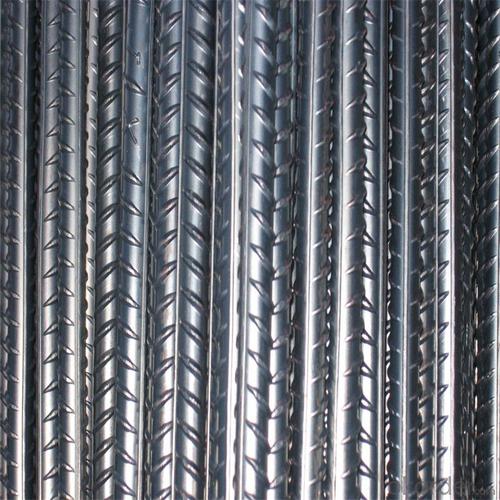
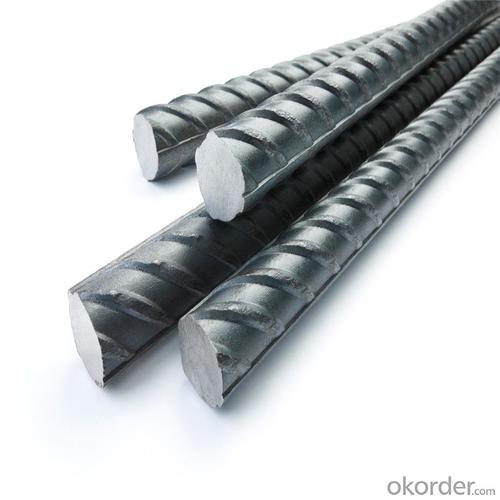
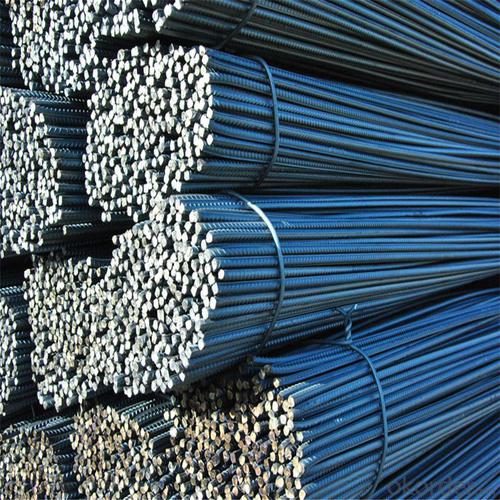
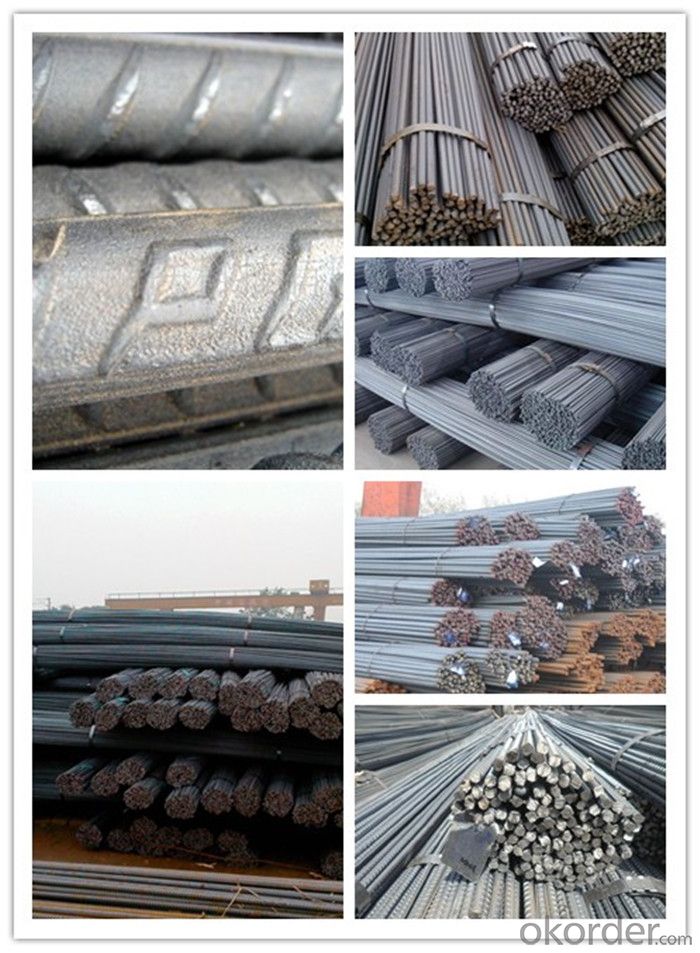
SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 160 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
Description of SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
10m- 40mm SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
Company Information
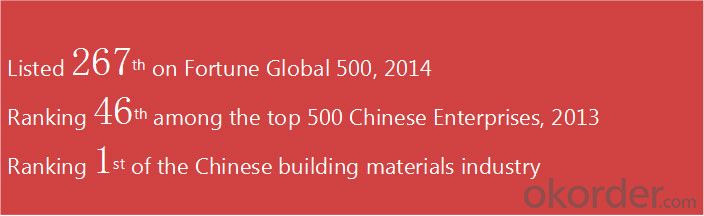
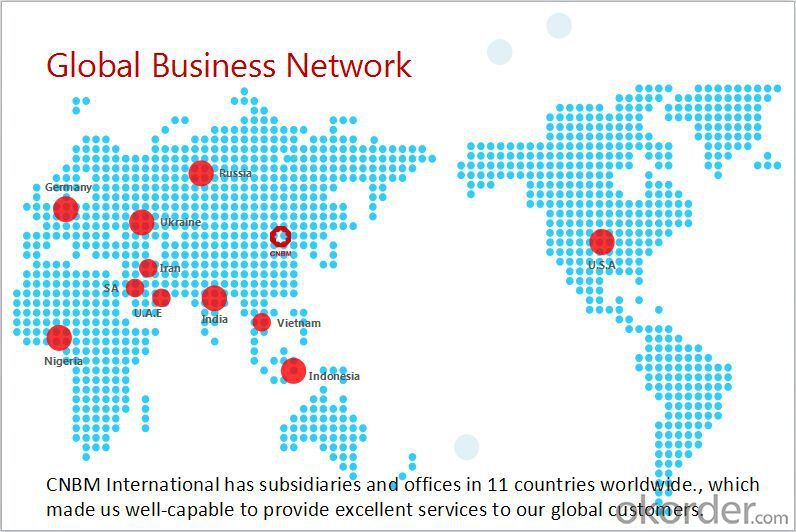
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the main applications of special steel in the medical implants?
- Special steels have numerous applications in the field of medical implants. They are commonly used in orthopedic implants such as joint replacements, screws, plates, and pins, due to their high strength and corrosion resistance. Special steels are also utilized in cardiovascular implants like stents and pacemaker leads, as they provide excellent biocompatibility and durability. Additionally, special steels find application in dental implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics, owing to their ability to withstand sterilization processes and maintain mechanical integrity.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the production of precision instruments?
- Special steel contributes to the production of precision instruments by providing the necessary strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Its unique properties allow for the manufacturing of intricate components with tight tolerances, ensuring the precision instruments function accurately and reliably.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the defense equipment manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the defense equipment manufacturing industry. Special steel alloys, such as high-strength and corrosion-resistant varieties, are often utilized in the production of various defense equipment components, including armored vehicles, missiles, aircraft, and naval vessels. These specific steel types offer superior mechanical properties, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions, making them highly suitable for defense applications.
- Q: What are the common challenges in welding titanium alloys?
- Welding titanium alloys presents various difficulties due to the unique properties of titanium. Firstly, the melting point of titanium is exceptionally high, reaching approximately 1668°C (3034°F). This necessitates the use of specialized equipment and techniques to attain optimal welding conditions. Moreover, this high melting point increases the risk of overheating, which can lead to distortion or warping of the welded components. Another challenge lies in titanium's strong reactivity with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. These gases can easily contaminate the weld pool during the welding process, resulting in the formation of brittle and porous welds. Therefore, it is essential to take rigorous measures such as utilizing inert shielding gases like argon or helium, maintaining a high level of cleanliness, and employing proper welding techniques like gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) to minimize contamination and achieve sound welds. Titanium also exhibits a significant affinity for carbon, which can cause the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds during welding. To prevent this, it is crucial to employ low-carbon filler metals and ensure appropriate heat input to avoid carbon diffusion into the weld zone. Furthermore, titanium alloys possess low thermal conductivity, causing heat generated during welding to concentrate in a small area. This concentration leads to localized overheating and potential damage. Hence, it is vital to control heat input and utilize suitable welding techniques to distribute heat evenly, thereby avoiding overheating and preserving the integrity of the welded joint. Lastly, titanium alloys display a high coefficient of thermal expansion, resulting in significant thermal expansion and contraction throughout the welding process. This can lead to distortion and residual stresses in the welded components. To mitigate these issues, preheating and post-weld heat treatment may be required to minimize distortion and relieve residual stresses. In conclusion, the challenges in welding titanium alloys encompass a high melting point, reactivity with gases, potential contamination, formation of intermetallic compounds, low thermal conductivity, and significant thermal expansion. By comprehending these challenges and implementing suitable welding techniques, it is possible to overcome these difficulties and achieve high-quality welds in titanium alloys.
- Q: Can special steel be used in marine applications?
- Marine applications can indeed utilize special steel. This type of steel, also referred to as marine grade steel, is specifically engineered to endure the demanding conditions found in marine environments. It possesses exceptional qualities, including heightened resistance to corrosion, increased strength, and enhanced durability, which render it suitable for a wide range of marine applications. The construction of ships, offshore structures, and marine equipment commonly employs special steel. Its capacity to withstand corrosion from saltwater, chemicals, and other environmental factors makes it an excellent choice for marine applications. Additionally, special steel finds use in the production of propellers, shafts, and other components that necessitate high tensile strength and fatigue resistance. All in all, special steel proves to be a dependable and efficient material for marine applications due to its unique properties and ability to withstand the challenges presented by the marine environment.
- Q: How does special steel perform in marine applications?
- Marine grade steel, also referred to as special steel, exhibits exceptional performance in marine applications. Designed and manufactured specifically to endure the harsh and corrosive conditions commonly found in marine settings, this type of steel offers a range of advantages. One of the primary benefits of special steel in marine applications is its remarkable resistance to corrosion. Traditional steel is susceptible to the corrosive effects of saltwater, which is abundant in marine environments. However, special steel incorporates additional alloying elements like chromium and nickel, which enhance its corrosion resistance. As a result, the steel remains structurally sound and retains its strength and integrity over time. Moreover, special steel possesses outstanding strength and toughness characteristics, rendering it highly suitable for marine applications. It can withstand extreme temperatures, heavy loads, and impacts, making it ideal for shipbuilding, offshore structures, and other marine equipment. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable resistance to fatigue, a crucial attribute for structures constantly exposed to dynamic loads and vibrations in marine environments. Additionally, special steel is renowned for its excellent weldability and machinability, facilitating easy fabrication and installation in marine applications. This steel can be effortlessly shaped into various forms and sizes, providing flexibility in design and construction. Overall, special steel is an extremely reliable and durable choice for marine applications due to its exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, toughness, and weldability. It guarantees the longevity and safety of marine structures and equipment, making it the preferred option for numerous industries within the marine sector.
- Q: How does precipitation hardening enhance the strength of special steel?
- The process of precipitation hardening, which is also referred to as age hardening, serves to boost the strength of specific steel alloys through a heat treatment technique. This technique involves a series of steps that lead to the formation of small particles or precipitates within the microstructure of the material. The strength of special steel is mainly determined by the arrangement and interaction of its atoms. Initially, the atoms of the alloy are randomly distributed, resulting in a relatively soft and malleable substance. However, through precipitation hardening, the formation of precipitates during the heat treatment process plays a vital role in strengthening the steel. The process commences by subjecting the steel to a high temperature, referred to as the solution treatment or aging temperature. This elevated temperature allows the atoms to dissolve and form a solid solution. Subsequently, the alloy is rapidly cooled to preserve the supersaturated state of the solution. After the rapid cooling, the steel is exposed to a lower temperature, known as the aging temperature. During this stage, the dissolved atoms start to migrate and cluster together, forming small precipitates within the microstructure of the material. These precipitates act as obstacles to the movement of dislocations, which are the primary carriers of plastic deformation in metals. The presence of these precipitates hampers the movement of dislocations, making it more challenging for them to glide through the crystal lattice. Consequently, the strength of the steel is significantly enhanced. The dislocation obstacles provided by the precipitates increase the resistance to deformation, resulting in improved hardness and strength. Furthermore, the size, distribution, and uniformity of the precipitates play a crucial role in determining the extent of strength enhancement. Smaller and more evenly distributed precipitates offer a higher density of obstacles, leading to a greater strengthening effect. Additionally, the process of precipitation hardening also influences other material properties, such as corrosion resistance and toughness. To conclude, precipitation hardening strengthens special steel by creating small precipitates within its microstructure. These precipitates impede the movement of dislocations, increasing resistance to deformation and resulting in improved hardness and strength. This heat treatment process is pivotal in the development of high-performance special steel alloys utilized in diverse industries.
- Q: How is special steel used in the food processing industry?
- Special steel is used in the food processing industry for various applications such as manufacturing equipment and machinery, utensils, and containers. Its unique properties, including corrosion resistance, durability, and hygiene, make it suitable for ensuring food safety and maintaining high standards in processing and handling.
- Q: What are the challenges in surface treating special steel?
- Some of the challenges in surface treating special steel include achieving uniform and consistent coatings, ensuring adhesion of the coating to the steel substrate, overcoming the high hardness of the steel, preventing distortion or warping during the treatment process, and managing the potential for thermal degradation or oxidation. Additionally, the presence of unique alloying elements in special steel may require specialized treatment techniques to achieve the desired surface properties.
- Q: How does special steel perform in cryogenic toughness?
- Special steel has gained recognition for its outstanding performance in cryogenic toughness. Unlike regular steel, which significantly loses its toughness when exposed to extremely low temperatures, special steel is specifically designed to withstand such extreme conditions and maintain its toughness and ductility. The composition and microstructure of special steel are carefully engineered to ensure its high performance in cryogenic environments. Through a unique combination of alloying elements and heat treatment processes, special steel can resist brittle fracture and retain its strength even at temperatures as low as -196 degrees Celsius (-321 degrees Fahrenheit). The exceptional cryogenic toughness of special steel makes it an ideal choice for a range of applications, including the storage and transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG), aerospace engineering, and medical equipment used in cryogenic medicine. It provides the necessary reliability and safety when subjected to extreme cold temperatures, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the materials and structures it is employed in. In conclusion, special steel's exceptional performance in cryogenic toughness distinguishes it from regular steel, making it the preferred choice for applications that demand reliable and durable materials in extremely low-temperature environments.
Send your message to us
SD390 Steel Rebar with JIS Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 160 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































