Hot Rolled Angle steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25m.t. m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Hot Rolled Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
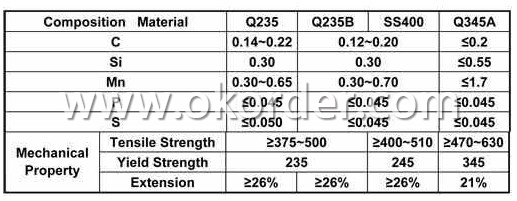
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
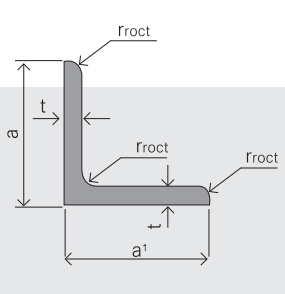
|
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
|
a(mm) |
a1(mm) |
thickness(mm) |
length |
|
25 |
25 |
2.5---3.0 |
6M/12M |
|
30 |
30 |
2.5---4.0 |
6M/12M |
|
38 |
38 |
2.5 |
6M/12M |
|
38 |
38 |
3.0---5.0 |
6M/12M |
|
40 |
40 |
3.0---6.0 |
6M/12M |
|
50 |
50 |
3 |
6M/12M |
|
50 |
50 |
3.7---6.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
60 |
60 |
5.0---6.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
63 |
63 |
6.0---8.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
65 |
65 |
5.0---8.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
70 |
70 |
6.0---7.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
75 |
75 |
5.0---10.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
80 |
80 |
6.0---10.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
90 |
90 |
6.0---10.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
100 |
100 |
6.0---12.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
120 |
120 |
8.0-12.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
125 |
125 |
8.0---12.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
130 |
130 |
9.0-12.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
140 |
140 |
10.0-16.0 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
150 |
150 |
10---15 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
160 |
160 |
10---16 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
180 |
180 |
12---18 |
6M/9M/12M |
|
200 |
200 |
14---20 |
6M/9M/12M |
6. Material details:
Usage & Applications Hot Rolled Angle Steel
According to the needs of different structures, Angle can compose to different force support component, and also can be the connections between components. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.

Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.


- Q: Can steel angles be used for wall bracing?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for wall bracing. Steel angles are commonly used for this purpose as they provide structural support and stability to walls, ensuring they can resist lateral forces such as wind or seismic loads.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for framing in residential construction?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for framing in residential construction. They are commonly used to provide structural support and stability in various applications, including framing walls, roofs, and floors. Steel angles offer strength, durability, and versatility, making them a suitable choice for residential framing projects.
- Q: What are the different dimensions used to specify steel angles?
- The different dimensions used to specify steel angles include the length of each leg, the thickness of the material, and the angle of inclination between the legs.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of bridges?
- Yes, steel angles can be commonly used in the construction of bridges. Steel angles are versatile structural components that can provide additional strength and support to bridge structures. They are often used in the construction of bridge decks, railings, and supports. Steel angles are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes them ideal for bridge construction. They can withstand heavy loads and provide stability to the bridge structure. Additionally, steel angles are durable and resistant to corrosion, which is essential for bridges that are exposed to various environmental conditions. In bridge construction, steel angles are often used in conjunction with other steel components, such as beams and columns, to create a strong and reliable structure. They are commonly used as bracing elements to reinforce the overall stability of the bridge. Steel angles can also be used as connection elements, allowing different parts of the bridge to be securely joined together. Overall, steel angles are a crucial component in bridge construction, providing strength, durability, and stability to the structure. Their versatility and reliability make them a preferred choice for engineers and designers when constructing bridges of various sizes and types.
- Q: What is the meaning of the number of angle steel
- The two sides of an equal angle steel are equal in width. The specifications are expressed in millimeters of edge width * edge width * edge thickness. Such as "/ 30 x 30 x 3", that is 30 mm width equal angle, edge thickness of 3 mm. The model can also be used, also the title number, number is the number of centimeters wide, such as the No. 3 angle angle 3#.
- Q: What are the different design considerations for steel angles in architectural applications?
- When it comes to using steel angles in architectural applications, there are several design considerations that need to be taken into account. These considerations include the load-bearing capacity of the angles, their structural integrity, aesthetics, and overall design flexibility. One of the primary design considerations for steel angles in architectural applications is their load-bearing capacity. Steel angles are often used to provide structural support in buildings, so it is crucial to ensure that they can withstand the anticipated loads. This involves calculating the maximum load that the angles will need to bear and selecting angles with the appropriate size and thickness to handle these loads safely. Another important consideration is the structural integrity of the steel angles. Architects and engineers need to consider factors such as the angle's resistance to bending, buckling, and shear. The design should take into account the angle's ability to distribute the loads evenly, minimizing the risk of failure or deformation. Aesthetics also play a significant role in architectural design, and steel angles can contribute to the overall visual appeal of a building. Architects may choose to incorporate angles with different profiles, finishes, or decorative elements to enhance the design and create a visually appealing structure. The angles should complement the overall architectural style and blend seamlessly with other building materials. Design flexibility is another crucial consideration when using steel angles. Architects often require angles that can be easily customized or fabricated to meet their specific design requirements. Steel angles can be cut, welded, or bent to create unique shapes and angles, allowing for creative architectural solutions. Lastly, it's important to consider the material properties and corrosion resistance of the steel angles. Architects need to evaluate the environmental conditions of the project site and select angles that can withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive agents. Proper coatings or treatments can be applied to protect the angles from corrosion and ensure their longevity. In conclusion, the design considerations for steel angles in architectural applications encompass load-bearing capacity, structural integrity, aesthetics, design flexibility, and corrosion resistance. By carefully considering these factors, architects can select steel angles that meet both the functional and visual requirements of their projects, resulting in safe, durable, and visually appealing architectural structures.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in conveyor systems or material handling equipment?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in conveyor systems or material handling equipment. They provide structural support and stability, making them suitable for constructing frames and supports in conveyor systems and material handling equipment.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for support structures in sports arenas or stadiums?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for support structures in sports arenas or stadiums. Steel angles are commonly used in construction due to their strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. They provide excellent support and stability, making them suitable for various structural applications, including supporting the weight of sports arenas or stadiums.
- Q: Are steel angles fire-resistant?
- Steel angles possess a certain degree of fire resistance. Steel, as a non-combustible substance, does not ignite or contribute to the combustion process. Its exceptional melting point, typically hovering at 1370°C (2500°F), ensures that it retains its structural integrity even when subjected to high temperatures. Nevertheless, it is crucial to recognize that the fire resistance of a structure or component reliant on steel angles hinges on various factors, such as the design, dimensions, and arrangement of said angles, as well as the implementation of fire protection measures. Fire-resistant coatings, fireproofing substances, or fire-resistant insulation can be employed to bolster the fire resistance of steel angles. These supplementary fire protection methods have the capacity to provide a certain level of insulation, impeding the transfer of heat to the steel and prolonging the time it takes for the steel to reach its critical temperature. This grants occupants more time to evacuate the premises and affords firefighters an extended period to manage the fire. In conclusion, steel angles inherently possess fire resistance due to the properties of steel. However, the implementation of appropriate fire protection measures can augment their fire resistance capabilities.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for manufacturing furniture?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for manufacturing furniture. They provide structural support and can be used to create strong and durable furniture pieces. Steel angles are commonly used in industrial and modern furniture designs due to their sleek and minimalist aesthetic.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Hebei, China |
| Year Established | 2003 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 500 Million |
| Main Markets | Southeast Asia; middle east; South Korea; Africa |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 30%-45% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 11-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 10,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 2 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM service offered |
| Product Price Range | high; average |
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Angle steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25m.t. m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























