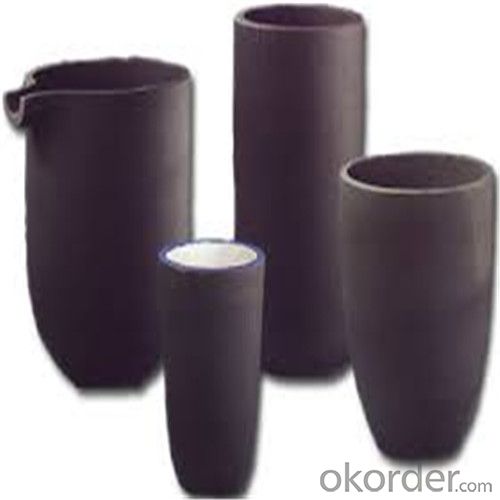
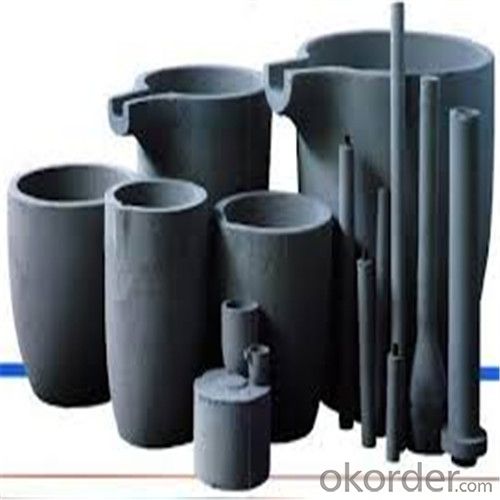
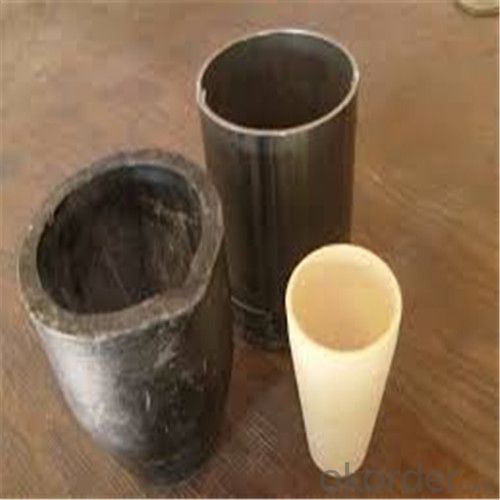
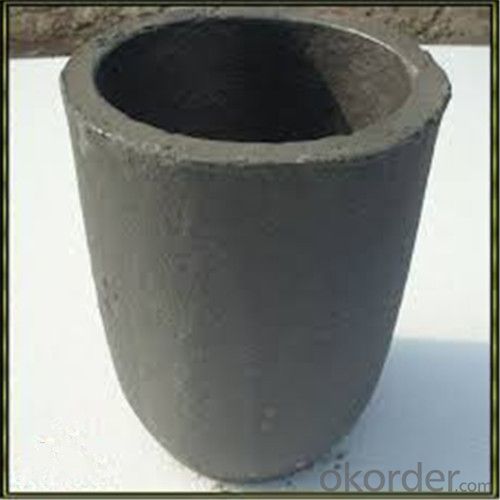
5 Kg Graphite Crucible - SIC Crucibles, SIC Graphite Crucible, Graphite Crucible 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
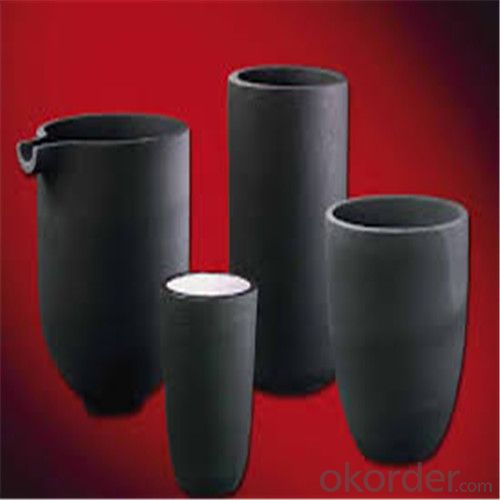

Graphite crucible can withstand the high temperature, and has good resistance to chemical erosions and thermal shock. Especially graphite crucible is ideal for the melting of aluminum, copper and etc.
Bulk Density | g/cc | 1.70-1.88 |
Specific Resistance | μΩ.m | 6.0-15.0 |
Compressive Strength | MPa | 30-80 |
Bending Strength | MPa | 20-45 |
Shore hardness | 30-70 | |
C.T.E.(100-600°C) | x10-6 /°C | 2.5-5.5 |
Ash | % | 0.01-0.2 |
Maximum Grain Size | mm | 0.044-0 |
- Q: How to break 40 low carbon steel smelting
- High pressure pipes are generally welded by argon arc welding, whether they are carbon steel, alloy steel or stainless steel;
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for laboratory analysis?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for laboratory analysis. They are commonly used in high-temperature applications such as melting and analyzing various materials, including metals, alloys, and minerals. Graphite crucibles offer excellent thermal stability, high resistance to chemical corrosion, and good heat transfer properties, making them suitable for laboratory analysis purposes.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting explosives?
- No, graphite crucibles should not be used for melting explosives as graphite is a highly flammable material and can potentially react with explosive substances, leading to dangerous situations. It is recommended to use specialized containers and equipment designed for handling explosives to ensure safety.
- Q: What are the different methods of measuring the temperature inside a graphite crucible?
- There are several methods for measuring the temperature inside a graphite crucible. One common method is using a thermocouple, which is a device that measures temperature by measuring the voltage difference between two different metals. Another method is using an infrared (IR) thermometer, which measures temperature by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by the crucible. Additionally, some crucibles have built-in temperature sensors or probes that can directly measure the temperature.
- Q: How does the hardness of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The hardness of graphite plays a crucial role in the performance of a crucible. A harder graphite crucible tends to have greater durability and resistance to wear and tear, resulting in a longer lifespan. Additionally, its higher hardness allows it to withstand higher temperatures without deforming or cracking, making it more suitable for use in high-temperature applications. So, the hardness of graphite directly impacts the performance and reliability of a crucible.
- Q: How do you prevent graphite crucibles from cross-contamination during use?
- To prevent graphite crucibles from cross-contamination during use, it is important to follow a few key steps. Firstly, it is crucial to properly clean the crucible before each use. This can be done by thoroughly washing it with a suitable cleaning agent and rinsing it with distilled water. It is important to ensure that all residual materials from previous use are completely removed. Secondly, it is advisable to dedicate specific crucibles for different types of materials or applications. This prevents the risk of cross-contamination between different substances. For example, one crucible can be used exclusively for metals, while another can be used for non-metals. Additionally, it is important to handle the crucibles with clean, gloved hands to avoid introducing any contaminants. Moreover, it is recommended to store the crucibles in a clean, dry environment to minimize the risk of contamination. During use, it is crucial to avoid overheating the crucible excessively, as this can lead to degradation or contamination of the graphite material. It is best to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for temperature limits and heating/cooling cycles. Lastly, it is good practice to regularly inspect the crucibles for any signs of wear or damage. If any cracks, chips, or other forms of damage are observed, it is important to replace the crucible to prevent any potential contamination. By following these preventive measures, one can minimize the risk of cross-contamination during the use of graphite crucibles, ensuring accurate and reliable results in various applications.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for both melting and casting?
- Both melting and casting can be done using graphite crucibles. Graphite is well-known for its exceptional heat resistance and high melting point, making it an ideal choice for containing molten metals during the melting process. Furthermore, graphite crucibles possess excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer and uniform heating of the molten metal. Once the metal has melted, the graphite crucible can also serve as a casting tool. The molten metal can be poured directly from the crucible into a mold, allowing for the creation of various shapes and forms. Graphite crucibles are typically durable and can withstand multiple heating and cooling cycles, making them suitable for both melting and casting procedures. However, it is essential to acknowledge that graphite crucibles may not be suitable for all types of metals. Some reactive or corrosive metals can react with graphite at high temperatures, leading to contamination of the molten metal. In such cases, alternative crucible materials, such as ceramic or refractory metals, may be more appropriate.
- Q: Are there any alternative materials to graphite for crucibles?
- Yes, there are alternative materials to graphite for crucibles. Some common alternatives include silicon carbide, alumina, zirconia, and boron nitride. These materials are often preferred for their specific properties and applications. For example, silicon carbide exhibits excellent thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Alumina, on the other hand, is known for its chemical inertness and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for handling reactive materials. Zirconia offers good thermal shock resistance and is often used in applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Lastly, boron nitride is preferred for its excellent thermal stability and lubricity. Each of these alternative materials has its own advantages and specific uses, making them viable options for crucibles depending on the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for bronze casting?
- Certainly, bronze casting can utilize a graphite crucible. The utilization of graphite crucibles is widespread in metal casting procedures due to their remarkable thermal conductivity, high melting point, and resistance to thermal shock. In contrast to graphite, bronze, an amalgamation of copper and tin, generally possesses a lower melting point, making it a fitting material for casting within a graphite crucible. Moreover, graphite crucibles provide commendable chemical stability, a pivotal factor when operating with molten metals. Nevertheless, it is imperative to underscore the significance of adequately seasoning and preheating the crucible to avoid any potential reactions between the molten bronze and the graphite crucible.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for titanium melting?
- It is not possible to use a graphite crucible for melting titanium. The melting point of titanium is extremely high, reaching 1,668 degrees Celsius (3,034 degrees Fahrenheit), surpassing the maximum temperature capability of graphite, which is approximately 3,000 degrees Celsius or 5,432 degrees Fahrenheit. Consequently, if a graphite crucible were employed for titanium melting, the crucible would degrade and potentially pollute the titanium. In lieu of this, a crucible composed of materials like zirconium or ceramic should be utilized for titanium melting, as they can endure the elevated temperatures necessary for the procedure.
Send your message to us
5 Kg Graphite Crucible - SIC Crucibles, SIC Graphite Crucible, Graphite Crucible 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords