cold roll forming steel channel for construction
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
cold roll forming steel channel for construction
Products Information
| 1.Product Size | Size : 5#--40# | ||||
| 2.Product length | Lengths : 6m--12m | ||||
| 3.Standard | Standard : GB, ASTM, JIS, DIN | ||||
| 4.Grade | Grades : Q235B, Q345B, SS400 | ||||
| 5.Application | Used or building structures, vehicle | ||||
| manufacturing and other industrial structures | |||||
| 6.Features | Can produce special specification products | ||||
| as per our customers' requirement | |||||
| 7.Delivery Time | 15-30 days after recieve the LC or pre-paid | ||||
| 8.Detail Package | Bundles, seaworthy wooden cases with or without | ||||
| edge protector, steel hoop and seals, or as per | |||||
| customers' requirements | |||||
Drawing and Detail DATA (help to know more information)
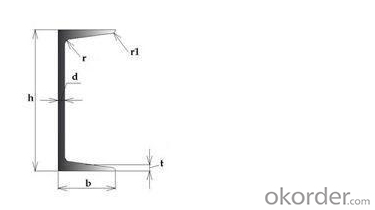
Specification | h | b | d | t | Cm2 | (kg/m) |
5 | 50 | 37 | 4.5 | 7 | 6.93 | 5.44 |
6.3 | 63 | 40 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 8.45 | 6.63 |
8 | 80 | 43 | 5 | 8 | 10.24 | 8.04 |
10 | 100 | 48 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 12.74 | 10 |
12.6 | 126 | 53 | 5.5 | 9 | 15.69 | 12.37 |
14a | 140 | 58 | 6 | 9.5 | 18.51 | 14.53 |
14b | 140 | 60 | 8 | 9.5 | 21.31 | 16.73 |
16a | 160 | 63 | 6.5 | 10 | 21.95 | 17.23 |
16 | 160 | 65 | 8.5 | 10 | 25.15 | 19.74 |
18a | 180 | 68 | 7 | 10.5 | 25.69 | 20.17 |
18 | 180 | 70 | 9 | 10.5 | 29.29 | 22.99 |
Other Steel Bar Specification:
1.Square bar:Size: 4mm*4mm~100mm*100mm
2.Round Bar:Diameter: 3mm~800mm
3.Angel Bar:Size: 3mm*20mm*20mm~12mm*100mm*100mm
4.Flat bar:Thickness: 2mm~100mm,Width: 10mm~500mm,
5.Hexagonal :Size: 2mm~100mm
- Q: What is the load-bearing capacity of stainless steel angles?
- The load-bearing capacity of stainless steel angles depends on various factors such as the grade of stainless steel, the dimensions of the angle, and the specific application it is being used for. Stainless steel angles are commonly used in construction and engineering projects where strength and durability are crucial. They are designed to support and distribute loads efficiently, making them suitable for structural applications. The load-bearing capacity of stainless steel angles can be determined by considering the ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, and the moment of inertia of the angle. The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum amount of stress the stainless steel angle can withstand before it fails, while the yield strength is the stress at which permanent deformation occurs. The load-bearing capacity can also be influenced by the dimensions of the angle, including the length, width, and thickness. Thicker and wider angles generally have higher load-bearing capacities compared to thinner and narrower ones. Additionally, the grade of stainless steel used in the angle plays a significant role in determining its load-bearing capacity. Different grades of stainless steel have varying strength properties, with higher grades generally having higher load-bearing capacities. It is essential to consult engineering design codes and standards, such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) Manual, to determine the specific load-bearing capacity requirements for a particular application. These codes provide guidelines and formulas to calculate the load-bearing capacity based on the properties and dimensions of the stainless steel angle. In summary, the load-bearing capacity of stainless steel angles is influenced by factors such as the grade of stainless steel, dimensions of the angle, and the specific application. Consulting engineering design codes and standards is crucial to determine the appropriate load-bearing capacity for a given situation.
- Q: What are the magnetic properties of stainless steel angles?
- Stainless steel angles typically have a non-magnetic property. This is due to the presence of chromium in their composition, which forms a passive layer on the surface of the steel. This passive layer acts as a protective barrier against corrosion and helps to maintain the stainless steel's non-magnetic characteristics. However, it is important to note that stainless steel angles can become slightly magnetic if they are exposed to certain external factors such as high temperatures or mechanical stress. In such cases, the austenitic stainless steel angles may transform into a martensitic structure, resulting in some magnetic properties. Overall, stainless steel angles are generally considered to be non-magnetic materials.
- Q: Can stainless steel angle be welded?
- Certainly, stainless steel angle is capable of being welded. Stainless steel possesses a reputation for its remarkable weldability, and this extends to stainless steel angle as well. However, it is vital to employ the appropriate welding methods and substances to ensure a robust and long-lasting weld. Techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are commonly employed when welding stainless steel angle. These techniques grant exceptional control over the welding process. Additionally, it is advisable to utilize filler materials specifically formulated for stainless steel welding to guarantee compatibility and achieve optimal outcomes. In general, with the correct techniques and materials, successful welding of stainless steel angle can be achieved.
- Q: What are the tolerances for stainless steel angles?
- The tolerances for stainless steel angles typically depend on the specific industry or application requirements. However, common tolerances for stainless steel angles are usually specified in terms of dimensional accuracy, straightness, and surface finish. These tolerances ensure that the angles meet the desired specifications and can vary from a few thousandths of an inch to a few hundredths of an inch. It is important to consult the relevant standards or specifications for accurate information on tolerances for stainless steel angles.
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be used in the production of renewable energy systems?
- Yes, stainless steel angles can be used in the production of renewable energy systems. Stainless steel is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material, making it well-suited for outdoor applications. It can be used in the construction of solar panel frames, wind turbine towers, and mounting systems for renewable energy systems. Stainless steel angles provide structural support and can withstand the challenging environmental conditions typically associated with renewable energy production.
- Q: How do you calculate the deflection of stainless steel angles?
- To determine the deflection of stainless steel angles, one can utilize the standard formulas for beam deflection. The deflection of a beam relies on a variety of factors, including the beam's length, the material properties of the stainless steel, the angle's cross-sectional shape and dimensions, and the applied loads. The Euler-Bernoulli beam equation serves as the most commonly employed formula for calculating beam deflection. This equation establishes a relationship between the deflection of a beam, the applied loads, and the beam's properties. The equation can be expressed as follows: δ = (5 * w * L^4) / (384 * E * I) Where: - δ represents the beam's deflection - w denotes the applied load per unit length - L signifies the beam's length - E represents the modulus of elasticity of the stainless steel material - I indicates the moment of inertia of the angle's cross-sectional shape To calculate the moment of inertia (I), one can employ the pertinent formula for the moment of inertia corresponding to the specific cross-sectional shape of the stainless steel angle. For instance, in the case of an angle with equal legs, the moment of inertia (I) can be calculated in the following manner: I = (b * h^3) / 12 Where: - b represents the angle's width - h denotes the angle's height Once all the necessary values have been obtained, they can be substituted into the Euler-Bernoulli beam equation to calculate the deflection (δ) of the stainless steel angle. It is essential to note that these calculations assume the stainless steel angle is subjected to linear elastic behavior, and that the applied loads remain within the material's elastic limit. If the loads surpass the elastic limit, the stainless steel angle may undergo plastic deformation, necessitating different calculations or considerations.
- Q: What are the magnetic properties of stainless steel angle?
- Stainless steel angle, like other stainless steel materials, generally exhibits weak magnetic properties. This is because stainless steel contains a high percentage of chromium, which forms a passive layer on the surface of the metal. This passive layer helps to protect the steel from corrosion and oxidation, but it also reduces the magnetic permeability of the material. However, it is important to note that the magnetic properties of stainless steel angle can vary depending on the specific alloy and manufacturing process used. Some stainless steel alloys, such as the austenitic grades (e.g., 304 and 316), are non-magnetic in their annealed condition. These grades can acquire some magnetism when cold worked or subjected to certain heat treatments, but they still generally exhibit weak magnetic properties. On the other hand, ferritic and martensitic stainless steels, such as grades 430 and 410, contain higher amounts of ferrite and martensite phases, respectively, which can make them more magnetic than the austenitic grades. These grades can exhibit moderate to strong magnetic properties, especially when cold worked or heat treated. In summary, the magnetic properties of stainless steel angle are generally weak due to the presence of a passive layer formed by chromium. However, the specific alloy and manufacturing process can influence the level of magnetism, with austenitic grades being typically non-magnetic and ferritic or martensitic grades having higher magnetic properties.
- Q: What are the weight capacities of stainless steel angles?
- The weight capacities of stainless steel angles vary depending on their specific dimensions, thickness, and design. It is best to consult the manufacturer or supplier for accurate information on the weight capacities of specific stainless steel angles.
- Q: What are the surface finish options for stainless steel angles?
- There are several surface finish options available for stainless steel angles. These options provide different aesthetic appearances and functional properties to suit various applications. Some common surface finishes for stainless steel angles include: 1. Mill Finish: This is the standard finish that stainless steel angles come with after being manufactured. It has a dull appearance with visible lines or grooves caused by the manufacturing process. Mill finish angles are often used in structural applications where aesthetics are not a priority. 2. Brushed Finish: Also known as satin or dull polished finish, brushed stainless steel angles have a smooth and matte appearance. This finish is achieved by brushing the surface with abrasive materials, creating a uniform grain pattern. Brushed finish angles are commonly used in architectural and decorative applications where a visually appealing surface is desired. 3. Mirror Finish: As the name suggests, mirror finish stainless steel angles have a highly reflective surface that resembles a mirror. This finish is achieved through a polishing process that removes any imperfections, resulting in a smooth and glossy appearance. Mirror finish angles are often used in decorative applications, such as furniture, fixtures, and ornamental structures. 4. Bead Blasted Finish: Bead blasting involves bombarding the surface of stainless steel angles with tiny glass beads or ceramic particles to create a textured finish. This finish gives the angles a uniform matte appearance with a slightly rough texture. Bead blasted finish angles are commonly used in applications where a non-reflective surface is desired, such as industrial equipment or architectural elements. 5. Powder Coated Finish: Powder coating is a popular surface finishing technique where a dry powder is applied electrostatically to the stainless steel angles and then cured under heat to form a hard, durable, and colorful coating. Powder coated finish angles offer a wide range of color options and provide enhanced protection against corrosion, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. 6. Passivated Finish: Passivation is a chemical treatment process that removes surface contaminants and promotes the formation of a protective oxide layer on stainless steel angles. This finish enhances the corrosion resistance of the angles and is commonly used in applications where the angles will be exposed to harsh environments or chemicals. These are just a few of the surface finish options available for stainless steel angles. The choice of finish depends on the specific requirements of the application, including aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and functionality.
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be used for decorative purposes?
- Yes, stainless steel angles can definitely be used for decorative purposes. Stainless steel is known for its sleek and modern appearance, making it a popular choice for various decorative applications. Stainless steel angles can be used to create clean lines and sharp edges, adding a contemporary touch to interior or exterior designs. These angles can be used to frame artwork, mirrors, or photographs, adding a sophisticated and stylish look to any space. Additionally, stainless steel angles can be used as decorative accents on furniture, architectural features, or in DIY projects. With its durability and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel angles offer both aesthetic appeal and long-lasting quality for decorative purposes.
Send your message to us
cold roll forming steel channel for construction
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

























