Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe STPG370 CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details
| Thickness: | 1.73 - 59.54 mm | Section Shape: | Round | Outer Diameter: | 10.3 - 914.4 mm |
| Secondary Or Not: | Non-secondary | Application: | Fluid Pipe | ||
| Technique: | Hot Rolled | Certification: | API | Surface Treatment: | Galvanized,vanish covering, black painting, galvenized ect. |
| Special Pipe: | API Pipe | Alloy Or Not: | Non-alloy | Length: | 5-12m as per customer's requirements |
| SCH: | SCH10~160, STD, XS & XXS | Payment Terms: | L/C T/T | Supply Ability: | 5000 Ton/Tons per Week |
| Product: | pipe prices | Grade: | 10#,20#,45#,A106(B,C),A53(A,B),12Cr1MoV,12Cr1MoVG,12Cr2Mo,13CrMo44,13CrMo45,15CrMo,15CrMoG,St52,St52.4,10#-45#,A53-A369,Cr-Mo alloy,ST35-ST52 | Standard: | API 5CT,API 5L,ASTM A106-2006,ASTM A53-2007,DIN 17175,GB 3087-1999,GB 5130,GB 6479-2000,GB 9948-2006,GB/T 17396-1998,GB/T 5312-1999,GB/T 8162-1999,GB/T 8163-1999,API,ASTM,DIN,GB |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Detail: | By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 5-15 days |
Specifications
1.pipe prices
2.Supply Ability:5000 Tons per Week
3.Payment Terms:L/C T/T
High quality Carbon steel pipe, Best pipe prices
1) Application: Overheat pipe for low and mediumpressure boiler,boiling water pipe, locomotive smoke pipe(big and small),Carry gas ,water or oil in the industries of petroleum and natural gas etc
2) Materials: 10#, 20#, 45#, 15CrMo, 12Cr1MoV, 13CrMo44, 12Cr2Mo, 13CrMo45, 12Cr1MoVG, 15CrMoG, API J55, API K55, API N80, API L80, API P110
3)Pipe according to standard: GB 3087-1999, GB/T 8163-1999, GB/T 8162-1999, GB 9948-2006, GB/T 17396-1998, GB/T 5312-1999, GB 6479-2000, GB 5130, DIN 17175, API 5CT, API 5L .
4)Packing: By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers.
Technical Parameters of Seamless Steel Pipe
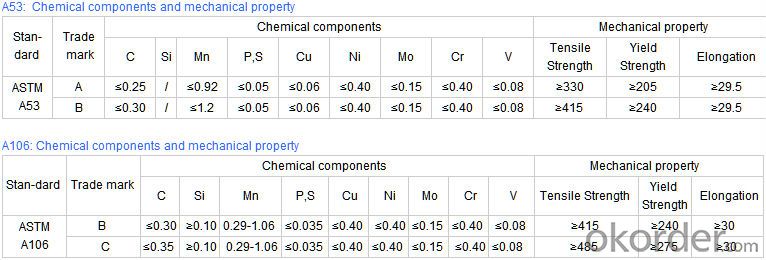
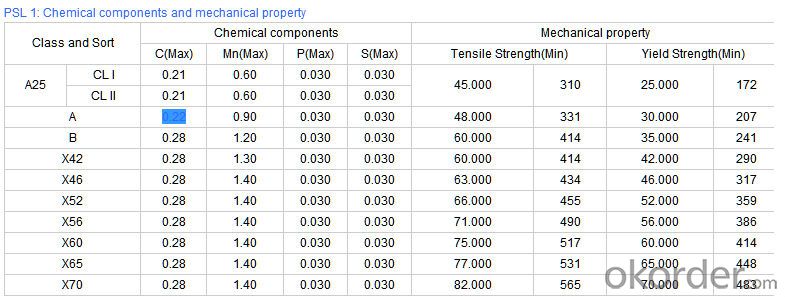
- Q: What are the different methods of pipe protection for steel pipes?
- There are several methods of pipe protection for steel pipes. These include corrosion-resistant coatings such as epoxy or polyethylene, cathodic protection systems, which use sacrificial anodes or impressed current to prevent corrosion, wrapping the pipes with protective tape or shrink sleeves, and using corrosion inhibitors to prevent the formation of rust. Additionally, proper installation practices, regular inspections, and maintenance can also contribute to pipe protection.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the telecommunications network infrastructure?
- Steel pipes are widely used in the telecommunications network infrastructure for various purposes. One of the primary uses of steel pipes in this industry is for the installation of underground cable conduits. These conduits protect the telecommunications cables from external factors such as moisture, rodents, and physical damage. Steel pipes provide excellent strength and durability, ensuring the long-term protection of the cables. Additionally, steel pipes are used in the construction of telecom towers and antenna masts. These structures need to be sturdy and able to withstand harsh weather conditions. Steel pipes offer the necessary strength, stability, and resilience required for telecom towers to support antennas and other equipment. They can be easily assembled, allowing for efficient deployment and maintenance of the network infrastructure. Moreover, steel pipes are essential for the installation of fiber optic cables. Fiber optic cables transmit data at high speeds using light signals. To ensure optimal performance, these cables need to be protected from any external interference. Steel pipes serve as a conduit for fiber optic cables, shielding them from electromagnetic interference and other potential disruptions. In summary, steel pipes play a crucial role in the telecommunications network infrastructure. They are used for the installation of underground cable conduits, construction of telecom towers, and protection of fiber optic cables. The strength, durability, and versatility of steel pipes make them an ideal choice for ensuring the reliability and functionality of telecommunications systems.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for flagpoles?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for flagpoles. Steel pipes are often used for flagpoles due to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. They can be easily fabricated to the desired height and thickness, making them suitable for flags of various sizes. Additionally, steel pipes can be painted or coated to prevent corrosion and enhance their aesthetic appeal.
- Q: How do you calculate the pipe head loss for steel pipes?
- The Darcy-Weisbach equation is utilized for calculating the pipe head loss in steel pipes. This equation establishes a connection between the head loss (hL) and various factors such as the flow rate (Q), pipe diameter (D), pipe length (L), fluid density (ρ), fluid velocity (V), and the friction factor (f). The formula can be expressed as: hL = (f * (L/D) * (V^2))/(2g) Where: - The head loss (hL) is measured in meters - The friction factor (f) is dimensionless - The pipe length (L) is measured in meters - The pipe diameter (D) is measured in meters - The fluid velocity (V) is measured in meters per second - The acceleration due to gravity (g) is typically taken as 9.81 m/s^2 The friction factor (f) relies on the Reynolds number (Re) of the flow, which is a dimensionless quantity representing the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces. The Reynolds number can be calculated using the following equation: Re = (ρ * V * D) / μ Where: - The Reynolds number (Re) is dimensionless - The fluid density (ρ) is measured in kg/m^3 - The fluid velocity (V) is measured in meters per second - The pipe diameter (D) is measured in meters - The dynamic viscosity of the fluid (μ) is measured in Pa·s or N·s/m^2 The friction factor (f) can be obtained from empirical correlations or from Moody's diagram, which establishes a connection between the Reynolds number, the relative roughness of the pipe surface, and the friction factor. By substituting the calculated friction factor (f) and other known values into the Darcy-Weisbach equation, the head loss in the steel pipe can be determined. It is important to note that the head loss represents the energy lost due to friction and other factors and is usually expressed in terms of pressure drop or height difference.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for steam distribution?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for steam distribution. Steel pipes are commonly used for conveying steam due to their high heat resistance and durability. They can withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with steam distribution, making them a suitable choice for this application.
- Q: How do you clean and maintain steel pipes?
- To clean and maintain steel pipes, start by removing any dirt, debris, or rust using a wire brush or sandpaper. Then, wash the pipes with a mild detergent and warm water solution, using a cloth or sponge to scrub away any remaining grime. Rinse thoroughly with clean water and dry the pipes completely to prevent moisture-related issues. To maintain steel pipes, regularly inspect them for signs of corrosion or damage, and apply a protective coating or paint if necessary. Additionally, ensure proper drainage, avoid exposure to harsh chemicals, and promptly address any leaks or repairs needed to extend the lifespan of the pipes.
- Q: How do you calculate the pipe pressure drop for steel pipes?
- To calculate the pipe pressure drop for steel pipes, you can use the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation. The Darcy-Weisbach equation is generally more accurate but requires more information. It takes into account the pipe diameter, length, roughness, fluid flow rate, and fluid properties such as viscosity and density. The equation is as follows: ΔP = (f * L * ρ * V^2) / (2 * D) Where: ΔP is the pressure drop f is the friction factor (which can be determined using Moody's chart or by using empirical equations such as the Colebrook-White equation) L is the pipe length ρ is the fluid density V is the fluid velocity D is the pipe diameter The Hazen-Williams equation is a simplified version that is commonly used for water flow calculations. It is less accurate but easier to use. The equation is as follows: ΔP = K * Q^1.85 / (C^1.85 * d^4.87) Where: ΔP is the pressure drop K is the Hazen-Williams coefficient (which depends on the pipe material and roughness) Q is the flow rate C is the Hazen-Williams roughness coefficient d is the pipe diameter It's important to note that these equations provide an estimate of the pressure drop, and actual conditions may vary due to factors such as fittings, bends, and valves in the pipe system. Additionally, it's crucial to ensure that the units used in the equations are consistent (e.g., using SI units or US customary units).
- Q: What is the difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 steel pipes?
- The main difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 steel pipes lies in their wall thickness. Schedule 40 pipes have a thinner wall, making them suitable for low-pressure applications, while Schedule 80 pipes have a thicker wall, enabling them to withstand higher pressure.
- Q: What is the buckling type thin-wall steel pipe? What is a tight set of thin-walled steel tubes? What's the difference between the two?
- The nut body and the junction box are connected at one end by adopting metric fine tooth thread, and the pipe is connected with the pipe, and one end is the same as the straight pipe joint (direct). Withhold the box joint points inside and outside teeth two. The diameter of straight pipe joint is divided into 16mm, 20mm, 25mm, 32mm, 40mm, 50mm.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the transportation of liquids and gases?
- Due to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion, steel pipes find wide applications in the transportation of liquids and gases. Various industries such as oil and gas, water supply, and chemical processing commonly employ them. For the transportation of liquids, steel pipes serve as conduits for crude oil, refined petroleum products, water, and other fluids. These pipes are designed to withstand high pressure and maintain the integrity of the liquid being transported. The smooth inner surface of steel pipes minimizes friction, enabling efficient flow and reduced energy consumption. Moreover, the strength of steel pipes ensures that they can support the weight of the liquid without deformation or failure. In gas transportation, steel pipes are indispensable for the safe conveyance of natural gas, propane, and other compressed gases over long distances. These pipes are engineered to endure high pressures and extreme temperatures. They are also designed to prevent leakage, which is of utmost importance when dealing with flammable or toxic gases. The strength and durability of steel pipes make them ideal for withstanding the stress and strain that may occur during gas transportation. Additionally, steel pipes are frequently utilized in the construction of pipelines for long-distance transportation of liquids and gases. These pipelines can span hundreds or even thousands of kilometers, and steel pipes are the preferred choice due to their high strength and long-term reliability. They can bear the weight of the pipe and the substance being transported, as well as external forces such as soil pressure and temperature fluctuations. In summary, steel pipes play a vital role in the transportation of liquids and gases. Their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion make them the preferred choice for conveying various substances over long distances. Whether it is for oil and gas, water supply, or chemical processing, steel pipes ensure the safe and efficient transportation of fluids and gases, contributing to the functioning of various industries and economies worldwide.
Send your message to us
Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe STPG370 CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























