New Arrival H Beam Profile with Grade A Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
1. Standard: GB700-88, Q235B2.
2. Grade: Q235, SS400 or Equivalent
3. Length: 6m,10m, 12m as following table
4. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
5.Payment: TT or L/C
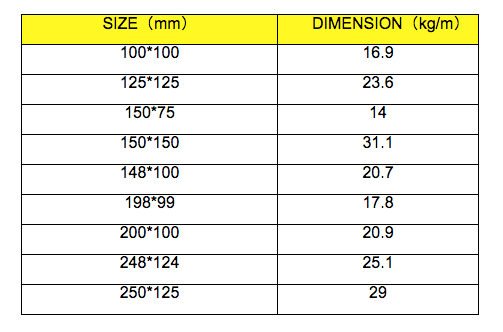
6. Sizes:
Usage & Applications of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
Commercial building structure ;Pre-engineered buildings; Machinery support structure; Prefabricated structure; Medium scale bridges; Ship-building structure. etc.
Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: Can fit in the containers of 20fts the steel beams of 6M?
A2: No proble, we can put them into the containers in the form sideling.
Q3: The products are invoicing on theoritical weight or on actual weight?
A3: We can do it in both manners, according to the customers' request.


- Q: Are steel H-beams suitable for supporting nuclear power plant facilities?
- Yes, steel H-beams are suitable for supporting nuclear power plant facilities. Steel H-beams are commonly used in construction due to their high strength and load-bearing capacity. They provide excellent structural support and stability, making them ideal for supporting the heavy equipment and structures found in nuclear power plants. Moreover, steel H-beams have a high resistance to fire, corrosion, and seismic activities, which are crucial characteristics for a facility with such sensitive operations. Additionally, steel H-beams can be manufactured to meet specific design requirements and can be easily modified or replaced if necessary. Overall, steel H-beams are a reliable and durable choice for supporting nuclear power plant facilities.
- Q: How do steel H-beams contribute to daylighting in buildings?
- The inclusion of steel H-beams is crucial in enabling daylighting within buildings as they offer structural reinforcement while also facilitating the use of larger, more expansive windows. Daylighting involves utilizing natural light to brighten the interior spaces of a structure, thus diminishing the dependence on artificial lighting and fostering a more sustainable and pleasant environment. Steel H-beams possess a robust load-bearing capacity, making it feasible for them to span considerable distances and bear heavy loads, thereby allowing for the incorporation of larger window openings. These windows can be strategically positioned on exterior walls or even within the roof, granting the entry of abundant natural light into the building's interior. The utilization of steel H-beams in construction additionally confers architects with the ability to create buildings featuring open floor plans and soaring ceilings. This architectural freedom permits the incorporation of atriums, skylights, and other light wells that augment the penetration of daylight. Furthermore, steel H-beams exhibit remarkable durability and resistance to deformation, thereby ensuring the preservation of the structural integrity of the building while simultaneously maximizing the ingress of natural light. This characteristic is particularly crucial for regions prone to earthquakes or high winds. Apart from their structural advantages, steel H-beams are also highly versatile in terms of design and aesthetics. They can be seamlessly integrated into various architectural styles, thus allowing for the realization of innovative and visually appealing building designs that prioritize daylighting. Overall, the inclusion of steel H-beams significantly contributes to the achievement of daylighting within buildings by providing the essential strength and support for larger windows, facilitating the creation of imaginative architectural designs, and guaranteeing the longevity of the structure. By harnessing natural light, buildings can diminish energy consumption, enhance the well-being of occupants, and establish more sustainable and inviting spaces.
- Q: Can Steel H-Beams be used in foundation or basement construction?
- Indeed, foundation or basement construction can incorporate steel H-beams. These beams are widely utilized in construction due to their robustness, longevity, and adaptability. They have the capability to establish a secure and firm base for buildings, including basements. Typically, steel H-beams are utilized in conjunction with other materials, such as concrete, to establish a sturdy foundation or basement structure. The H-shape of these beams allows for improved load distribution and heightened structural stability, rendering them an optimal choice for these construction endeavors. Furthermore, steel H-beams possess resistance against weathering, corrosion, and pests, thus further enhancing their suitability for foundation and basement construction.
- Q: What are the considerations when designing for acoustical isolation of Steel H-Beams?
- When designing for acoustical isolation of Steel H-Beams, several considerations need to be taken into account. Firstly, it is important to analyze the structural properties of the H-Beams, such as their dimensions, material composition, and connection details, as these factors can influence their ability to transmit sound. Additionally, the design should incorporate appropriate measures to mitigate the transmission of airborne and impact noise through the beams. This may involve incorporating soundproof materials, such as acoustical barriers or resilient mounts, into the design. It is also crucial to consider the surrounding environment and potential sources of noise, as well as the desired level of acoustic isolation required. Overall, a comprehensive approach that addresses both the structural and acoustic aspects is necessary to achieve effective acoustical isolation of Steel H-Beams.
- Q: How do steel H-beams contribute to the load-bearing capacity of a structure?
- Steel H-beams contribute to the load-bearing capacity of a structure by providing strength and support. These beams are designed to withstand heavy loads and distribute them evenly, making them ideal for carrying the weight of floors, walls, and roof systems. The H-shape of the beam allows for a higher strength-to-weight ratio, which means it can support more weight without being excessively heavy itself. Additionally, the wide flanges of the H-beam provide stability and prevent buckling, ensuring the overall structural integrity of the building.
- Q: Can steel H-beams be used in earthquake-resistant construction?
- Yes, steel H-beams can be used in earthquake-resistant construction. Steel is a popular material choice for earthquake-resistant buildings due to its high strength and ductility. H-beams, also known as I-beams or universal beams, are commonly used in construction due to their structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities. During an earthquake, buildings experience dynamic forces that can cause significant stress and deformation. Steel H-beams are designed to withstand these forces and can effectively resist lateral loads and seismic movements. The shape of H-beams provides excellent load distribution and structural stability, which is crucial in earthquake-prone areas. Additionally, steel has high tensile strength, allowing it to flex and absorb seismic energy without breaking or collapsing. This property makes steel H-beams more resistant to earthquake-induced damages compared to other materials like wood or concrete. To enhance earthquake resistance, H-beams can be further reinforced with steel plates, braces, or other structural elements. These reinforcements help to strengthen the connections between beams and columns, increasing the overall stability of the building. Overall, steel H-beams are a reliable choice for earthquake-resistant construction due to their strength, ductility, and load-bearing capabilities. However, it is important to consider other factors such as proper design, construction techniques, and adherence to building codes and regulations to ensure the overall seismic performance of the structure.
- Q: Can steel H-beams be used for signage structures?
- Indeed, signage structures can indeed utilize steel H-beams. Renowned for their remarkable strength and durability, steel H-beams prove themselves capable of supporting immense burdens, signage included. In construction endeavors, these beams are frequently employed due to their structural soundness and ability to withstand diverse weather phenomena. Additionally, H-beams offer exceptional support and stability, rendering them an optimal selection for signage structures that demand both steadfastness and longevity. Moreover, steel H-beams can be effortlessly fabricated and tailored to meet precise design necessities, thus affording the opportunity to fashion distinctive and visually captivating signage structures.
- Q: What are the different bolt sizes used for steel H-beams?
- Steel H-beams commonly utilize various bolt sizes, which depend on the particular application and load requirements. M12, M16, M20, and M24 are among the most frequently employed bolt sizes for steel H-beams. The selection of these bolt sizes is determined by the desired strength and load capacity of the specific steel H-beam structure. Furthermore, the length of the bolts can vary depending on the thickness and width of the H-beam. To guarantee optimal strength and stability, it is crucial to refer to engineering specifications and calculations when determining the suitable bolt sizes for a given steel H-beam structure.
- Q: Can steel H-beams be used for rooftop structures?
- Yes, steel H-beams can be used for rooftop structures. They are commonly used in construction for their strength, durability, and ability to support heavy loads. Steel H-beams provide structural support and can be an ideal choice for rooftop structures due to their high load-bearing capacity.
- Q: Are steel H-beams resistant to ultraviolet (UV) radiation?
- Steel H-beams do not possess inherent resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Over time, UV radiation from the sun can lead to degradation and discoloration of steel surfaces. However, the extent of this degradation depends on factors such as the specific type of steel used, as well as the duration and intensity of UV exposure. To counteract the effects of UV radiation on steel H-beams, one can apply protective coatings. These coatings serve as a barrier, safeguarding the steel from direct UV ray exposure. Common protective coatings for steel include paint, powder coating, and galvanizing. Paint coatings offer a layer of protection against UV radiation, but they may require periodic maintenance and reapplication to maintain effectiveness. On the other hand, powder coating provides greater durability and UV resistance. Galvanizing is an alternative option, involving the application of a zinc layer to protect against UV radiation and corrosion. It is important to note that even with protective coatings, the long-term durability of steel H-beams under UV exposure depends on factors like coating quality, installation environment, and maintenance practices. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify signs of degradation or damage, allowing for timely repairs or reapplication of protective coatings if necessary. In conclusion, while steel H-beams lack inherent resistance to UV radiation, the use of protective coatings can significantly enhance their ability to withstand UV degradation and prolong their lifespan.
Send your message to us
New Arrival H Beam Profile with Grade A Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























