parallel flange channel steel in U shaped
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Products Information:
| 1.Products size | Size : 5#--40# | ||||
| 2.Products length | Lengths : 6m--12m | ||||
| 3.Product standard | Standard : GB, ASTM, JIS, DIN | ||||
| 4.Product Grade | Grades : Q235B, Q345B, SS400 | ||||
| 5.Application | Used or building structures, vehicle | ||||
| manufacturing and other industrial structures | |||||
| 6.Customized requirement | Can produce special specification products | ||||
| as per our customers' requirement | |||||
| 7.Delivery Time | 15-30 days after recieve the LC or pre-paid | ||||
| 8.Detail Package | Bundles, seaworthy wooden cases with or without | ||||
| edge protector, steel hoop and seals, or as per | |||||
| customers' requirements | |||||
Drawings and Datas (for know more about the structure and size)
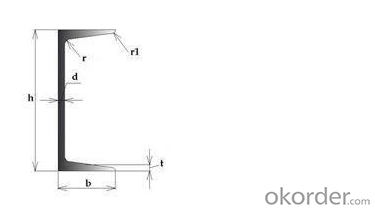
Specification | h | b | d | t | Cm2 | (kg/m) |
5 | 50 | 37 | 4.5 | 7 | 6.93 | 5.44 |
6.3 | 63 | 40 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 8.45 | 6.63 |
8 | 80 | 43 | 5 | 8 | 10.24 | 8.04 |
10 | 100 | 48 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 12.74 | 10 |
12.6 | 126 | 53 | 5.5 | 9 | 15.69 | 12.37 |
14a | 140 | 58 | 6 | 9.5 | 18.51 | 14.53 |
14b | 140 | 60 | 8 | 9.5 | 21.31 | 16.73 |
16a | 160 | 63 | 6.5 | 10 | 21.95 | 17.23 |
16 | 160 | 65 | 8.5 | 10 | 25.15 | 19.74 |
18a | 180 | 68 | 7 | 10.5 | 25.69 | 20.17 |
18 | 180 | 70 | 9 | 10.5 | 29.29 | 22.99 |
- Q: Are stainless steel angles suitable for the production of street signs?
- Yes, stainless steel angles are suitable for the production of street signs. Stainless steel is a durable and corrosion-resistant material that can withstand harsh weather conditions and the wear and tear of outdoor environments. The use of stainless steel angles ensures that the street signs are strong and stable, with the ability to withstand impacts and remain in place for a long time. Additionally, stainless steel is easy to clean and maintain, which is important for keeping street signs visible and legible. Overall, stainless steel angles are a reliable choice for the production of street signs due to their durability, resistance to corrosion, and low maintenance requirements.
- Q: How are stainless steel angles measured?
- When measuring stainless steel angles, two main dimensions are commonly used: the length of each leg and the thickness of the material. The length of each leg represents the distance from the intersection point to the end of the leg, while the thickness refers to the measurement from one edge to the other. These dimensions are typically expressed in inches or millimeters. Moreover, the angle itself is often identified by its nominal size, which is determined by the length of the legs. For instance, a stainless steel angle with equal leg lengths of 2 inches would be called a 2-inch angle. In conclusion, measuring stainless steel angles involves considering the leg length, material thickness, and nominal angle size.
- Q: How are stainless steel angles measured and specified?
- Stainless steel angles are measured and specified based on their dimensions, which include the length, width, and thickness of the angle. The standard unit of measurement for stainless steel angles is usually in inches or millimeters, depending on the region or country. To measure a stainless steel angle, you need to determine its length, which is the longest side of the angle. This can be done by using a measuring tape or a ruler. The length is typically expressed in inches or millimeters. Next, you need to measure the width of the angle, which is the shorter side. This measurement is also expressed in inches or millimeters and is usually taken perpendicular to the length. Finally, the thickness of the stainless steel angle needs to be determined. This is the distance between the two parallel sides of the angle and is measured in inches or millimeters. Once the measurements are known, stainless steel angles are specified by stating the length, followed by the width and then the thickness. For example, a stainless steel angle could be specified as 2 inches by 2 inches by 1/4 inch or 50 millimeters by 50 millimeters by 6 millimeters. In addition to the dimensions, the grade of stainless steel used in the angle may also be specified. Stainless steel comes in various grades, such as 304 or 316, which have different properties and applications. Overall, the measurement and specification of stainless steel angles involve determining the length, width, and thickness, and also considering the grade of stainless steel used.
- Q: What is the average lead time for stainless steel angle orders?
- Several factors can affect the average lead time for stainless steel angle orders. These factors include the quantity of the order, the specific dimensions and specifications required, and the current demand and availability of stainless steel angles in the market. For standard-sized stainless steel angle orders, the average lead time usually ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks. This timeframe includes the processing of the order, sourcing the materials, and arranging for transportation or delivery. It is important to note that lead times may be longer for custom or non-standard orders. These orders often require additional time for manufacturing, fabrication, or special processing based on the specific requirements of the customer. For a precise estimate of the lead time for a stainless steel angle order, it is advisable to directly contact the supplier or manufacturer. They can provide detailed information considering the current availability, production capabilities, and any other factors that may influence the lead time for the order.
- Q: What are the seismic resistance properties of stainless steel angles?
- Due to their inherent material characteristics, stainless steel angles offer superb seismic resistance. This is because stainless steel, being a highly durable and corrosion-resistant alloy, possesses exceptional strength and toughness, making it capable of withstanding seismic forces. One notable advantage of stainless steel angles in seismic applications is their remarkable tensile strength. They can withstand the tensile forces generated during seismic events, thereby minimizing the risk of structural failure. Furthermore, stainless steel angles possess a high yield strength, enabling them to effectively absorb and distribute seismic energy. Another crucial factor contributing to the seismic resistance of stainless steel angles is their ductility. Stainless steel exhibits excellent ductility, allowing it to undergo significant deformation without fracturing. This property proves especially important during seismic events when structures experience intense vibrations and ground motion. The ductility of stainless steel angles aids in the absorption and dissipation of seismic energy, thereby reducing the potential for damage. Moreover, stainless steel is a non-combustible material, meaning it does not burn or contribute to the spread of fire. This characteristic enhances the seismic resistance of stainless steel angles, as fire incidents can occur during earthquakes. The use of non-combustible materials like stainless steel helps prevent further hazards. Furthermore, stainless steel exhibits high resistance to corrosion, even in harsh environments. This corrosion resistance ensures the long-term durability of stainless steel angles, making them suitable for seismic applications in various settings, including coastal areas prone to saltwater exposure. In conclusion, stainless steel angles offer excellent seismic resistance properties due to their high tensile strength, ductility, non-combustibility, and corrosion resistance. These characteristics make stainless steel angles a reliable choice for structural applications in seismic zones, providing enhanced safety and durability during earthquake events.
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be used in the construction of support structures?
- Yes, stainless steel angles can be used in the construction of support structures. Stainless steel is known for its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for support structures that need to withstand heavy loads or harsh environments. The angles provide structural support and stability, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the construction.
- Q: What are the thermal conductivity properties of stainless steel angles?
- Good thermal conductivity properties are possessed by stainless steel angles. The term "thermal conductivity" pertains to a material's capability to conduct heat. Stainless steel is renowned for its elevated thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer between different points. This characteristic renders stainless steel angles suitable for applications emphasizing heat transfer, such as in heat exchangers, radiators, and other thermal management systems. Moreover, stainless steel angles exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, and durability, making them the preferred option in diverse industries where thermal conductivity plays a vital role.
- Q: Can stainless steel angle be used in food processing equipment?
- Certainly, food processing equipment can utilize stainless steel angle. The food processing industry extensively employs stainless steel due to its numerous appealing characteristics. It exhibits resistance against corrosion, ease of cleaning, and no reactivity or alteration of food flavor. Stainless steel angle, frequently employed for equipment's structural support or framework, offers equivalent advantages. It endures, maintains hygiene, and withstands the challenging conditions of food processing environments. Moreover, stainless steel adheres to the stringent sanitary standards and regulations established by food safety organizations. Thus, stainless steel angle serves as an appropriate option for food processing equipment.
- Q: Are stainless steel angles suitable for outdoor use?
- Stainless steel angles are indeed appropriate for outdoor use due to their remarkable resistance to corrosion. This quality has made stainless steel a popular option for outdoor purposes, as it can endure harsh weather conditions, including rain, snow, and UV radiation, without succumbing to rust or corrosion. Furthermore, stainless steel angles possess resistance to chemicals and environmental pollutants, making them ideal for outdoor environments that may be heavily polluted or exposed to corrosive substances. Moreover, these angles exhibit strength and durability, enabling them to withstand the challenges of outdoor use and maintain their structural integrity over time. Hence, whether it be for construction, architecture, or any other outdoor applications, stainless steel angles are a dependable and suitable choice.
- Q: What is the fracture toughness of stainless steel angles?
- The fracture toughness of stainless steel angles can vary depending on a few factors such as the specific grade of stainless steel, the manufacturing process, and the presence of any defects or impurities. Generally, stainless steel is known for its good fracture toughness, which refers to its ability to resist crack propagation and failure under applied stress. Stainless steel is often chosen for structural applications due to its high strength and toughness, making it suitable for withstanding heavy loads and impacts. However, it is important to consult the specific technical data or material specifications for the particular grade and condition of stainless steel angles to determine their fracture toughness values.
Send your message to us
parallel flange channel steel in U shaped
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























