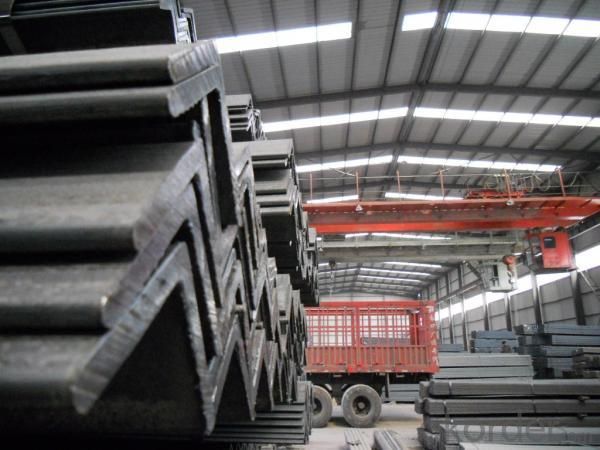
GB Q235 Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of GB Q235 Angle Steel
1. Standards: GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3. Material:Material: GB Q235B, Q345B or Equivalent; ASTM A36; EN 10025, S235JR, S355JR; JIS G3192, SS400;
SS540.
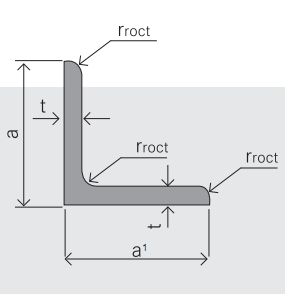
4. Sizes:
|
Sizes: 25mm-250mm | ||
|
a*t | ||
|
25*2.5-4.0 |
70*6.0-9.0 |
130*9.0-15 |
|
30*2.5-6.6 |
75*6.0-9.0 |
140*10-14 |
|
36*3.0-5.0 |
80*5.0-10 |
150*10-20 |
|
38*2.3-6.0 |
90*7.0-10 |
160*10-16 |
|
40*3.0-5.0 |
100*6.0-12 |
175*12-15 |
|
45*4.0-6.0 |
110*8.0-10 |
180*12-18 |
|
50*4.0-6.0 |
120*6.0-15 |
200*14-25 |
|
60*4.0-8.0 |
125*8.0-14 |
250*25 |
5. Material details:
|
Alloy No |
Grade |
Element (%) |
|||||
|
C |
Mn |
S |
P |
Si |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q235 |
B |
0.12—0.20 |
0.3—0.7 |
≤0.045 |
≤0.045 |
≤0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alloy No |
Grade |
Yielding strength point( Mpa) |
|||||
|
Thickness (mm) |
|||||||
|
≤16 |
>16--40 |
>40--60 |
>60--100 |
||||
|
≥ |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Q235 |
B |
235 |
225 |
215 |
205 |
||
|
Alloy No |
Grade |
Tensile strength (Mpa) |
Elongation after fracture (%) |
||||
|
Thickness (mm) |
|||||||
|
|
≤16 |
>16--40 |
>40--60 |
>60--100 |
|||
|
≥ |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q235 |
B |
375--500 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
23 |
|
Usage & Applications of GB Q235 Angle Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of GB Q235 Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.



- Q: What are the welding techniques used for steel angles?
- Different welding techniques can be used for steel angles, depending on the specific application and desired result. Some commonly used techniques include: 1. Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), involves using a consumable electrode coated in flux. It is versatile, cost-effective, and suitable for various thicknesses of steel angles. 2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, utilizes a welding gun to feed a wire electrode. The wire melts and joins with the base metal, while an inert gas shield protects the weld from contamination. GMAW is commonly used for thin to medium thickness steel angles. 3. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is similar to GMAW, but the wire electrode is filled with flux, eliminating the need for external shielding gas. FCAW is suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications and is known for its high deposition rates. 4. Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (GTAW), also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), involves using a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a separate filler metal if necessary. This technique produces precise, high-quality welds and is commonly used for thinner steel angles or when precise control is required. 5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) uses a continuously fed wire electrode submerged in a granular flux. The flux acts as a protective layer, preventing contamination and enhancing weld quality. SAW is commonly used for thicker steel angles or when high deposition rates are needed. When selecting the appropriate welding technique, it is important to consider factors such as the thickness of the steel angles, the welding environment, and the desired quality and strength of the weld. Consulting with a professional welder or engineer can help determine the best technique for a specific application.
- Q: What is the maximum load capacity of a steel angle?
- The maximum load capacity of a steel angle is determined by various factors including its dimensions, thickness, grade, and quality. Steel angles are generally built to withstand significant loads due to their structural characteristics. However, it is essential to refer to engineering specifications and relevant building codes to determine the specific maximum load capacity of a steel angle in a particular application. The load capacity is usually calculated by considering the angle's cross-sectional area, the material's yield strength, and the applied load factors. Furthermore, factors such as the angle's length, support conditions, and the presence of any additional reinforcement or bracing can also affect the maximum load capacity. It is vital to ensure that the steel angle is chosen, designed, and installed correctly to safely support the intended loads and comply with the necessary structural standards.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for bracing purposes?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for bracing purposes. Steel angles are commonly used as structural components in construction due to their strength and durability. They are often used to provide additional support and stability to various structures, including buildings, bridges, and industrial equipment. Steel angles can be easily bolted or welded to the main framework of a structure, providing additional rigidity and resisting forces such as compression, tension, and lateral loads. Their versatile shape allows for a wide range of bracing applications, making them a popular choice for bracing purposes in construction and engineering projects.
- Q: How are steel angles protected against corrosion?
- Steel angles are protected against corrosion through various methods such as galvanization, painting, or applying a protective coating. These protective measures create a barrier between the steel surface and corrosive elements, preventing direct contact and ensuring the longevity and durability of the steel angles.
- Q: How are steel angles protected against fire damage?
- Fire-resistant coatings and fireproofing materials are commonly used to protect steel angles from fire damage. These measures aim to prevent or delay the steel from reaching its critical temperature, which can compromise its structural integrity. One popular method of safeguarding steel angles involves applying intumescent coatings. These coatings expand when exposed to high temperatures, creating a protective char layer that insulates the steel and slows down heat transfer. This process effectively hinders the steel from rapidly increasing in temperature, thus enhancing its fire resistance capabilities. Another approach is to utilize fireproofing materials, such as concrete or gypsum-based sprays or boards. These materials act as a barrier between the steel angles and the fire, providing insulation and preventing the heat from reaching the steel. Fireproofing materials are commonly employed in buildings with higher fire resistance requirements, such as tall buildings or industrial facilities. In certain cases, steel angles can be enclosed within fire-rated enclosures for added protection. This entails enclosing the steel angles within fire-rated walls, floors, or ceilings made of materials with exceptional fire resistance properties. These enclosures effectively isolate the steel angles from potential fire sources, adding an extra layer of defense. It is important to acknowledge that the specific fire protection measures for steel angles can vary based on building codes, fire safety regulations, and the intended use of the structure. Consulting with fire protection engineers and adhering to the appropriate guidelines will ensure that the steel angles are adequately shielded against fire damage.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of railway bridges?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in the construction of railway bridges. Steel angles are versatile structural elements that can be used in various applications, including bridge construction. They are commonly used in the fabrication of bridge girders, braces, and supports. Steel angles provide excellent strength and load-bearing capabilities, making them suitable for railway bridges that require high structural integrity and durability. Additionally, steel angles can be easily welded, bolted, or riveted together, allowing for efficient and cost-effective construction. Overall, steel angles are a viable and commonly used component in the construction of railway bridges.
- Q: Can steel angles be recycled or reused?
- Yes, steel angles can definitely be recycled and reused. Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world due to its durability and high value. When steel angles are no longer needed or become scrap, they can be collected, sorted, and sent to recycling facilities. The recycling process involves melting down the steel angles to remove impurities and then shaping the molten steel into new products. Recycled steel angles can be used in various industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing, just like newly produced steel angles. This not only conserves natural resources but also helps reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with producing new steel. Recycling steel angles is an effective way to promote sustainability and contribute to a circular economy.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for solar panel mounting?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for solar panel mounting. Steel angles are commonly used in solar panel mounting systems due to their strength, durability, and flexibility. They provide a sturdy and secure structure to support the weight of the solar panels and withstand environmental conditions such as strong winds and heavy snow loads. Steel angles also allow for easy adjustment and positioning of the solar panels to maximize sunlight exposure. Additionally, steel angles can be easily customized and fabricated to meet specific project requirements, making them a popular choice in the solar industry.
- Q: Are steel angles suitable for earthquake-prone areas?
- Yes, steel angles are suitable for earthquake-prone areas. Steel is a strong and durable material that can withstand seismic forces and provide structural stability during earthquakes. The use of steel angles helps distribute the load and reinforce the structure, making it more resistant to seismic activity.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for stair stringers?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for stair stringers. Steel angles are commonly used in construction for their strength and durability. When used as stair stringers, steel angles provide the necessary support and stability for the stairs. They can be easily cut and welded to the desired shape and size, making them a versatile option for stair construction. Additionally, steel angles are resistant to rot, termites, and other forms of damage, ensuring the longevity of the stair structure. However, it is important to consult with a structural engineer or a professional contractor to ensure that the steel angles meet the specific requirements and load-bearing capacity for the intended stair design.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Tangshan, China |
| Year Established | 1996 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 300 Million |
| Main Markets | Middle East; Korea; Southeast Aisa |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008; |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin; |
| Export Percentage | 70% - 80% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-30 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese; |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 900,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 3 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered; |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
GB Q235 Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























